![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If you noticed an exposure
drifting toward darkened images overtime check what? |
Check the flash tube or
schedule a thorough cleaning of camera |
|
|
What 2 types of dilation drops?
|
Mydriatics and Cycloplegics
|
|
|
What do mydriatics do?
|
They cause the dilator muscle
to contract |
|
|
What is another term/name
for mydriatics? |
Sympathomimetics
|
|
|
What do cycloplegics do?
|
They relax iris sphincter muscle
and |
|
|
Name 5 reasons pupils may be small.
|
Diabetic, glaucoma, dark iris, corneal scaring, old
|
|
|
What are 4 things you can do to help get a photo of a retina with small pupils?
|
Increase flash setting, choose smaller angle of view, insert small-pupil diaphragm. If none of those work place the "dark cloud" away from pathology you're photographing.
|
|
|
If the pupil is significantly smaller than the outer diameter of the illuminating doughnut what artifact appears?
|
Dark Cloud
A portion of the retina will receive inadequate illumination. |
|
|
What filter will help you
bring an image into focus? |
Red-free or Green filter
(540-570 nm) |
|
|
What layers of the retina
make up the inner retina? (3) |
ILM, NFL, GCL combine
to form the inner retina |
|
|
What blood vessels and
pathology are at the inner retinal layers? (5) |
- Large retinal blood vessels
- Cotton-wool spots, - NFL defects - myelinated nerve fibers, - flamed-shaped hemorrhages |
|
|
What layers of the
retina make up the central retina? (4) |
IPL, INL, OPL, ONL
|
|
|
What blood vessels and
pathology are at the central retinal layers? (4) |
- Smaller blood vessels
branches - Hard exudates - DM microaneurysms - FAZ |
|
|
What layers of the retina
make up the outter retina?(3) |
-Rods & Cones
-RPE - Bruch's membrane |
|
|
ICG 8-12 min is what phase
|
Isofluorescent
|
|
|
Explain Inversion Phase
and how long into test it occurs. |
When the choroidal vessels have emptied and appear dark agains a bright background
about 20 min into test |
|
|
Describe recirculation phase.
|
- When the arteries and veins are
equally faded - Disc appears "HOT" - Is in a F/A exam |
|
|
What 4 basic steps are required in processing black and white film?
|
- Development
- Stop bath - Fixation - Washing |
|
|
Name two types of Luminescence
|
Fluorescence
Phsophorescence |
|
|
What is differential focus?
|
In stereo photos when focusing in
two different plains. |
|
|
When an image "floats" in the air
space both in front of and behind the clear glass is termed... |
Aerial Image
|
|
|
Developer's 2 most
important ingredients are? |
Metol and Hydroguinone
|
|
|
The arm to retinal time is
usually how long? |
8 to 16 sec.
|
|
|
If your patient is less than 100lbs
the 10% (F.S.) is how many mg's per pound of body weight |
3.5 mg's per pound
|
|
|
What times are images recorded
after initial phase in ICG? |
2-3min, 5-7min, 10-12min, 20min,
40min, 60min NOTE: Late phases maybe more informative depending on pathology |
|
|
What are contraindications for F/A's
(who wouldn't you perform this test on?) |
- Pregnant
- Recent history of chest pains - Juvenile asthma |
|
|
What are contraindications for ICG?
(who wouldn't you perform this test on?) |
- Pregnant
- Caution if Iodine allergy - Had allergic reaction before - Uremia on hemodialysis are at risk of reaction. |
|
|
What is Pseudofluorescence?
|
Produced by poorly matched fliters
or worn out filters. |
|
|
What is Auto-fluorescence?
|
Ocular tissue having appearance
of fluor. without fluor in system. (Optic Nerve Drusen) |
|
|
How much fluorescein would you
give a child? |
35mg per pound of 10% fluoresceine
|
|
|
Maximum light absorption and
fluorescent excitation of F.S. is ? (In nm) |
Light Blue wavy length or
485nm to 530 nm |
|
|
When would the "inversion phase"
occur and what is it? |
About 20 min after ICG was injected.
