![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Prokaryotic |
- Has no membrane bound organelles - eg: bacteria |
|
|
Eukaryotic |
Contains membrane bound organelles that are held in place by protein filaments known as a cytoskeleton |
|
|
Apoptosis |
The self destruction of cells for the good of the whole organism. Known as programmed cell death Two pathways: 1. Signals from outside the cell 2. Signals from inside the cell - mitochondrial pathway Involves the release of caspase enzyme to fragment DNA
|
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Fluid mosaic that controls the entry and exit of material. Flexible Phospholipid bilayer Contains cholesterol and proteins Semipermeable. Allows rapid absorption of lipid soluble substances and small substances such as water, carbon dioxide and oxygen. |
|
|
Membrane phospholipids |
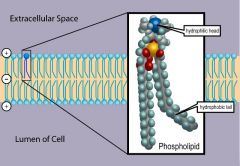
Hydrophilic head. 2 hydrophobic fatty acid tails.
|
|
|
Membrane cholesterol |
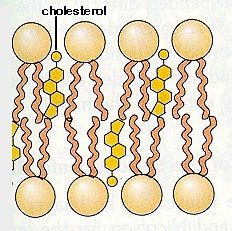
Fit between the phospholipids. makes the membrane more flexible. Gives rigidity to the membrane. |
|
|
Membrane Proteins |
Surface proteins - glycoproteins are proteins with carbohydrates attached. They are involved in cell to cell recognition
Transmembrane proteins - protein channels for the entry and exit of material
|
|
|
Cell wall |
Rigid outrage layer surrounding the cell membrane. Provides protection and shape. Found in plants (cellulose), fungi (chitin), bacteria (peptidoglycan). Prevents over expansion of the cell when water enters. |
|
|
Nucleus |
Contains the DNA which holds the code for the proteins. Bound by a double membrane with pores.
|
|
|
Cytosol |
A fluid consisting manly of water that contains dissolved substances. cytoplasm = cytosol + organelles except nucleus protoplasm = cytosol + all organelles |
|
|
Mitochondria |
The "powerhouse" of the cell. The site of cellular respiration which is the process that produces ATP. Contains a double membrane. The inner membrane is highly folded. The fingerlike projections are called christae and the matrix is the space between. |
|
|
Ribosomes |
The site of protein synthesis. Has no membrane. Those on ER produce proteins for transport to other parts of the cell or for export. Those that are free produce proteins for local use within the cell. |
|
|
Chloroplasts |
Capture radiant energy and transform it to chemical energy present in organic molecules. Made of: Grana - Stacks of membrane structures called thylakoids. Stroma - Gel like matrix |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum |
A continuous folded plasma membrane creating a series of channels. Rough - Has ribosomes attached. Makes and transports proteins within the cell. Smooth - Site of phospholipid and fatty acid production. |
|
|
Golgi Body |
A network of folded membranes. Packages the protein into vesicles for transport across the plasma membrane and out of the cell. Large numbers found in cells concerned with secretion eg. Glands. |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Fluid filled sacs containing dissolved digitise enzymes. These enzymes destroy unwanted cell parts or damaged molecules from within or outside the cell. |
|
|
Peroxisomes |
Small membrane bound organelles rich in the enzyme catalase and irate oxidase. Detoxify various toxic materials that entre the blood stream such as alcohol and hydrogen peroxide.
Found in plant and animal cells |
|
|
Endosomes |
Membrane bound organelles found in animal cells. Pass newly ingested material in the cell to the lysosomes for digestion. |
|
|
Vaculoles |
Membrane bound cavities used for storage. Large in plants and small in animals. |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
An internal framework of protein microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments. Maintains the shape of the cell, provides a support structure for components within the cell, aids the movement of materials within the cell and aids in cell replication. |
|
|
Occluding junctions |
Involves cell membranes coming together in contact with each other. There is no movement of material between cells. Found in animal cells
|
|
|
Communicating junctions |
Small, open protein lined channels that directly link the cytoplasm of adjacent cells, permitting passage of different substances (eg, salt ions, sugars, amino acids) and electrical impulses (eg, the control of the beating heart)
Found in animal cells |
|
|
Anchoring junctions |
Also called desmosomes. Help hold cells together in tissue that is subject to stretching ( skin, uterus). Found in animal cells |
|
|
Plasmodesmata |
Cell to cell connection in plants. Allows for communication between a large number of cells. The plasma membrane between the two cells is continuous. |

