![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Havelock Ellis |
Questioned the myths on nocturnal emmissions. He at first believed that he would have brain damage and die from emmissions. After realizing that he wasn't dying, he dedicates himself to sex research and found that |
|
|
Kinsey |
Interviewed over 18,000 participants about sexual activities and prefrences. Criticized for sampling bias |
|
|
Sex |
Biological maleness and femaleness, including chromosomal sex. Also includes sexual behaviors such as masturbation and intercourse. |
|
|
Gender |
Psychological and sociocultural meanings added to biological maleness and femaleness. 1. Gender identity (self-definition) 2. Gender role: societal expectation for appropriate male and female behavior. Gender roles influence oir lives from birth to death. |
|
|
Social learning theory of gender role development |
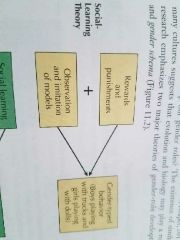
Emphasizes the power of immediate situations and observable behaviors on gender role development. A child learns what it means to be male or female. |
|
|
Gender schema theory |
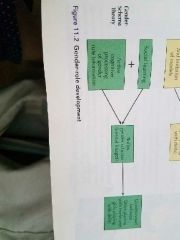
Gender roles are acquired through social learning and active cognitive processing. Children build schemas for correct behavior for boys vs. Girls. |
|
|
Androgyny |
Exhibiting both masculine and feminine traits. Encouraging this may help prevent rigid gender appropriate behaviors. Since masculinity is associated with higher self esteem, academic scores, and creativity (since masculinity is valued by society) androgynous people also have these positive traits. |
|
|
Jung |
Masculine-animus Feminine-anima Believed we must develop both in order to become fully functioning adults. |
|
|
Gender identity |
Self identification as being either a man or a woman. The case study of bruce/brenda/david revealed that although brenda received hormones, genital changes, and social pressure from parents, she still decided that she identified with male. |
|
|
Transsexual |
Having a gender identity opposite to biological sex. Transsexuals are born one sex, but have a deep and lasting discomfort with their sexual anatomy. At one point, more men wanted to be women than vice versa. Change decreased since then. |
|
|
Sandra bem |

Created a test for androgyny. It challenged the one dimensional view, and allowed people to be more accepting to androgynous people. |
|
|
Transvestism |
Involves individuals who adopt cross dressing, and often the behavior of the opposite sex. Transsexuals may cross dress, but the motivation would be to look like the right body rather than to cross dress. |
|
|
Sexual orientation |
Primary erotic attraction toward members of the same sex, both sex, or the other sex |
|
|
Sex differences: physical |
Body size: men are on avg, heavier, taller, and stronger than women Brain: the corpus callosum is larger in women. Women can more easily integrate information from the two halves of the brain and more easily perform more than one task simultaneously. - hypothalamus causes men to have constant levels of sex hormones. Whereas women have cyclic hormones -differences in cerebral hemispheres accounts for differences in verbal and spatial skills. |
|
|
Gender behavior differences |
Sexual: men begin masturbating earlier and more frequently, more likely to recognize own sexual arousal Touching: touched, kissed, and cuddled less by parents than women. Friendship: men have more friends, express through shared activities. Women through talking Personality: more aggressive, self confident, achievement task oriented, self validation, and higher self esteem Cognitive abilities: higher in math and visuospatial tests. Women in verbal skills |
|
|
Aggression |
Men more aggressive Nature: male gonadal hormone testosterone to aggressive behavior Nurture: we should examine gender role training and the context in which aggressive behaviors take place |
|
|
Sexual response cycle |
1. Excitement phase: arousal is initiated through touching, fantasy, or erotic stimuli 2. Plateau: biological and sexual arousal continues at heightenes levels 3. Orgasm: highly intense and pleasurable release of tension 4. Resolution: when body returns to unaroused state Refractory period: phase following orgasm. Further orgasm considered physiological impossible for men. More variable for women |
|
|
Masters and johnsons study |
Purpose was to understand human sexuality through studyung actual sexual behaviors rather than what people perceive or believe their sexual experiences to be. 1. Relationship focus 2. Investigation of both biological and psychological factors. 3. Emphasis on cognitive factors 4. Specific behavioral techniques |
