![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
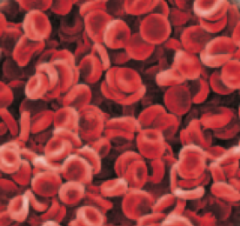
What type of cells are shown in the picture?
|
Red blood cells
|
|

Label the parts of the microscope.
|
1. Eyepiece
2. Coarse adjustment knob 3. Fine adjustment knob 4. Revolving nosepiece 5. Objective lenses 6. Stage 7. Stage clips 8. Diaphragm 9. Lamp 10. Arm 11. Base |
|
|
What device magnifies our vision to the point where we can see cells and their components clearly?
|
Microscope
|
|
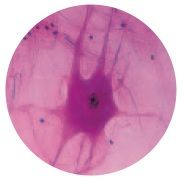
What type of cell is this, plant or animal?
|
Animal
|
|
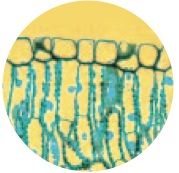
What type of cell is this, plant or animal?
|
Plant
|
|
|
What 6 things do all living things have in common?
|
• are made of cells
• need energy • grow and develop • respond to the environment • reproduce • have adaptations for their environment |
|
|
What are organisms?
|
Living things
|
|
|
What is the basic unit of life?
|
A cell
|
|
|
What are nutrients?
|
Substances that provide the energy and materials that organisms need to grow, develop, and reproduce.
|
|
|
What is metabolism?
|
The sum of energy-using processes and the energy-creating processes in an organism.
|
|
|
What is a stimulus?
|
Anything that causes a response in an organism
|
|
|
What is a response?
|
Reaction to a stimulus.
|
|
|
What is the difference between growth and development?
|
Growth indicates an increase in size while development means changes in body shape and functions because of maturation.
|
|
|
Define reproduction.
|
The process of living things coming from other living things.
|
|
|
Define adaptation
|
A characteristic that allows an organism to live in its environment.
|
|
|
What is the difference between structure and function?
|
Structure is how something like an organism is built (body parts), while function is how the structures are used to do something specific.
|
|
|
What is the relationship between an organ and an organ system?
|
Organ systems are made up of organs.
|
|
|
List 5 components of the circulatory system
|
• heart
• blood • veins • arteries • capillaries |
|
|
What does the circulatory system do?
|
• transport oxygen, food, and other substances throughout the body
• transport some wastes to other organs for elimination • defend the body against diseases • connect all other organ systems |
|
|
What are the structures in the respiratory system?
|
• nose
• mouth • trachea • diaphragm • bronchi • lungs |
|
|
What are the functions of the respiratory system?
|
• transport oxygen from the outside air to the blood
• transport carbon dioxide from the blood to the outside air |
|
|
List 6 of the 9 components in the digestive system.
|
• salivary glands
• mouth • esophagus • stomach • liver • pancreas • gall bladder • small intestine • large intestine |
|
|
What is the function of the digestive system?
|
To break down food pieces into much smaller pieces (particles) so they can be absorbed and transported throughout the body
|
|
|
What are the functions of the nervous system?
|
• coordinate and control the actions of all organs and organ systems
• detect, process, and respond to changes in external and internal environments |
|
|
List the structures of the nervous system
|
• brain
• spinal cord • nerves • eyes, ears, and other sensing organs (hands, nose, etc.) |
|
|
What are the structures of the excretory system?
|
• kidneys
• bladder • lungs • skin • liver |
|
|
What is the function of the excretory system?
|
Removes chemical and gaseous wastes from the blood
|
|
|
Which system is made up of bones and cartilage?
|
The skeletal system
|
|
|
What does the skeletal system do?
|
• provides a movable support frame for the body
• protects soft-tissue organs such as the heart and lungs |
|
|
What are the functions of the muscular system?
|
• move bones
• move organs that contain muscle tissue (such as the heart and stomach) |
|
|
What are the structures in the muscular system?