When the choroidal vessels have emptied making them dark against a brighter background. |
|
|
What two terms are used to describe
when the choroidal vessels are emptied against a brighter background? |
Inversion Phase or Retrofluorescene
|
|
|
Name mild adverse reactions to
F/A (3) |
- Nausa/vomiting
- Sneezing,hives,itchy - Pain & swelling if site was extravasated |
|
|
Plebitis
|
Moderate adverse reaction to F/A
Inflammation to vein that was injected. Goes away within day. DO NOT use that vein again!!!! |
|
|
If you have a color slide that has
image that seems 1/2 cut off, What would be the cause? |
Shutter not synchronized with
flash. |
|
|
For an 8-bit monitor what is the
number of bits it goes up to? |
0 to 255 pixels
|
|
|
What does the "BIT" do in
digital photos? |
The bit determines how much
light will hit a pixel |
|
|
Resolution = number of _______
Sensitivity = number of _______ Contrast is ___________ |
Pixels
Bits Difference between light and dark |
|
|
Height and width or "Aspect" of
Digital photo Film photo |
Digital 1x1
Film 2 x 3 for 35mm |
|
|
What is Irvin-Glass
syndrome? |
When post cat pt has CME
(centeral macular edema) after uneventful cat sx. |
|
|
Small pupils can be
photographed better with what angle of view? |
35 or 20 degrees
also set camera to "S" if less than 5mm |
|
|
What do the arteries do?
|
Carry oxygen rich blood
from lungs and heart to the tissue. |
|
|
What do veins do?
|
Carry blood containing
carbon dioxide and waste away from the cells. |
|
|
What does the "Illumination
diaphragm lever" control? |
The amount of light from
the camera to the eye. |
|
|
Discribe leakage in a F/A.
|
- Early hyperfluorescence
- increases in intensity in lates - Diffusion and enlargment of dye |
|
|
Name ICG phases and
times (4) |
- Early 10-20 sec
(increases in brightness) - Isofluorsent 8-12 min - Inversion/Retrofluorescence about 20min - Lates 30 - 60 min |
|
|
If a hypoglycemic pt is
unconscious what injections can be used to help them regain consciousness? |
- Glucagon
- D-50 |
|
|
What is Glucagon? Where
is it injected? |
It is a hormone that causes
sudden increase in sugar. (1/2 cc & goes into muscular) |
|
|
What is D-50? Where is it
injected? |
- An injection that goes into
the veins. - Amount determined by sugar level & weight of pt (Dr., RN, & paramatic ONLY) |
|
|
How soon after received the
sugar sould the Hypoglycemic episode end? |
5 to 15 minutes
|
|
|
Fluorscein Sodium (F.S.)
maximum emission is ? nm |
520 nm to 530 nm
|
|
|
What filters would be used
for color f/a's? |
Wratten 12, 31 or 34
(Absorbsion filters) |
|
|
What does the hemoglobin
do during F/A's? |
Absorbs the F.S. along with
the Albumins. |
|
|
What does the term
"extinction" mean regarding F.S.? |
Refers to the suppresion
of fluorescein. |
|
|
What is the apeture?
|
It controls the size of the
hole that allows the light to hit the film. ( It is the cameras pupil) |
|
|
Explain Isofuorescent and
what test is this phase in? |
- 8 to 12 min in to an ICG test
- Equal distribution between choroidaal vessels and the surroundings |
|
|
Name the phase 20 min
into and ICG. |
- Inversion phase or
Retrofluorscent |
|
|
In film developing if the slide
film has overlapping images. What may have occured? |
The film did not advance
properly. |
|
|
Color slide has some frames
only part of the image is clear & some looks like it didn't develope properly. What may have occured? |
Cameras back opened before
re-wound. |
|
|
What is extinction by
contamination? |
When F.S. is absorbed by
albumins. |
|
|
What is extinction by
concentration? |
When to much F.S. is
administered. |
|
|
What are Albumins?
|
It is the plasma proteins that
absorbs f.s. in the choroid. |
|
|
What is fenastration?
|
Choroidal area, little breaks
in blood vessels that f.s. leaks out of. |
|
|
After taking your photo the periphery of the image is dark.
What is the problems and how would you correct it? |
You are to far away from the
pt or the pupil is to small. -Go back and forth -Change diaphragm level to S -Take photo w/35 - 20 deg |
|
|
What is retrofluorescence?
|
In ICG when choroid
vessels are dark against bright background. |
|
|
What is window defect? (3)
|
- Hyperfluorescent at 1st
- No change in shape or size - Slowly decreases in intensity |
|
|
What is staining? (2)
|
- Hyperfluorescent at end
- No change in shape or size |
|
|
What is pooling? (3)
|
- Hyperfluorescent
- Slowly developes - Sharp, demarcated boarders |
|
|
Congenital early cyanosis
|
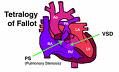
Tetralogy of Fallot
|
|
|
Name four different terms that can
be used to describe hyperfluorescence. |
- Window Defect/transmission
- Staining - Leaking - Pooling |
|
|
Name two different terms that
can be used to describe hypofluorescence |
- Filling defect
- Blockage |
|
|
What 2 filters are needed to
perform F/A's? For ICG's? |
Exciter Barrier
F/A blue 490nm Green 530nm ICG red 640nm Green 530nm |
|
|
Explain interference filters.
