![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The roles of membranes within and at the surface of cells
|
separating cell contents from the outside environmentseparating cell components from the cytoplasmcell recognition and signallingholding the components of some metabolic pathways in placeregulating the transport of materials in and out of cells
|
|
|
The plasma membranes are ________________ barriers
|
Partially permeable
|
|
|
What is the structure of the fluid mosaic model of a membrane structure?
|
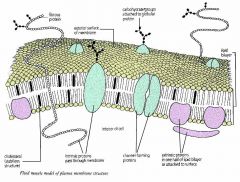
A bilayer of phospholipid molecules forming the basic structure
various protein molecules forming the basic structure, some completely freely some bound to other components of structures within the cell some proteins partially embedded in the bilayer on the inside or outside |
|
|
Describe the role of phospholipids
|
They form the membranes that surround the cell and intracellular organelles.
separates the cells contents from the environment |
|
|
Describe the role of cholesterol
|
Gives the membranes of some eukaryotic cells mechanical stability
fits between the fatty acid tails and makes the barrier more complete so substances like water molecules and ions cannot pass easily and directly through the membrane |
|
|
Describe the role of glycolipids
|
To provide energy
serve as markers for cellular recognition |
|
|
Describe the roles of glycoproteins
|
Allow hormones to bind onto them
|
|
|
Describe the role of channel proteins
|
Allow the movement of some substances across the membrane. (larger molecules)
|
|
|
Describe the role of carrier proteins
|
Actively move some substances across the membrane using ATP
|
|
|
What is the effect of changing temperature on the membrane
|
Increasing temperature gives molecules more kinetic energy
increased movement makes the membranes leaky which allows substances that usually do not do so enter or leave the cell |
|
|
What is cell signalling?
|
Cells can communicate with one another by signals.
many molecules act as signals- some signal during processes taking place inside cells; others signal from one cell to another |
|
|
What is the role of membrane-bound receptor sites where hormones and drugs can bind?
|
Any cell with a receptor for the hormone molecule is called a target cell
A hormone binds to a receptor on a target cell surface membrane. Binding of the hormone and receptor causes the target cell to respond in a certain way |
|
|
What is passive transport? (diffusion and facilitated diffusion)
|
Transport that relies on molecules moving freely.
the molecules possess kinetic energy that keeps them moving They diffuse down a concentration gradient |
|
|
What is active transport?
|
The movement of molecules or ions across membranes
which uses ATP to drive protein 'pumps' within the membrane |
|
|
What is endocytosis?
|
Moves large quantities of materials into the cell (ATP)
|
|
|
What is exocytosis?
|
Moves large quantities of materials out of the cell (ATP)
|
|
|
What is meant by osmosis in terms of water potential
|
It refers to the movement of water molecules via diffusion and across a partially permeable membrane
The movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration to low concentration |
|
|
The effect that solution of different water potentials have upon plants and animals
|
High water potential: water will go inside the cell. the cell will swell in animal cells this will eventually cause them to burst
low water potential: Water will go outside the cell, the cell with shrink and the membrane will wrinkle up. In plant cells the membrane will pull away from the cell wall |

