![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which ocean freezes the most and which is saltiest |
Artic - freeze Atlantic - salty |
|
|
Salt water freezes at higher or lower temp than freshwater |
Lower |
|
|
% of dissolved minerals in salt water |
3.5% |
|
|
Major dissolved mineral in salt water |
Sodium chloride (metal + gas) |
|
|
#1#2#3 dissolved particles in salt water |
#1 chloride #2 sodium #3 magnesium |
|
|
Sources of salts |
-chemical weathering -outgassing |
|
|
What proccess' effect salinity |
-change in water content(freeze/dry) -precipitation. Runoff. Iceberg melt. Sea ice melt |
|
|
Warm salt water=more or less salinity |
More |
|
|
Thermocline |
Cool off temp as depth increases |
|
|
Thermocline in High alititude |
High latitude= polar regions so it's already cold Therefore Little to none thermocline |
|
|
Low altitude and thermocline |
Low latitude = equator (high temp) Therefore Thermocline occurs |
|
|
Ocean temp fluctuates more or less rapid than land |
More |
|
|
Pycnocline |
Density changes Happens in colder weather |
|
|
Low and high latitudes and pycnocline |
Low latitude - more pycnocline (density increases as depth increase) High latitude- little/no pycnocline highly dense cold water already at surface (little change in density with depth) |
|
|
Layers of ocean 3 of them |
1 surface mix zone 2% 2 transition zone 18% 3 deep zone 80% |
|
|
Thermocline and pycnocline happen at which zone |
The middle layer, the transition layer |
|
|
Tempurature increase=salinity increase except for? |
Equator=highest tempurature but because of precipitation and discharge of freshwater from the Amazon river salinity isn't the greatest |
|
|
Most organisms live in which layer |
Surface water |
|
|
Plankton and phytoplankton |
Plankton=Floaters Phytoplankton=algae |
|
|
Plankton and zooplankton |
Zooplankton=animals Bacteria Most of earth's biomass |
|
|
Nekton |
All animals that can swim independent from ocean currents |
|
|
Benthos |
Bottom dwellers |
|
|
Zones of availability of light in ocean |
Photic(light) zone- upper part Aphotic(w/out light) zone-little sun Deep ocean- no sunlight |
|
|
Distance from shore zones |
Intertidal zone-land and ocean overlap Nertic zone-seaward from the low tide line, the continental shelf to the shelf break Oceanic zone-beyond the continental shelf |
|
|
Water depth zone |
Pelagic zone -open ocean of any depth Benthic zone-include any sea bottom surface Abyssal zone-subdivision of the benthic zone (deep, low temp, high pressure, hydro thermal vents) |
|
|
Picture of all the zones |
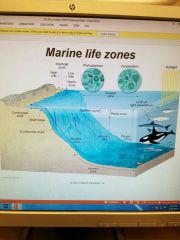
|
|
|
Energy systems |
Photosynthesis- yields o2 & sugar Chemosynthesis-chemical reactions, yields sulfur dioxide and sulfuric acid |
|
|
Most Marine life live where there is |
Sunlight And Nutrients |
|
|
Productivity in Polar oceans |
Nutrients rise up from deeper waters Low solar energy limits photo synthetic productivity |
|
|
Zooplankton and diatom peak at same time of different times of the year |
Different times of the year |
|
|
Tropical ocean |
Surface water- warm and low nutrient Deep water- cold, more nutrients |
|
|
Oceanic producers |
Marine algae Plants Bacteria Bacteria like archaea |
|
|
Big or small % transferred from on level to the next |
Small |
|
|
Feeding stage |
Trophic level |
|
|
What % transfer between trophic levels |
2% |
|
|
Food chain vs food web |
Chain: sequence of organisms through which energy is transferred Web: feed off a variety of different animals |
|
|
Animals more likely to survive if they eat from a (web or chain) |
Web |

