![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the levels of organization in the human body.
|
Chemical, Cellular, Tissue.
|
|
|
List the cellular components that make up a cell.
|
Plasma membrane, nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosome and mitochondria
|
|
|
List the four types of tissue in the body.
|
Muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue.
|
|
|
List the ten systems that make up the human body.
|
a. Digestive system,
b. Integumentary system c. Reproductive system d. Circulatory system e. Respiratory system f. Endocrine system g. Urinary system h. Muscular system i. Nervous system j. Skeletal system |
|
|
Explain the respiratory system and its role in our bodies.
|
The respiratory system supplies oxygen, regulates blood pH levels, and removes carbon dioxide.
|
|
|
Explain the circulatory system and its role in our bodies.
|
The circulatory system acts as the mode of transport in our bodies, aiding in the delivery of oxygen rich blood to parts of the body, as well as returning oxygen depleted blood to the lungs to be refilled.
|
|
|
What are the components of blood?
|
Erythrocytes, Leukocytes, Platelets, Plasma
|
|
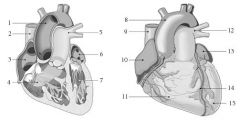
Label the heart diagram.
|
1. Ascending Aorta
2. Superior Vena Cava 3. Right Atrium 4. Right Ventricle 5. Pulmonary Artery 6. Left Atrium 7. Left Ventricle 8. Ascending Aorta 9. Superior Vena Cava 10. Right Atrium 11. Right Ventricle 12. Pulmonary Artery 13. Left Atrium 14. Left Anterior Descending Branch 15. Left Ventricle |
|
|
Explain the role of the heart in training.
|
The heart delivers oxygen rich blood to the entire body, as well as returning oxygen depleted blood to the lungs to be re-oxygenated.
|
|
|
Explain the nervous system and its two major parts.
|
The two major parts of the nervous system are the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is comprised of your brain and spinal column, the peripheral nervous system relays messages from the CNS to the body and relays messages from the body to the CNS.
|
|
|
Explain the role of hormones in the body.
|
Hormones regulate growth and development, help cope with mental and physical stress, regulate forms of training responses including protein metabolism, fat mobilization, and energy production. Basically, they do it all.
|
|
|
What happens if blood glucose levels are too high?
|
Insulin is released.
|
|
|
What does insulin do?
|
It signals fat and muscle to absorb glucose.
|
|
|
What does insulin do to the liver?
|
It tells the liver to make glycogen for storage.
|
|
|
What happens if blood glucose levels are too low?
|
Glucagon is released.
|
|
|
What does glucagon do?
|
It signals the liver to breakdown glycogen and release glucose.
|
|
|
What does the pancreas do?
|
Monitors blood glucose concentrations.
|
|
|
The main purpose of hormones is to what?
|
Alter the rate of synthesis of your cellular protein, change the rate of enzyme activity, and change the rate of transport of nutrients through the cell wall
|
|
|
Hormones are classified as what?
|
steroids, amino acid derivatives, and peptides.
|
|
|
What is the respiratory system responsible for?
|
Supplying oxygen to the body, eliminating carbon dioxide in the body, and regulating the body's pH balance.
|
|
|
What are the two parts of the nervous system?
|
The peripheral and central nervous systems.
|
|
|
True or false, about 98% of the human body is composed of only six elements: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium, and phosphorous.
|
True
|
|
|
What does the circulatory system consist of?
|
Heart, arteries, and veins
|
|
|
What is hemoglobin?
|
An oxygen transporting protein in red blood cells.
|
|
|
Excretion is a function of what system?
|
The digestive system.
|
|
|
Explain what the musculoskeletal system is.
|
The musculoskeletal system is the system of bone and connective tissue that help support and protect the body. It consists of the bones, joints, muscles, and connective tissue existent in the body.
|
|
|
List the four functions of the skeletal system in our body.
|
Bones serve as levers that transmit muscular forces. The skeletal system protects our organs. The skeletal system serves as a framework for other tissues and organs. Bones serve as banks for storage and release of minerals like calcium and phosphorus.
|
|
|
How many bones compose the overall skeleton?
|
206
|
|
|
How many bones compose the axial skeleton?
