![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
GDP:
|
Gross Domestic Product.
It is the total market value of the products produced in a country or economy during a period. This counts for final products only. Separate components do not count. GDP also includes rental value for owner-occupied housing. Government services (at cost). |
|
|
GDP: Income Approach.
|
+ Earning of all households
+ business + government = GDP |
|
|
GDP: Expenditure Approach
|
C = Consumption spending
+ I = business investment (capital equipment + change in inventories) + G = Government purchases + X = Exports - I = Imports Sum of market values of all final goods and services produced in the economy. or Sum all the increases in value at each stage of the production process (Value added). |
|
|
Final Value Added:
Give example and explain: |
Material --> Fabricator
Fabricator --> Assembly Assembly --> Consumer Each of these stages added value. This value can be looked at in two ways: as a total of the value added and as a final price given to consumers. The final price given to consumer should be equal to the value added. |
|
|
Nominal GDP:
|
∑(Qt x Pt)
P = Price Q = Quantity |
|
|
Real GDP:
|
With base year = t-5: ∑(Qt x Pt-5)
Uses base year prices because if it did not P could rise while Q is decreasing thereby giving the illusion that the GDP is not changing. Therefore a base price is given in order to give the real GDP. |
|
|
GDP Deflator:
|
Nominal GDP / Real GDP
This is really a measure of inflation. |
|
|
GDP
|
= National Income
+ Capital Consumption Allowance + statistical discrepancy (not in CFA) |
|
|
Capital Consumption Allowance:
|
The output that goes to replace the stock that is wearing out.
Basically like allocating money towards depreciation of money making objects. |
|
|
National Income =
|
= Employee wages and Benefits
+ + corporate and government profits pre-tax + Interest income + unincorporated business owners' income + rent + indirect business taxes - subsidies. ( taxes and subsidies included in final prices) |
|
|
Personal Income:
|
= National Income
+ Transfer payments to households - Indirect business taxes - Corporate income taxes - Undistributed corporate profits |
|
|
Personal Disposable Income:
|
= Personal income - personal taxes
= After-tax income. This money can either be saved or spent. |
|
|
Fundamental Relationship:
|
S = I + (G-T) + (X-M)
Savings = Investment +Government Expenditures - Tax Collections + Exports - Imports Savings are either invested, used to finance government deficit, pr used to fund a trade surplus, when both exist. |
|
|
What is monetary supply?
|
The management of money & credit supply.
|
|
|
How does monetary policy work?
|
Through expansionary and contractionary actions.
Expansionary referers to the increase in money supply which can be viewed as an increase in inventory for banks which thereby reduces borrowing costs (lower interest rate). Contractionary is just the opposite. |
|
|
What are the tools of Fiscal Policy?
|
Fiscal policy implements spending and tax revenue.
Expansionary increases spending and decreases taxes. Contractionary decreases spending and increases taxes. |
|
|
What is the policy called when a bank have to keep a certain amount of money that it lends out in the reserves?
|
Fractional Reserve.
|
|
|
M1:
|
Currency in circulation & currency in circulation.
|
|
|
M2:
|
Savings deposits
Time Deposits Mutual funds. |
|
|
Describe the types of competitions.
What are the nature of competition? |
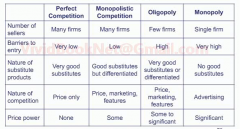
|
|
|
What is a price taker?
What type of companies (competition) are price takers? |
Price takers are companies which have to "take" whatever price the market has set.
Perfect competition. |
|
|
Perfect competition.
|
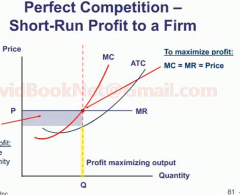
Must take market price.
Homogenous products. Large number of small firms each small percentage of the total market. Perfectly elastic demand curve. No barriers to entry and exit. Do not make economic profit in the long run. |
|
|
What is the economic profit of perfect competition in the long run?
|
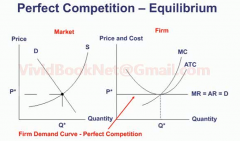
MR = AR = D
|
|
|
When does a firm shut down in the short run and why?
|
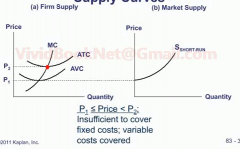
When P is less than the AVC. In order to limit expenditure of variable costs.
|
|
|
What are the effects of permanent increase in demand for a perfect competition?
Draw a chart. |
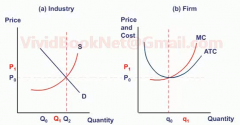
New firms will enter the market place driving down the price to a new equilibrium until there is no economic profit.
|
|
|
Explain monopolistic competition and its characteristics.
|

Competition with many companies but the products differentiate.
Each firm has a small market share. Collusion not possible. Low barriers to entry. No economic profit in the long run. Very similar perfect competition except the products slightly differentiate. |

