![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Atom
|
The smallest part of a substance that can exist by itself or be combined with other atoms to form a molecule
|
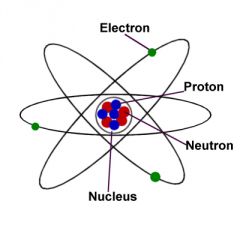
Ex: He
Sentence: Each kind of matter, such as paper is made up of... |
|
|
Molecule
|
The smallest amount of a particular substance that has all the characteristics of something
|
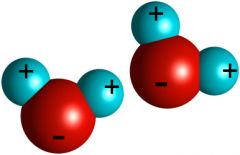
Ex: H2O
Sentence: A ____ of water contains one oxygen atom, and two hydrogen atoms |
|
|
Element
|
One of the basic substances that are made of atoms of only one kind and that cannot be separated by ordinary chemical means into simpler substances
|
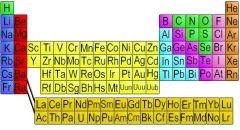
Ex: He
Sentence: The Periodic Table of.... |
|
|
Proton
|
A very small particle of matter that is part of the nucleus of an atom and that has a positive electrical charge
|
Ex: +
Sentence: _____ has a positive charge |
|
|
Electron
|
A very small particle of matter that has a negative charge of electricity and that travels around the nucleus of an atom
|
Ex: -
Sentence: _____ has a negative charge |
|
|
Neutron
|
A very small particle of matter that has no electrical charge and is part of the nucleus of all atoms except hydrogen atoms
|
Ex: Neutral
Sentence: _____ has no charge |
|
|
Ion
|
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative electric charge from losing or gaining one or more electrons
|
Ex: Ca+2
Sentence: Calcium has a positive charge because it lost two electrons |
|
|
Isotope
|
Any one or more forms of a chemical element, having the same number of protons in the nucleus, or the same atomic number, but having different numbers of neutrons in nucleus, or different atomic weight
|
Ex: Carbon-14
Sentence: A ____ is formed when there is not a usual # of neutrons |
|
|
Ionic Bond
|
The electrostatic bond between two ions formed through through the transfer of one or more electrons
|
Ex: NaCl
Sentence: When sodium and chlorine combine, it is called a... |
|
|
Covalent Bond
|
The bond formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms
|
Ex: CO2
Sentence: When one carbon atom, and two oxygen atoms form together they make a... |
|
|
Polar Covalent Bond
|
A bond between two atoms in which electrons are shared unequally
|
Ex: H2O
Sentence: In H2O electrons are unequally shared, which makes it a ____ |
|
|
Law of Conservation of Matter
|
Matter is neither created or destroyed
|
Ex: H2+O=H2O
Sentence: However many atoms you start with, you must end with. |
|
|
Activation Energy
|
The minimum quantity of energy that the reacting species must possess in order to undergo a specified reaction
|
Ex: striking a match
Sentence: Before two molecules react, they must have the required ________ |
|
|
Hydrogen Bond
|
A weak bond between two molecules resulting from a electric attraction between a proton in one molecule and an electronegative atom in the other
|
Ex: H2O
Sentence: Water molecules bonding together to form ice |
|
|
pH Scale
|
A measure of how acidic or basic a substance is
|
Ex: Acidic- battery acid, Neutral- milk, Basic- sodium hydroxide
Sentence: The measurement of how basic or acidic a object is |
|
|
Acid
|
A molecule that can donate a proton or accept an electron pair in reactions
|
Ex: Battery acid
Sentence: ___ would be considered anything under 7 on the pH scale |
|
|
Base
|
A chemical species that donates electrons or hydroxide ions or that accepts protons
|
Ex: Ammonia- NH3
Sentence: There are three different types of _____, Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis |
|
|
Organic Compounds
|
Any number of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon
|
Ex: Acetone
Sentence: _____ is a substance that contains the element carbon |
|
|
Macromolecules
|
A molecule containing a very large number of atoms, such as protein, nucleic acid, or synthetic polymer
|
Ex: Proteins
Sentence: The skin and tissues change in response to the build up of fluid, proteins, and other ________ |
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
Any large group of organic compounds occurring in foods and living tissues and including sugars, starch, and cellulose
|
Ex: CH2O
Sentence: _____ are used for short term energy |
|
|
Lipids
|
Any of a class of organic compounds that are fatty acids or their derivatives and are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents
|
Ex: fats
Sentence: _____ are the building blocks of the fats and fatty substances found in animals and plants |
|
|
Proteins
|
Any class of nitrogenous organic compounds of one or more long chains of amino acids and are an essential part of all living organisms
|
Ex: Fibrous, globular, and membrane
Sentence: _____ is the base component of living cells and is made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and one or more chains of amino acids. |
|
|
Nucleic Acids
|
A complex organic substance present in living cells, especially in DNA and RNA, whose molecules consist of many nucleotides linked in a long chain
|
Ex: Guanine, cytosine, thymine
Sentence: _____ is part of DNA |
|
|
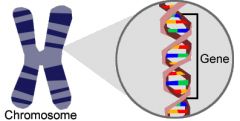
Gene
|
A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristics of the offspring
|
Ex: Eye color
Sentence: Inherited from your mother and father |
|
|
Monosaccharides
|
Any class of sugars that cannot be hydrolyzed to give a simple sugar
|
Ex: Glucose
Sentence: Polysaccharides can be made up of hundreds or thousands of linked ______ |
|
|
Fatty Acids & Glycerol
|
Part one- a carboxylic acid consisting of a hydrogen chain and a terminal carboxylic group, especially any of those occurring as esters in fats and oils.
Part two- a colorless, sweet, viscous liquid formed as a byproduct in soap manufacture. Can be used to make explosives and antifreeze. |
Ex: Fats
Sentence: Glycerolipids are composed of ______ and _______ |
|
|
Amino Acid
|
A simple compound containing both a carboxyl and an amino group
|
Ex: Arginine
Sentence: Each set of three bases, or codon, specifies a particular _____ |
|
|
Nucleotides
|
A compound consisting of a nucleoside liked to a phosphate group
|
Ex: Palindromic sequence
Sentence: Each strand is made up of a series of small molecules called _____ |
|
|
Disaccharide
|
Any of sugars whose molecules contain two monosaccharides residues
|
Ex: Table sugar
Sentence: Tabla sugar is sucrose, a glucose-fructose _____ |
|
|
Polysaccharide
|
A carbohydrate whose molecules consist of a number of sugar molecules bonded together
|
Ex: Cellulose
Sentence: ____ can be found in the cell wall of plants |
|
|
Polypeptide
|
A linear polymer consisting of a large number of amino-acid residues bonded together in a chain, forming part of a protein molecule
|
Ex: The biological process
Sentence: Hydrophobic _____ and proteins play a crucial role in the biological process |
|
|
DNA
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid, a self replacing material presence in nearly all living organisms as the main constant of chromosomes
|
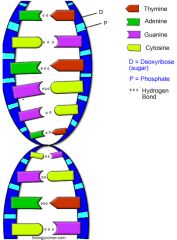
Ex: A, T, G, C
Sentence: Every strand of ___ is different |
|
|
Gene
|
A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristics of the offspring
|
Ex: Eye color
Sentence: Inherited from your mother and father |

