![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

|
Integumentary |
|
|
|
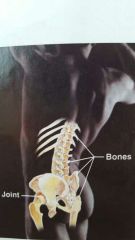
Skeletal |
|
|
|
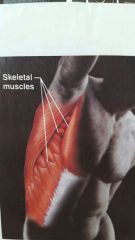
Muscular |
|
|
|
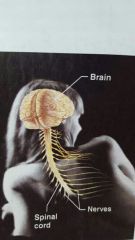
Nervous |
|
|
|
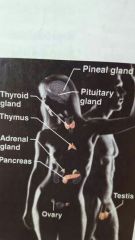
Endocrine |
|
|
|
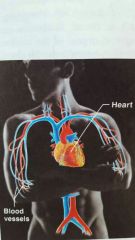
Cardiovascular |
|
|
|
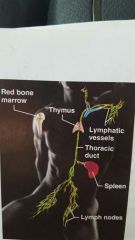
Lymphatic/Immune |
|
|
|
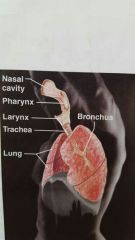
Respiratory |
|
|
|
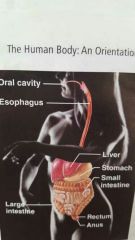
Digestive |
|
|
|
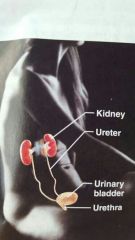
Urinary |
|
|
|
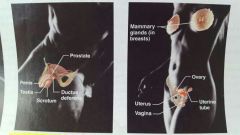
Male and Female Reproductive |
|
|
|
The study of large body structures visible to the naked eye |
Gross (macroscopic) anatomy |
Heart, lungs, kidneys |
|
|
Structures in a particular section of the body are examined at the same time |
Regional anatomy |
Gross anatomy subdivision |
|
|
Body structure studied system by system |
Systemic anatomy |
Subdivision of gross anatomy |
|
|
Study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin |
Surface anatomy |
Gross anatomy subdivision |
|
|
Study of structures too small to be seen by the naked eye |
Microscopic anatomy |
|
|
|
Cystology |
Subdivision of microscopic anatomy; studies the cells of the body |
|
|
|
Histology |
Subdivision of microscopic anatomy; studies the tissues of the body |
|
|
|
Traces structural changes that occur through the life span |
Developmental anatomy |
|
|
|
Embryology |
Subdivision of developmental anatomy; developmental changes that occur before birth |
|
|
|
Cephalic region |
The head; includes frontal (forehead), orbital (eyes), oral (mouth), nasal (nose), and mental (chin) in the anterior region and otic (ear) occipital (back of head) in posterior region. |
Name all subdivisions as well as overall region. |
|
|
Cervical region |
Neck |
|
|
|
Thoracic Region |
Chest; anterior; includes sternal (sternum), axillary (near underarm), and mammary (breasts/nipples) |
|
|
|
Abdominal region |
Stomach to abdomen; anterior; includes umbilical (belly button) |
|
|
|
Pelvic region |
Anterior; Lower abdominal region and includes inguinal (groin) |
|
|
|
Pubic region |
Genitals; anterior |
|
|
|
Upper limb region |
The arms; includes acromial (shoulder), brachial (arm/bicep), antecubital (anterior elbow), olecranal (posterior elbow), antebrachial (forearm), and carpal (wrist) |
|
|
|
Manus region |
Hands; includes metacarpal (posterior hand), palmar (anterior, lower hand), pollex (thumb), digital (fingers) |
|
|
|
Lower limb region |
Legs; includes coxal (hip), femoral (thigh), patellar (anterior knee), popliteal (posterior knee), crural (anterior leg; shin), sural (posterior leg; calf), fibular/peroneal (outer side of leg) |
|
|
|
Pedal region |
Feet; includes tarsal (ankle), calcaneal (heel), metatarsal (top of foot), digital (toes), plantar (bottom of foot), and hallux (big toe) |
|
|
|
Dorsal |
Back; posterior; includes scapular (shoulder blades), vertebral (spine), lumbar (lower back, beside spine), sacral (lower spine), gluteal (booty), and perineal (between anus and external genetalia) |
|
|
|
Superior/cranial |
Above; toward the upper region of the body |
|
|
|
Inferior/caudal |
Below; toward the lower body |
|
|
|
Anterior/ventral |
In front of; toward the front of the body |
|
|
|
Posterior/dorsal |
Behind; toward the back |
|
|
|
Medial |
On the inner side of; toward the midline |
|
|
|
Lateral |
On the outer side of; away from the midline |
|
|
|
Intermediate |
Between a more medial and lateral structure |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Closer to the origin or point of attachment of the limb to the trunk |
|
|
|
Distal |
Farther from the origin or point of attachment of a limb to the trunk |
|
|
|
Superficial/external |
Toward the body surface |
|
|
|
Deep/internal |
Away from surface; more internal |
|
|
|
Axial region |
Axis of the body; head, neck, trunk |
|
|
|
Appendicular region |
Appendages/limbs connected to the body axis |
|
|
|
Sagittal plane |
Vertical line dividing the body into right and left parts |
|
|
|
Median plane |
Sagittal plane directly on the midline |
|
|
|
Parasagital plane |
Any other sagittal plane other than the median plane |
|
|
|
Frontal/coronal plane |
Divide the body into anterior and posterior sections |
|
|
|
Transverse/horizontal plane |
Horizontal division of the body from right to left, divides into superior and inferior parts |
|
|
|
Cross section |
A transverse section |
|
|
|
Oblique sections |
Cuts made diagonally between horizontal and vertical planes |
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity |
Nervous system protection; divides into vertebral/spinal (spinal cord) and cranial cavities (brain) |
|
|
|
Ventral body cavity |
Houses the viscera or visceral organs; Divides into the thoracic (chest) and abdominopelvic (abdomen/pelvis) cavities separated by the diaphragm |
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
Ventral; surrounded by the ribs and chest muscles; subdivided into the pleural (lungs) cavity and medial mediastinum cavity which contains the pericardial (heart and remaining thoracic organs) cavity |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Subdivided into the abdominal cavity (stomach, intestines, spleen, etc.) and pelvic cavity (bladder, rectum, etc.) |
|
|
|
Serosa/Serous membrane |
Thin, double-layered membrane thar folds in on itself to form the visceral serosa; Covers the walls (parietal serosa) of the ventral body cavity and its organs (visceral only) and the membranes are separated by the Serous fluid that they secrete, reducing friction |
|
|
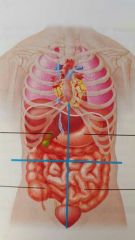
Name the abdominopelvic quadrants |
Right upper (RUQ) | Left upper (LUQ) Right lower (RLQ) | Left lower (LLQ) |
|
|
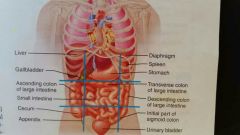
Name the regions of the abdominopelvic cavity |
Right hypochondriac | epigastric | Left hypochondriac Right lumbar | umbilical | Left lumbar Right iliac (inguinal) | hypogastric (pubic) | Left iliac (inguinal) |
|
|
|
Oral/digestive cavities |
Oral - mouth Digestive - digestive organs |
|
|
|
Nasal cavity |
Within and posterior to the nose |
|
|
|
Orbital cavity |
Eyes |
|
|
|
Middle ear cavities |
Medial to the eardrums |
|
|
|
Synovial cavities |
Joints |
|

