![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Which artery supplies the Pons?
|
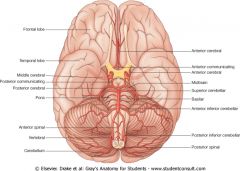
Branches from the Basilar artery supply the pons. Describe Cushing's triad (Cushings Reflex)
|
If mean arterial pressure is less than intracranial pressure as is the case with increased pressure from hemorrhage in brain, the hypothalamus kicks in. In emergency medicine people look out for these symptoms: hypothalamus increases sympathetic drive causing vasoconstriction and increased contractility to right the pressure difference. The carotid body senses the pressure change and trys to compensate via the vagus. This causes bradycardia. The intracranial pressure causing all of this pushes like a tonsilar hernia and affects the medulla, the result is irregular breathing. Look for wide pulse pressure.
|
|
|
The Basilar Artery, at the center of things, is supplied by which two arteries?
|
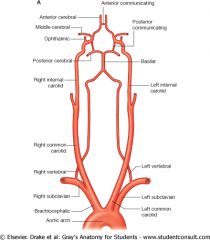
The basilar is made up of the left and right vertebrals from the left subclavian and brachiocephalic respectively.
* Remember BCS bowl game |
|
|
|
The anterior communicating connects which two arteries in the circle?
|
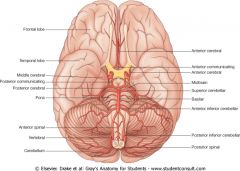
Anteriocebral branches from the internal carotid
|
|
|
|
The posterior communicating artery of the circle of Willis connects which two arteries?
|
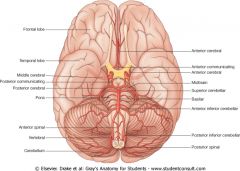
Internal carotid and posterior cerebral.
It's easy the anterior connects the anteriors. the posterior connects posterior to internal carotid. |
|
|
|
Deep Branches of what artery supply the Putamen?
|
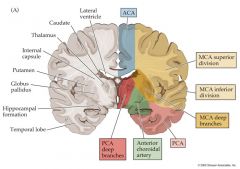
The Deep branches of the MCA supply the Putamen.
|
|
|
|
The head of the caudate is supplied by deep branches of what artery?
|
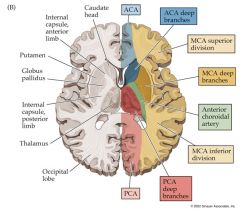
ACA deep branches supply the head of the caudate. notice the anatomy. caud-put-thal with the capsule seperating the thal and put
|
|
|
|
The lenticulostriate arteries supply which structures?
|
Putamen and Caudate. LS arteries are deep MCA branches
|
|
|
|
MCA or ACA: I supply the anterior temporal lobe
|
MCA
|
|
|
|
MCA or ACA: I supply the medial aspects of the parietal lobe and frontal.
|
ACA
by medial I mean close to the Great hemispheric sulcus so supperior on sagital view. |
|
|
|
The genticulate formation of the hippo and the internal capsule are supplied by this artery
|
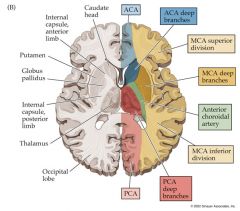
Anterior Choroidal, don't sleep! on it.
|
|
|
|
WATER SHED CLOCK:
on coronal section the major water sheds are at 4:05 and 7:55 and represent which arteries? |
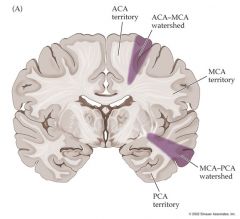
The hour hands are on the MCA-PCA. the Minute hands are on the ACA-MCA
|
|
|
|
WATER SHED CLOCK TIME:
On axial section 5:05 6:55 |
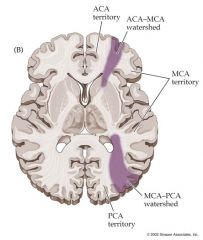
Hours MCA-PCA
Min ACA MCA Note this informs the area supplied by the ACA goes to the midline and so does the PCA's. |
|
|
|
The posterior circulation is supplied by what arteries?
|
Vetebrobasilar. they come up through the foramina on the transverse processes of the verterbrae
|
|
|
|
What is the leading cause of hemorrhagic stroke?
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
From what? |
Berry Aneurysm.
Recall the branch points of the posterior circulation are most often affected. |
|
|
Where do most Berry Aneurysms arise?
|
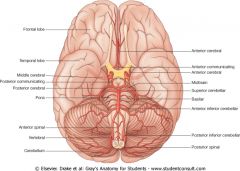
Anterior Circulation branch points: Anterior and posterior Communicators. The latter at the junction of the PCA and IC.
Which CN are most often compressed? |
CN II and CN III
|
|
|
I most commonly occur on a hemisphere and can cause bleeding.
|
AVMs. Atrioventricular malformations.
What are AVMs? |
Nests of directly connected veins and arteries without intervening capilaries.
|
|
|
Watch out for this cause of stroke which originates in the walls of large arteries at branch points.
|
Thrombus.
|
|
|
|
Anterior Circulation and Posterior Circulation Thrombus result in CONTRALATERAL upper limb, Lower limb or face weakness or sensory loss.