|
Filters that will reflects light waves
Sharper images |
|
|
Explain absorption filters.
|
Filters that absorb or block light
waves. Muddy image |
|
|
Emulsion of black and white film is
made up of ____ ____ ____ which is suspended in gelatin layer. |
Silver Hyloid Crystals
|
|
|
What does hyperfluorescence mean?
|
Greater fluorescence in an area
than normal. |
|
|
What does background fluorescence?
|
Uniform fluorescence of choroicapillaries during early phase
of F/A. "Choroid flush" |
|
|
What are major adverse reactions
in F/A? (4) |
- Bronchospasm
- Laryngeal Edema - Cardiac Arrest - Anaphylactic Shock |
|
|
What are moderate adverse
reactions in F/A? (3) |
- Fainting
- Plebitis - Seizure |
|
|
Explain how to take photos of the
7 standard positions of gaze. |
1=optic nerve head, 2= macula,
3=temp to macula, 4=superior temporal 5=Iinferior temporal, 6= superior nasal, 7=inferior nasal |
|
|
How does drusen appear on f/a?
|
Late Hyperfluorescence
There will be late staining |
|
|
Defective pixels are always
what color? |
BLACK
|
|
|
Name filters are used for ICG tests
and the locations of these filters. |
Exciter: in front of the light: Red 640
Barrier: in front of the film: Green 530 |
|
|
What are albumins?
|
Plasma proteins in the choroid that
absorb the f.s. |
|
|
Name filters are used for F/A tests
and the locations of these filters. |
Exciter: in front of light: Blue 490nm
Barrier: in front of film: Green 530 |
|
|
When taking a photo and the image
appears like a white curtain came down over it, what is the problems? |
Patient blinked
|
|
|
If the photo image has a crescent at
the edge of the frame, what is occurring and how do you correct it? |
Camera is off center, getting a
shadow from the pupil. Move camera toward shadow. |
|
|
Name all the phases of a F/A and
in their order. |
- Early/Pre-arterial/Background fluo.
- Arterial - Arterial venous - Venous - Recirculation/Late |
|
|
What conditions are best noted in
"late" phase of a F/A? |
- Cystoid macular edema
- Significant macular edema - Central Serious Maculopathy |
|
|
Name the nm for
- blue - green - red |
- Blue: 490nm (485nm-530nm)
- Green: 540nm-575nm - Red: 640nm |
|
|
The _________ filter enhances
the choroidal detail and the borders of pigmented lesions (nevi) |
- Red 640nm
|
|
|
The _________ filter enhances
retinal vasculature and hemorrhages on black and white film. |
- Green 540nm-575nm
|
|
|
The _________ filter enhances
the nerve fiber layer on black and white film. |
- Blue 485nm-530nm
|
|
|
How does ICG come, how long is
it good for, and how does it work? |
- Powder form
- Good for 10 hours after being mixed - Does NOT leak out of veins & albumins. |
|
|
When ICG is injected within
_____ sec the image becomes _____ and the light needs to be turned ________. |
- 10 sec
- very bright - turned down quickly |
|
|
Extinction by concentration
means what? |
This is when the f/a becomes
absorbed into the system. |
|
|
What 3 muscles control
the pupil size? |
- Cilliary muscle
- Iris sphincter muscle - Dilator muscle |
|
|
What 2 people did the 1st
F/A and what year? |
- H.R. Novtny
- D.L. Alvis - 1961 |
|
|
When injected into the bloodstream
F.S. is absorbed by _______ and _______ ______ particularly the __________. |
- Hemoglobin
- Plasma proteins - Albumins |
|
|
When taking a photo there are white
spots on the retinal image. What is occurring? |
Dust on the lens
|
|
|
What has happened when the
color slide comes back black after developing? |
Either flash not working or film
did not advance. |
|
|
1. From 2-6 hours f.s. stains ___ ___,
___, ___. 2. From ___ to ____ hours f.s. stains the urine |
1. Mucous membranes, sclera, skin
2. 24 to 36 hours |
|
|
Prochlorperazine (compazine)
and Promethazine (phenergan) can be given ____ min orally prior to f/a to help provent what? |
Given 45 min prior
To provent nausea and vometting. |
|
|
What degree is considered the
"normal" angle of view? |
30 degrees
|