|
|
Sexual prejudice and consequences |
Negative attitudes toward an individual because if his or her sexual orientation. Consequences: verbal and physical attacks, disrupted family and peer relationships, high rate of anxiety, depression, substance use disorders, and suicide |
|
|
Sexual dysfunction |
Male: erectile dysfunction - chronic illness, diabetes, heart disease -performance anxiety, difficulty expressing desires, antisexual upbringing Premature ejaculation (rapid) -primarily psychological: guilt, fear if discover6, hurried experiences Females: Orgasmic dysfunction -lifetime lack of orgasm, was orgasmic, under specific conditions - chronic illness, diabetes, etc. -psychological same as premature Vaginismus, penile insertion impossible - primarily psychological, inadequate lubrication, antisexual upbringing Both Inhibited sexual desire: avoids sexual relations due to disinterest Sexual aversion: due to overwhelming fear or anxiety - partner pressure, gender identity confusion, sex trauma Dyspareunia: painful intercourse |
|
|
Sexual dysfunction |
Male: erectile dysfunction - chronic illness, diabetes, heart disease -performance anxiety, difficulty expressing desires, antisexual upbringing Premature ejaculation (rapid) -primarily psychological: guilt, fear if discover6, hurried experiences Females: Orgasmic dysfunction -lifetime lack of orgasm, was orgasmic, under specific conditions - chronic illness, diabetes, etc. -psychological same as premature Vaginismus, penile insertion impossible - primarily psychological, inadequate lubrication, antisexual upbringing Both Inhibited sexual desire: avoids sexual relations due to disinterest Sexual aversion: due to overwhelming fear or anxiety - partner pressure, gender identity confusion, sex trauma Dyspareunia: painful intercourse |
|
|
Biopsychosocial for sexual dysfunction |
Bio: -Spinal cord and sympathetic nervous system -Sex is partially similar to reflexes -Sexual arousal stems from nerve impulsed from skin receptors to spinal cord to organs or glands -negative thoughts or high emotional stated may block sexual arousal. -Parasympathetic: initial excitement and plateau. Sympathetic: orgasm and ejaculation Psychological Anxiety causes sympathetic dominance, which blocks sexual arousal. -performance anxiety: fear of being judged in connection with sexual activity. Anxiety may block blood flow to genitals -double standard: beliefs, values, and norms that subtlt encourage male sexuality and discourage female sexuality |
|
|
Biopsychosocial for sexual dysfunction |
Bio: -Spinal cord and sympathetic nervous system -Sex is partially similar to reflexes -Sexual arousal stems from nerve impulsed from skin receptors to spinal cord to organs or glands -negative thoughts or high emotional stated may block sexual arousal. -Parasympathetic: initial excitement and plateau. Sympathetic: orgasm and ejaculation
Psychological Anxiety causes sympathetic dominance, which blocks sexual arousal. -performance anxiety: fear of being judged in connection with sexual activity. Anxiety may block blood flow to genitals -double standard: beliefs, values, and norms that subtlt encourage male sexuality and discourage female sexuality |
|
|
Sexual scripts |
Socially dictated descriptions of appropriate behaviors for sexual interactions. Many do not fit these standards, but ee internalize these messages. Woman virgin, man is experienced is preferres. |
|
|
STIs |
Sexually transmitted infections Can cause infertility, ectopic pregnancy, cancer, and even death. Most are curable in early stages, but many lack obvious symptoms -male: unusual discharge from penis, soreness |
|
|
Prevention of aids and stis |
1. Remain abstinent or have sex with one mutually faithful, uninfected partner 2. Do not use intravenous illicit drugs or have sex with someone who does 3. Avoid contact with blood, vaginal secretion, or semen 4. Avoid anal intercourse, with or without a condom 5. Do not have sex if u or ur partber are impaired by alcohol or other drugs |
|
|
AIDS |
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome Starts with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) which destroy the immune systems ability to fight diseasr, leaving the body vulnerable to infections and cancers -symptoms dont show for months or years, so people may infect others without knowing -attacks brain and spinal cord, possibly leading to neurological anf cognitive deterioration |