|
80 (Skull, spine, ribs, sternum)
|
|
|
How many bones compose the appendicular skeleton?
|
126
|
|
|
What is the appendicular skeleton bone breakdown?
|
60 in the upper extremities
60 in the lower extremities 2 in the pelvic girdle 4 in the shoulder girdle |
|
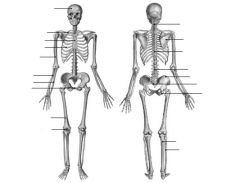
Label the parts of the skeleton, starting from the front, in descending order.
|
1. Cranium 2. Clavicle
3. Sternum 4. Rib 5. Humerus 6. Ulna 8. Pubis 9. Femur 10. Patella 11. Cervical Vertebrae (7) 12. Scapula 13. Thoracic Vertebrae (12) 14. Lumbar Vertebrae (5) 15. Illium 16. Sacrum 17. Ischium 18. Tibia (front) 19. Fibula (rear) |
|
|
What are the three layers that make up bone.
|
Bone marrow, compact bone, and the periosteum.
|
|
|
What is the red marrow?
|
The red marrow produces red blood cells and white blood cells and platelets
|
|
|
What is the yellow marrow?
|
The yellow marrow consists mostly of fat cells.
|
|
|
What is the compact bone?
|
The compact bone surrounds the marrow, and houses nerves and blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the bone.
|
|
|
What is the periosteum?
|
The periosteum is a layer of specialized connective tissue that acts as the skin of the bone, and contains cells that produce bone.
|
|
|
What are the five categories of bone?
|
Flat bones, short bones, long bones, sesamoid bones, and irregular bones.
|
|
|
What are the six categories of joints?
|
Arthroidal (Gliding), Ginglymus (Hinge), Condyloidal (Ellipsoid), Enarthroidal (ball and socket), Sellar (Saddle), Trochoidal (Pivot)
|
|
|
Define "tendon."
|
Tendons are extensions of the muscle fiber that connect muscle to bone.
|
|
|
Define "joint."
|
A joint (articulation) is formed when two bones connect.
|
|
|
Explain the role of the muscular system in our bodies.
|
The 600 muscles in our bodies work together with the support of the skeletal system to create movement. An additional 30 or so are required to insure the passage of food through the digestive system, to circulate blood, and to operate specific internal organs.
|
|
|
What type of joint is the shoulder?
|
Ball and Socket
|
|
|
What type of joint is the neck?
|
Pivot
|
|
|
What type of joint is the elbow?
|
Hinge
|
|
|
What type of joint is the thumb?
|
Saddle
|
|
|
What type of joint is the wrist?
|
Ellipsoid
|
|
|
What are the three types of muscle in the body?
|
Cardiac, Smooth, and Skeletal
|
|
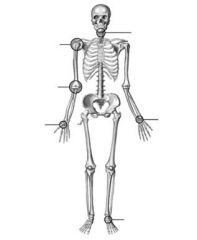
Label the types of joints in descending order.
|
Neck = Pivot Joint
Shoulder = ball and socket Elbow = hinge Thumb = saddle Wrist = Ellipsoid Ankle = Gliding |
|
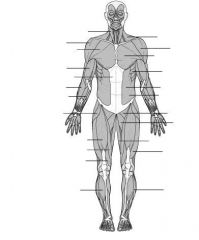
Label the muscles in descending order.
|
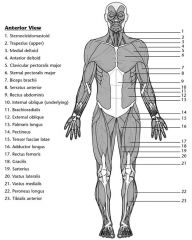
|
|
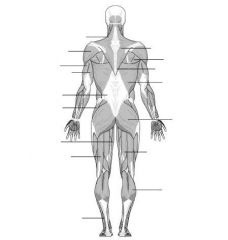
Label the muscles in descending order.
|
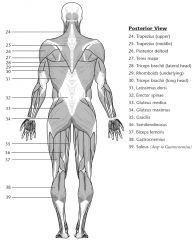
|
|
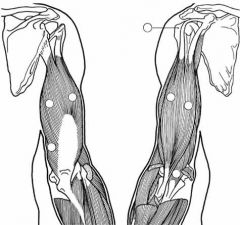
Label the muscles.