|
• muscles
• tendons |
|
|
What is the integumentary system?
|
The skin
|
|
|
What is the intricate network of thin, hair-like vessels connecting arteries and veins in the lung tissues made of?
|
Capillaries
|
|
|
What is the relationship between cells, tissues and organs?
|
The same types of cells group together to form tissues which group together with other tissue types to form organs.
|
|
|
Under the microscope it looks like a thin line that surrounds the whole cell. What is it?
|
Cell membrane
|
|
|
Under the microscope it looks like a rigid, frame-like covering that surrounds the cell membrane. What is it?
|
Cell wall
|
|
|
Under the microscope it looks like a liquid inside the cell, which has grainy-looking bits in it. What is it?
|
Cytoplasm
|
|
|
Under the microscope it looks like a fairly large, dark, spherical structure that's usually near the centre of the cell. What is it?
|
Nucleus
|
|
|
Under the microscope it looks like clear, liquid-filled spaces in various places within the cytoplasm. What is it?
|
Vacuoles
|
|
|
What are the 4 common types of tissues found in humans and other animals?
|
• connective
• epithelial • nervous • muscle tissues |
|
|
What are the three tissue types in plants?
|
• photosynthetic/storage
• protective • transport |
|
|
What are the three organs that make up plants?
|
• leaves
• roots • stems |
|
|
What is osmosis?
|
The diffusion of water particles through a selectively permeable membrane.
|
|
|
What is diffusion?
|
The water particles move from an area of higher concentration (where there are more water particles) to an area of lower concentration (where there are fewer water particles).
|
|
|
What does "selectively permeable" mean?
|
The cell membrane allows the particles of some substances to pass through it, but not others.
|
|
|
What are cilia?
|
Hair-like structures which move back and forth.
|
|
|
What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular?
|
Unicellular organisms are made up of only a single cell while multicellular organisms are made up of two or more cells.
|
|
|
Define mycoplasma.
|
The smallest kind of organism scientists have discovered so far.
|
|
|
What are mitochondria?
|
The “powerhouses” of the cell where chemical reactions occur that convert the energy the cell receives into a form it can use.
|
|
|
What are chloroplasts?
|
The “solar panels” of the cell. They are found in the cells of the green parts of plants. They carry out photosynthesis, converting the sun’s energy into food for the cell.
|
|
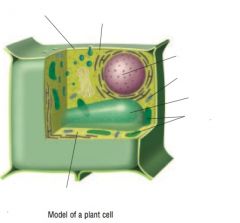
Identify the parts of the plant cell
|
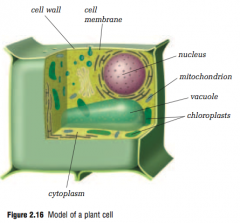
|
|
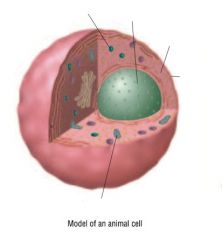
Identify the parts of the animal cell
|
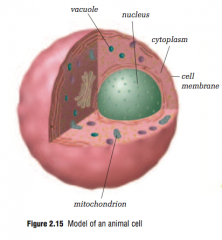
|
|
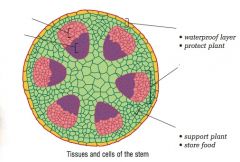
Identify the tissues and cells of the plant stem
|
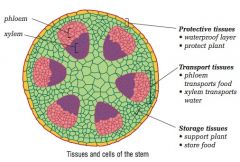
|
|
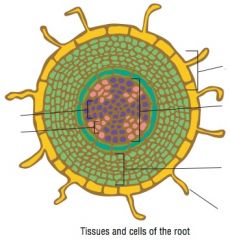
Identify the tissues and cells of the plant root
|
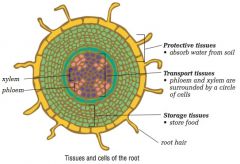
|

