![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the general structure of a membrane? |
It is a fluid mosaic model. |
it's termed as a model |
|
|
What is the function of the lipids in terms of a cell membrane? |
- It maintains the bilayer organisation spontaneously. - It also helps the membrane fuse during phagocytosis and vesicle formation. |
2 main functions |
|
|
How does the membrane vary in composition? |
it varies in... - the type of phospholipid - the length of fatty acid chains - the degree of saturation - the phosphate groups |
4 main points |
|
|
What is the % of cholesterol in the cell membrane? |
25% |
|
|
|
What 4 components make up a phospholipid? |
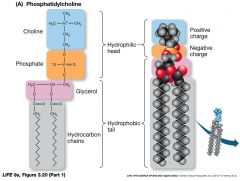
|
Make sure you mention the Hydrophilic and phobic parts. |
|
|
Define the word amphipathic |
a molecule (protein) that has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic components. |
|
|
|
Give an example of an amphipathic molecule. |
a phospholipid |
|
|
|
Why is a phospholipid amphipathic? Other than - having hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts. |
- water is polar (slightly charged e.g. H+ and O-) - phosphate is -ve charged and they attract each other. Therefore hydrophilic. - Amine is +ve |
3 points |
|
|
In what which direction does the phospholipid bilayer move? |
the molecules of the membrane move laterally (sideways). |
|
|
|
What helps the lateral movement of the cell membrane? |
the phospholipid bilayer is flexible and the interior is fluid which allows movement. |
|
|
|
How do the proteins and lipid intereact? |
They interact independently and non covalently |
|
|
|
What are the two types of membrane protiens? |
Integral membrane protein and peripheral membrane protein. |
|
|
|
what is the integral membrane protein? |
protein which spans (goes through) the bilayer, the hydrophilic ends protrude on either side. |
|
|
|
What is the peripheral membrane protein? |
the protein which does not penetrate the layer. |
|
|
|
What is a transmembrane protein? |
a protein which has different domain on either side of the membrane |
|
|
|
Where can proteins be anchored other than the phospholipid bilayer? |
cytoskeleton elements or the lipid rafts ( lipids in semisolid state.) |
|
|
|
What does it mean when membranes are described as dynamic? |
they constantly for,, transform, fuse and break down. |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the carbohydrates that are on the outer surface of the membrane? |
they serve as recognition sites for other cells and molecules. |
|
|
|
Give examples of carbohydrates which are present on the outer part of the membrane |
Glycolipids and glycoproteins. |
|
|
|
What does it mean when membranes are described as selectively permeable? |
Some substances are able to pass through but others cannot. |
|
|
|
Define passive transport and give an example. |
No outside energy is required. |
|
|
|
Define active transport |
Outside energy is required |
|
|
|
Define Diffusion |
the process of random movement towards equilibrium |
|
|
|
Define Equilibrium |
Particles which continue to move, but there's no net change in distribution |
|
|
|
Define Net movement |
An overall directional movement of molecules until equilibrium is reached. |
|
|
|
What factors does the rate of diffusion depend on? |
- the diameter of the molecules or ions - temperature of the solution - Electric charges - - conc gradient |
4 points |
|
|
Is diffusion effective over long or short distances? |
short distances |
|
|
|
What is the main property of the membrane in terms of permeability? |
it is permeable to solutes that move across more easily and impermeable to other solutes. |
|
|
|
define simple diffusion |
small molecules pass through the lipid bilayer. |
|
|
|
Give examples of what can and cannot be passed through the membrane |
Water and lipid solute can but electrically charged and polar molecules cannot diffuse though the membrane. |
|
|
|
Define osmosis |
diffusion of water |
|
|
|
what does the rate of osmosis depend on? |
On the number of solutes present and not the type of molecule. |
|
|
|
What solution causes water to flow out? |
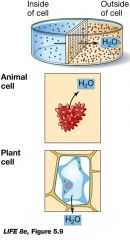
Hypertonic causes the cells to become flaccid. |
|
|
|
What solution causes water to flow into the cell? |

Hypotonic causes the cells to become turgid. |
|
|
|