|
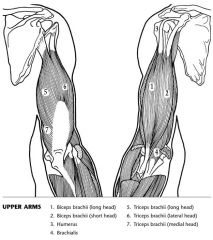
|
|
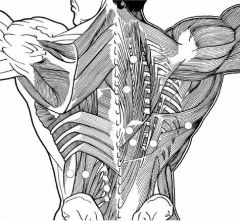
Label the muscles.
|
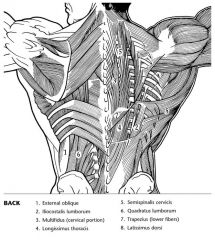
|
|
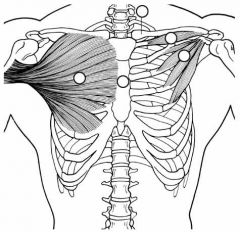
Label the muscles.
|
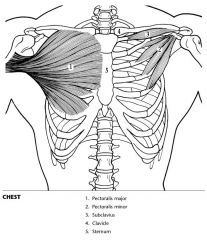
|
|
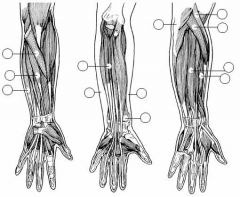
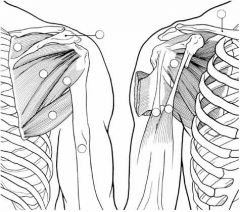
Identify the muscles.
|
|
|
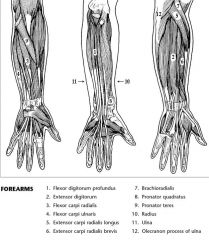
Identify the muscles.
|
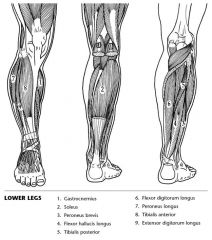
|
|
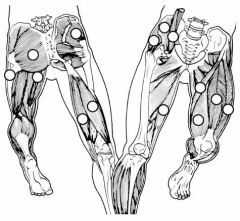
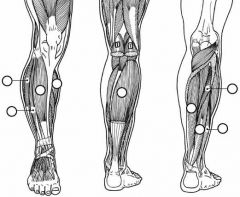
Label the muscles.
|
|
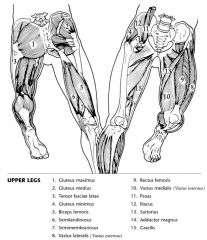
|
Label the muscles.
|
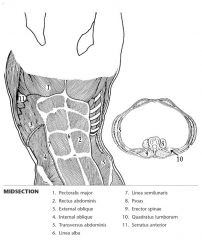
|
|
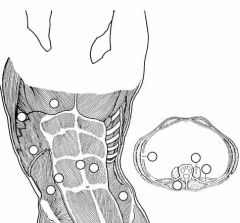
Label the muscles.
|
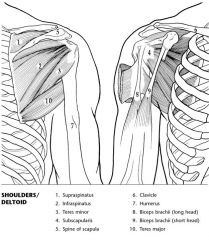
|
|
|
What is a muscle?
|
A group of motor units with the main purpose of contraction.
|
|
|
What are the points of muscle attachment known as?
|
The insertion and the origin.
|
|
|
What are the three types of muscle fiber found in skeletal muscle?
|
Type I - slow twitch
Type IIA - fast twitch Type IIB - very fast twitch |
|
|
What's the difference between Type IIa and Type IIb muscle fibers?
|
Type IIa Red fibers. Fast oxidative (also called fast twitch A or fatigue resistant fibers). Type IIb White. Fast glycolytic (also called fast twitch B or fatigable fibers)
|
|
|
Define caudal
|
below in relation to, inferior
|
|
|
Define contralateral
|
the opposite side
|
|
|
Define cephalic
|
above in relation to, higher, superior
|
|
|
Define dorsal.
|
relating to the back
|
|
|
Define ipsilateral
|
on the same side
|
|
|
Define ventral
|
relating to the belly button or abdomen
|
|
|
define volar
|
relating to the palm
|

