![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
FIFO Inventory |
LIFO inv + LIFO reserve |
|
|
FIFO COGS |
LIFO COGS - (ending LIFO reserve - beginning LIFO reserve) |
|
|
LIFO/FIFO |
FIFO results in more: Lower COGS Higher net income Higher inventory balance Lower cash flow Higher net and gross margins Higher current ratio Lower inventory turnover Lower debt-to-equity |
|
|
LIFO to FIFO |
To adjust LIFO financial statements to FIFO Add the LIFO reserve to current assets (ending inventory Subtract the income taxes on the LIFO reserve from current assets (cash) Add LIFO reserve, net of tax, to shareholder's equity Subtract change in LIFO reserve from COGS Add the income taxes on the change in the LIFO reserve to income tax expense |
|
|
Investment in Financial Assets |
Less than 20% of company and no influence Held-to-maturity at cost on balance sheet; interest and unrealized and realized gain/loss on income statement Available for sale at FMV with unrealized gains/losses in equity on B/S; dividends, interest, realized gains/losses on I/S Held for trading at FMV; dividends, interest, realized and unrealized gains/losses on I/S |
|
|
Investments in Associates |
20%-50% owned, significant influence Equity method Pro-rata share of earnings increases B/S invst. account, also in I/S Dividends received decrease investment account |
|
|
Business Combinations |
>50% owned, control Acquisition method required under US GAAP and IFRS. Goodwill not amortized subject to annual impairment test All assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses are combined with parent <100% create minority interest account |
|
|
Joint venture |
50% owned equity method |
|
|
Differences Between IFRS and GAAP for investments |
IFRS: FX changes on income statement, full or partial goodwill GAAP: FX changes on OCI, full goodwill only |
|
|
Capitalizing vs Expensing |
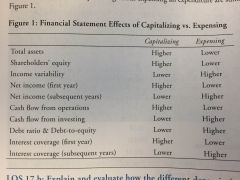
|
|
|
Amortization Expense |
Expense used to account for portion of intangible asset that is used
|
|
|
Depreciation Expense |
Used to spread 1 time cost of purchase over multiple years of tangible assets life |
|
|
Straight Line Depreciation
|
(Original Cost - Salvage Value) / Usable life in Years |
|
|
Double Declining Balance Depreciation |
Depreciation expense = (2/asset life) * Book value at beginning of year x |
|
|
Average age (in years) |
accumulated depreciation / annual depreciation expense |
|
|
Average depreciable life |
ending gross investment / annual depreciation expense |
|
|
Remaining useful life |
ending net investment / annual depreciation expense |
|
|
Finance Lease vs Operating Lease |
Finance lease - Similar to purchase including debt. Balance sheet reflects transfer of ownership. Operating Lease - Similar to rental agreement. No transfer of assets. Accounts receivables created. Interest payment is CFO and prepayment of principal is CFF |
|
|
VIE Charachteristics
|
Insufficient at risk investment Shareholders lack decision making rights Shareholders do not absorb losses No residual benefits Primary beneficiary consolidate the VIE |
|
|
PBO Components |
PBO Components = Current Service Cost, interest cost, actuarial gains/losses, benefits paid |
|
|
Funded Status (Balance Sheet) |
Funded Status = plan assets - PBO = balance sheet asset (liability) |
|
|
Total periodic pension cost |
total periodic pension cost = contribution - ending funded status - beginning funding status |
|
|
Where is TPPC reported |
Total Periodic Pension Cost is reported on income statement for IFRS and OCI for GAAP |
|
|
GAPP Periodic Pension Cost |
PPC = Service Cost + interest cost +- amortization of actuarial gains and losses + amortization of past service cost - expected return on plan assets |
|
|
IFRS Reported Pension Expense |
pension expense = service cost + past service cost + net interest expense Discount rate = expected return on plan assets Net interest expense = discount rate x beginning funded status. Make negative if positive funded |
|
|
Cash Flow Adjustments |
if TPPC < Firm contribution, difference is change in PBO (reduce CFF and increase CFO) if TPPC > Firm Contribution, difference = borrowing (reduce CFO and increase CFF) |
|
|
Translating Subsidiaries Accounting - FX |
For self contained subsidiary, functional currency will not be the presentation currency, use current rate method |
|
|
Current Rate Method |
Current Rate: Assets/Liabilities Common Stock: Historical Rate Average Rate: Income Statement Shareholder's Equity = Exposure Rate When Paid: Dividends |
|
|
Translating Subsidiaries Accounting: FX |
If Subsidiary is fully integrated, functional currency should be the same as presenting Use temporal method |
|
|
Temporal Method |
Current Rate : Monetary Assets/Liabilities Non Monetary Asset/Liabilities : Historical Rate Average Rate : Sales, SGA Historical Rate : COGS, Depreciation Exposure = Monetary Assets - Monetary Liabilities |
|
|
Hyperinflation |
Cumul infl. > 100% over three years: GAAP: Use Temporal Method IFRS: 1) Restate foreign currency st. for inflation 2) Translate with all current rates 3) Net purchase power change reported in income statement |
|
|
Bernish Model |
8 variables used to detect earnings fraud |
|
|
High Quality Earnings |
Sustainable (will continue in future) and Adequate (is enough to cover costs of capital) |