What solution is at equilibrium? |
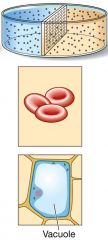
Isotonic solution |
|
|
|
State the solute conc from each of the following solutions: Hypertonic sol Isotonic Sol Hypotonic Sol |
Hypertonic Solution = higher solute conc. Isotonic Solution = equal solute conc (equal water conc) Hypotonic solution = low solute conc |
|
|
|
If 2 solutions are separated by a membrane which allows water, but not solutes to pass though, how does the water diffuse? |
Water diffuses from the region of high conc (low solute conc) to a region of low conc (high solute conc). |
|
|
|
How does osmosis occur in terms of hypertonic and hypotonic solutions? |
In a hypertonic solution (High solute conc), the H2O moves out of the cell into the hypetonic solution across a membrane. |
|
|
|
What happens when plants and animals cells are placed in a hypotonic solution? |
Animals cells burst due to water diffusing into the cell. Whilst plant cells that have rigid cell walls build up internal pressure which keeps more water from entering (turgor pressure) |
|
|
|
Is facilitated diffusion passive or active? |
passive |
|
|
|
How does facilitated diffusion occur? |
Polar molecules cross the membrane through channel proteins and carrier proteins. |
|
|
|
What feature do channel proteins which assist them in facilitated diffusion? |
channels proteins have a central pore lined with polar amino acids. |
|
|
|
How is a electrochemical gradient achieved by the membrane? |
Its achieved by an imbalance of charge across a membrane. |
|
|
|
What type of gradents are there? |
conc gradient of ions and electrochemical gradients. |
|
|
|
Define membrane potential |
its the charge imbalance across a membrane |
|
|
|
What si the membrane potential of an animal cell? |
-70mV (lots of potential energy) |
|
|
|
How does glucose carry out facilitated diffusion? |
Glucose binds to the carrier protein which results in a conformational change. (changes shape) |
|
|
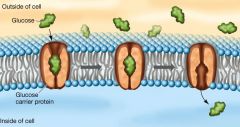
What process is taking place in this image? |
Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
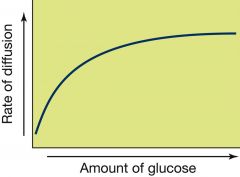
Describe the graph in terms of rate of diffusion and the amount of glucose |
As the amount of glucose increases the rate of diffusion increases until optimum. After that, the graph plateaus due to the saturation of glucose. |
|
|
|
Define active transport |
- moves substances against a conc gradient and requires ATP. |
|
|
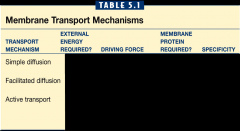
Complete the Table |
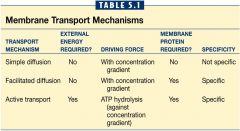
|
|
|
|
What pump uses active transport? |
Sodium and postassium pump |
|
|
|
What features does this pump have? |
A glycoprotein integral membrane. - its an antiport |
|
|
|
Define antiport |
a mechanism of transport which allows 2 compounds across the membrane in opposite directions. |
|
|
|
What is the other name for the pump? What structure is the pump? |
E1-E2ATPase and is a tertameric (carrier protein) |
|
|
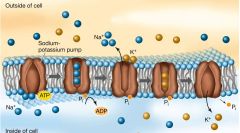
What process is taking place between the ions and the pump? |
Active Transport |
|
|
|
Macromoleules are able to cross the membrane. TRUE OR FALSE |
FALSE |
|
|
|
Give examples of Macromolecules |
proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids. |
|
|
|
What process allows the macromolecules in and out of a eukarytic cell? |
Endocytosis |
|
|
|
What happens during Endocytosis? |
the plasma membrane dolfs ina or invaginates around the material forming a vesicle. |
|
|
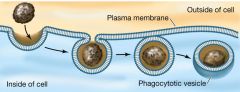
What process is taking place in this image? |
Endocytosis |
|
|
|
How does chloestrol enter the mammalian cell? |
Cholesterol enters the cell by receptor-mediated endocytosis |
|
|
|
What does the liver in terms with lipids? |
- Lipids are packaged into lipoproteins and secreted into the bloodstream.
|
|
|
|
Is low or high density lipoproteins recycled by the liver? |
Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL) |
|
|
|
What is the function of LDL? |
They bind to the specific receptor proteins. |
|
|
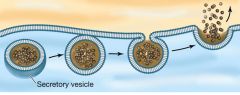
What process is taking place in this image? |
Exocytosis |
|
|
|
Define Exocytosis |
Materials in vesicles are expelled from a cell. |
|
|
|
Give examples of materials which are removed by exocytosis |
Indigestible matter along with digestive enzymes and neurotransmitters |
|

