![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are size of cells?? |
5-20 micrometers |
|
|
What is basic structure of plasma membrane? |
Lipid bilayer, cholesterol, protiens |
|
|
What are functions of lipid bilayer? |
Selective barrier( nutrients enter, waste exit, receptors) fluidity, integridy |
|
|
What is most abundant in lipid bilayer |
Phospholipids |
|
|
What is structure of phospholipid? And characteristics |
2 carbon glycerol and polar phosphate head. Amphiphatic(polar and not polar) double bonds allow fluidity. |
|
|
What is structure of cholesterol? |
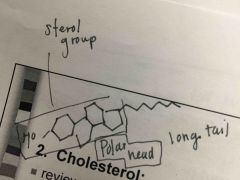
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Where are cholesterols? What type interaction? |
Within membrane. Structure the same as phospholipid= non covalent hydrophobic |
|
|
What are functions of cholesterol?? Where are a lot of cholesterol sites? |
Precursor!! -for bile -for vit. d -for hormones(adrenal gland-cortisol or sex glands-estrogen) |
|
|
What is a glycolipid? Where is it? What is it part of? What is similar to it in shape, location, and function? |
Lipid with sugar attached on outside of cell membrane. Part of glucocalyx. Also glycoprotiens. They aid in cell recognition, protect and absorb water fir slimy surface. |
|
|
What are two types proteins? And their interactions in membrane? What are 3 locations of integral? |
Integral-non covalent Transmembrane, extracellular or intracellular Peripheral- non covalent |
|
|
What are the 3 functions of membrane proteins |
1. As receptors 2. As enzymes 3. Transporters |
|
|
What are three examples how membrane protein act as receptor? |
1. Chemical ( pancreas release glucagon which travels to cells of liver and stimulates c-amp(protein) to initiate metabolic cascade to change glycogen to glucose 2.electrical signal( acetly colone receptors(integral protiens) Na+ channels open and contraction 3. Internalized ligand-LDL carrys cholesterol to liver or adrenal/sec cells with lots of LDL receptors. |
|
|
Explain how membrane proteins act as enzymes? |
Proteins may be enzyme with active site sticking out, with rite piece can trigger metabolic pathway |
|
|
How membrane proteins act as transporters ? |
Transports glucose |
|
|
What two pieces make up cytoskeleton and which isnt grid part in cytoplasm matrix? functions? reactions? |
Tubeals give shape and filamets anchor organelles plus liquid. ( waste water nutrients) **glycolysis, fatty acid synthesis?? |
|
|
Opthalmoplasty |
Repair of eye |
|
|
Otoplasty |
Repair of ear |
|
|
Opthalmoscopy |
Visual examination of eye |
|
|
Dermatoplasty |
Repair of skin |
|
|
Angiorraphy |
Suture of blood vessel |
|
|
Amniocentesis |
Puncure of amnion(sac in uterous) |

