![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Biochemistry |
The study of chemical reactions in the cell, and the molecules and the processes involved in them |
Reactions |
|
|
Polar |
Word used to describe oppositely charged "poles" |
Opposites |
|
|
Organic compounds |
Molecules that contain both carbon and hydrogen |
|
|
|
Macromolecules |
Very large molecules composed of smaller subunits |
Macro means large |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Carbons with water attached to them. They provide short-long term energy storage |
|
|
|
Monosaccharide |
A carbohydrate with 3-7 carbon atoms, a simple sugar |
|
|
|
Disaccharide |
Made up of two simple sugars |
Di means two |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Many simple sugars linked together |
Poly means many |
|
|
Function of starch |
Energy storage in plants |
Potato light bulb |
|
|
Function of glycogen |
Energy storage in animals |
|
|
|
Cellulose |
A large polysaccharide macromolecule produced by plants |
|
|
|
Lipids |
Macromolecules that doesn't dissolve in water |
|
|
|
5 Lipids purposes |
1. Long term nutrient/energy storage 2. Insulation 3. Cushioning of internal organs 4. Hormones to send messages 5. Structural component in cell membrane |
|
|
|
Fatty acid |
Hydrocarbon chain with a COOH group of atoms instead of a hydrogen |
|
|
|
3 protein functions |
1. Facilitate chemical reactins as enzymes 2. Transport substances 3. Chemical messenger |
|
|
|
Amino acid |
Building blocks of protein |
|
|
|
Peptide bond |
A chemical linkage |
|
|
|
Essential amino acids |
Eight amino acids that must be consumed by humans because the body can't make them |
|
|
|
Nucleic acids purpose |
Direct the growth and development of living things using a chemical code |
|
|
|
Nucleotides |
Long chains of links subunits in nucleic acids |
|
|
|
Explain diffusion |

When molecules go through the membrane because there is a low concentration of it in the cell or vice versa. Small, uncharged cell. |
High to |
|
|
Concentration Gradient |
Difference in concentrations between two regions |
|
|
|
What is osmosis |
Diffusion of a solvent (WATER) |
|
|
|
Describe isotonic conditions |
When the water concentration inside the cell is the same as the outside of it |
|
|
|
Describe hypotonic conditions |
When the water concentration is greater than in the cell, so water goes into the cell |
The cell swells |
|
|
Describe hypertonic |
When the water concentration in the cell is greater than outside of it, so water moves out of the cell |
The cell shrinks |
|
|
Describe facilitated diffusion |

When a certain shaped, sized and charged transport protein helps big or insoluble molecules get through the bilayer |
Think of the claw |
|
|
What does a carrier protein do? |
Facilitates the movement of molecules through the membrane |
|
|
|
What is the function of channel proteins? |

A tunnel like shape that lets charged particles to pass through the membrane. |
|
|
|
What is the difference between active and passive transport? |
Active transport uses ATP to get molecules into the cell, while passive transport doesn't |
|
|
|
What is ATP |
Adenosine triphosphate; universal energy unit in cells. |
|
|
|
Define Active transport |
Moving substances across the membrane against the concentration gradient |
|
|
|
Define homeostasis |
Maintaining steady conditions in a living thing |
"Home" |
|
|
4 examples of active transport in the body |
1. Kidney cells get glucose/amino acids out of urine and into blood 2. Intestine cells get in nutrients 3. Root cells get nutrients from soil 4. Gill cells(fish)get out sodium ions |
|
|
|
Describe the active transport pump |

Trades 3 positive sodium ions in the cell for 2 positive potassium ions outside the cell |
|
|
|
What's endocytosis? |
The cell fold in on itself, trapping matter, and getting it in the cell |
Endo means within |
|
|
What are 3 types of endocytosis |
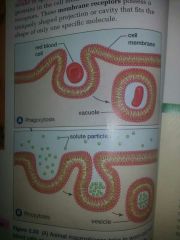
Pinocytosis (cell drinking) Phagocytosis (cell eating) Receptor-assisted endocytosis(picky eater) |
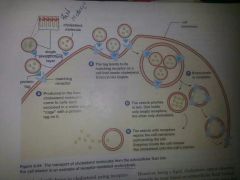
|
|
|
What is exocytosis? |
A vehicle in the cell binds with the cell membrane, spitting its contents into extracellular fluid |
Exo...exit...cytosis |

