![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atom |
Smallest identifiable unit of an element, the theory that all matter is composed of atoms grew out of laws and observations |
|
|
The Law of Conservation of Mass |
In a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed- Antoine Lavoisier |
|
|
The Law of Conservation of Mass |
Law is consistent with the idea that matter is composed of small indestructible particles |
|
|
Law of Definite Proportions |
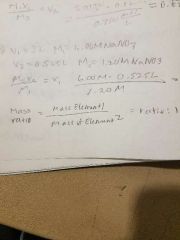
All samples of a given compound, regardless of their source or how they were prepared, have the same proportions of their constituent elements. |
|
|
Law of Multiple Proportions |
When two elements from two different compounds, the masses of element B that combine with 1 g of element A can be expressed in whole number ratios. Ex. Mass ratio of O to C in CO2 is 2.67:1 therefore 2.67g of oxygen reacts with 1 g C. For carbon monoxide it is 1.33 g to 1. The ratio of these 2 numbers is a whole number 2.67/1.33=2 |
|
|
Daltons Atomic Theory |
1. Each element is composed of tiny particles 2. All atoms of an element have the same mass 3.atoms combine in whole number ratios 4.atoms of one element cannot change to another |
|
|
Cathode ray |
J.J. Thomson co sucked experiments using this tube and applied high electrical voltage between two electrodes. He found that particles traveled in straight line. They carried negative electrical charge. Discovery of electron |
|
|
Isotopes |
Atoms of an element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons |
|
|
Natural Abundance |
Relative amount of isotope in a naturally occurring sample |
|
|
Mass Number |

Number of protons + number of neutrons |
|
|
Ions |
In a chemical change atoms can lose or gain electrons and become charged particles. The charge depends of the number of electrons lost or gained. Cations and anions |
|
|
Alkali metals |
Group 1A, tendency to lose an electron 1+ |
|
|
Alkaline earth metals |
Group 2A, not as reactive as group 1A. Lose 2 electrons ions 2+ |
|
|
Halogens |
Group 7A very reactive nonmetals, gain electron 1- ions |
|
|
Noble Gas |
Group 8A mostly unreactive, gain electrons 2- Ions |
|
|
Atomic mass |
Directly beneath the element symbol, represents the average mass of the isotopes that compose that element. Weighted according to natural abundance |
|
|
1 mol= |
6.022e23 of something |
|
|
Molar mass |
The mass of 1 mol of atoms of an element, is equal to it's atomic mass units . Exa: 12.01 g C = 1 mol C= 6.022e23 atoms of C |