Which circulation is associated with apraxia? |
Anterior.
also aphasia and agnosia |
|
|
|
Anterior Circulation and Posterior Circulation Thrombus result in CONTRALATERAL upper limb, Lower limb or face weakness or sensory loss.
Which circulation is associated with ataxia and hemianopsia |
Posterior:
think cerebellum. also the majority of the cranial nerve deficits will be seen in this circulation. |
|
|
|
Who is at risk for lacunar infarcts?
|
Diabetics! weakening of deep branches
|
|
|
|
Man in a barrel distribution? what is this
|
Weakness/Anesthesia in arm and shoulder
Anesthesia in trunk Weakness/Anesthesia in legs Why? |
This is usually from a massive internal carotid stroke. MCA causes arm trunk problems. ACA causes leg problems
|
|
|
Doctor, my symptoms started with this dark shade comming down over my left eye. then i couldn't see! What is this
|
The shade was lowered for love...Amore...Amaurosis fugax. This is caused by TIA or loss of blood flow to the retina.
|
TIA or no flow to retina.
|
|
|
In all areas of the spinal cord, this circulation is constant. Where is it not?
|
The anterior spinal artery is constant. aorta is responsible for most others.
The Lumbar and Sacrum is from a radicular artery: of Adamkiewicz |
|
|
|
In all areas of the spinal cord, this circulation is constant. Where is it not?
|
The anterior spinal artery is constant. aorta is responsible for most others.
The Lumbar and Sacrum is from a radicular artery: of Adamkiewicz |
|
|
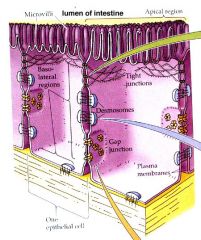
These layers TDG are analogous to which layers of the CNS?
|
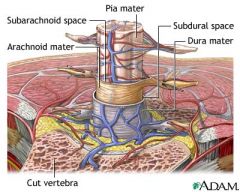
DAP. gimmee some dap boyeee. Elevations in Ig in the CSF imply what?
|
Auto immune process...Think Muscular Sclerosis before you think about anything else.
|
|
|
An issue where the eye on one side is affected but the body on the other side is
|
Central. Kernohan's phenomenon happens when hematomas causes a herniation which compresses things around the tentoral notch.
|
|
|
|
What is the organum vasculom?
|
It is a circumventricular organ of the 3rd ventricle. It monitors the osmolarity and along with the Subfornical organ of the 3rd ventricle influences angiotensin ii and vasopressin.
|
|
|
|
What is the area postrema
|
it sits at the end of the 4th ventricle and samples for things that should cause vomiting vis CTZ.
|
|
|
|
3rd CVO
4th CVO |
Organum vasculum and Subfornicate: BP
Area postrema: CTZ |
|
|
|
I link the 3rd and 4th ventricles
|
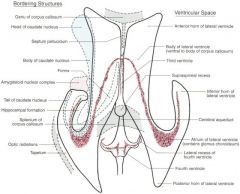
Cerebral Aqueduct
or The Sylvian duct. Besides the ventricles, where is the CSF? How can the brain be 'bathed' if it is just the ventricles? |
Subarachnoid space!
|
|
|
There are subarachnoid villi up into the ventricles, but there are only two places where the subarac and CSF communicate.
|
Both are in the 4th ventricle
Megendie and Luschka |
|
|
|
400-500 ml of CSF is made per day, but the ventricles only contain 25ml. Where does the rest go?
|
Arachnoid Granulations. that poke up like polys into the superior venous sinus. thus the venous circulation is the final destination.
|
|
|
|
Both normal pressure and communicating hydrocephalus is caused by what?
|
Mal absoprtion: Failure of the Arachnoied Granulations
|
70% of the CSF is secreted by the choroid plexus and 30% is metabolic waste discharged by the CNS.
|
|
|
Where do CSF obstructions occur?
|
Babes: Sylvius
Everybody else: Lushka Magendie, and Monro Babies with hydrocephalus have these three Ws |
Wacky, wet, wobbly
|
|
|
Anrnold Chiari herniation appears with this
|
Syringomyleia. these are cysts that form in the spinal cord.
|
|
|
|
Dandy-Walker. how to think about it
|
Fourth ventricle gets so big that it obliterates the vermis.
|
|
|
|
Arnold Chiari is a congenital herniation of what?
|
Cerebellar tonsils the foramen magnum. or a vermis herniation. It is associated with syringomyelia.
|
|
|
|
What does coarctation mean?
|
Narrowing as in the aorta. Check femoral pulse
|
|
|
|
Why does a subdural ematoma look like crescent?
|
Shearing forces severe bridging veins at low pressure. Unlike in the epidural where there are adhesions between the dura and the skull, the subdural can spread it self out more.
|
|
|
|
Why does a epidural hematoma look like a lense or a finger pushing in on the brain?
|
The dura has adhesions to the calvaria and the blood is high pressure arterial blood.
|
|
|
|
Signs of brain hernia.
|
dilated pupil from III issues. hemiperisis.
Tosilar hernias compress the medulla and its breathing centers causing death. Subfalcine happens in such a way as the ACA is compromised, making things worse. |
|
|
|
These two circumventricular organs are secretory
|
The median eminence (makes the vasopressin that the Neurohypophysis secretes)
The pineal gland (melatonin, seratonin, chocytikinin) |
|

