![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell cycle
|
A series of events from the time a cell forms until its cytoplasm divides.
|
|
|
A typical cell spends most of its life in _____
|
interphase
|
|
|
interphase
|
In a eukaryotic cell cycle, the interval between mitotic divisions when a cell enlarges, roughly doubles the number of its cytoplasmic components, and replicates its DNA.
|
|
|
Cell cycle (image)
|
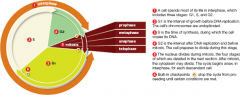
|
|
|
Stages of interphase
|
G1, S, G2
|
|
|
G1
|
the first interval (or gap) of cell growth, before DNA replication
|
|
|
S
|
the time of synthesis (DNA replication)
|
|
|
G2
|
the second interval (or gap), when the cell prepares to divide
|
|
|
Actually, most cells going about their metabolic business are in ___.
|
G1
|
|
|
During ____, they make the proteins that will drive cell division
|
G2
|
|
|
Mitosis
|
Nuclear division mechanism that maintains the chromosome number. Basis of body growth and tissue repair in multicelled eukaryotes; also asexual reproduction in some plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
|
|
|
In multicelled species, ______ and _______ increase cell number during development, and replace damaged or dead cells later in life
|
mitosis; cytoplasmic division
|
|
|
Asexual reproduction
|
Reproductive mode by which offspring arise from a single parent only.
|
|
|
______ ___________ have the same length, shape, and genes (hom– means alike). Typically, each member of a pair was inherited from one of two parents.
|
Homologous chromosomes
|
|
|
Homologous chromosomes
|
Chromosomes with the same length, shape, and set of genes.
|
|
|
Most differentiated cells in a human body are in ___, and some types never progress past that stage
|
G1
|
|
|
When a nucleus divides by _____, each new nucleus has the ____ chromosome number as the parent cell.
|
mitosis; same
|
|
|
Four main stages of mitosis
|
Prophases; metaphase; anaphase; telophase
|
|
|
Prophase
|
Stage of mitosis during which chromosomes condense and become attached to a newly forming spindle.
|
|
|
When a nucleus divides by mitosis, each new nucleus has the ____ chromosome number as the parent cell.
|
same
|
|
|
During __________, a cell's chromosomes are loosened to allow transcription and DNA replication
|
interphase
|
|
|
Stage of mitosis during which chromosomes condense and become attached to a newly forming spindle.
|
Prophase
|
|
|
A typical centrosome consists of two _______, which are barrel-shaped organelles that help microtubules assemble, surrounded by a region of dense ______.
|
centrioles; cytoplasm
|
|
|
The centrosome gets duplicated just before _____.
|
prophase
|
|
|
Spindle
|
Dynamically assembled and disassembled network of microtubules that moves chromosomes during nuclear division.
|
|
|
Plant cells have spindles and structures that organize them, but no ______.
|
centrosomes
|
|
|
Metaphase
|
Stage of mitosis at which the cell's chromosomes are aligned midway between poles of the spindle.
|
|
|
Anaphase
|
Stage of mitosis during which sister chromatids separate and move to opposite spindle poles.
|
|
|
Telophase
|
Stage of mitosis during which chromosomes arrive at the spindle poles and decondense, and new nuclei form.
|
|
|
______ begins when the two clusters of chromosomes reach the spindle poles.
|
Telophase
|
|
|
What is the sequence of events in mitosis?
|
Each chromosome in a cell's nucleus was duplicated before mitosis begins, so each consists of two DNA molecules.
Mitosis proceeds in four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During these four stages, sister chromatids of the duplicated chromosomes are separated and packaged into two new nuclei. Each new nucleus contains the same number and types of chromosomes as the parent cell. |
|
|
In most eukaryotes, the cell cytoplasm divides between late ______ and the end of _____. The mechanism of division differs between plants and animals.
|
anaphase; telophase
|
|
|
A cell's cytoplasm usually divides after _____, so two cells form.
|
mitosis
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic division
|
Cytokenisis
|
|
|
The process of cytoplasmic division, which is called cytokinesis , differs among _____.
|
Eukaryotes
|
|
|
The spindle begins to disassemble during ______.
|
telophase
|
|
|
In a dividing animal cell, the indentation where cytoplasmic division will occur.
|
Cleavage furrow
|
|
|
Cyotplasmic division (image)
|
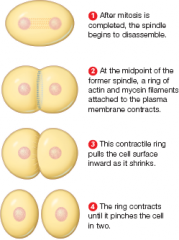
|
|
|
Cell plate
|
After nuclear division in a plant cell, a disk-shaped structure that forms a cross-wall between the two new nuclei.
|
|
|
When the cell ____ attaches to the membrane, it partitions the cytoplasm.
|
plate
|
|
|
Plant cell cytoplasmic division (image)
|
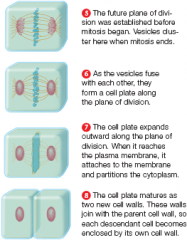
|
|
|
How do eukaryotic cells divide?
|
After mitosis, the cytoplasm of the parent cell typically is partitioned into two descendant cells, each with its own nucleus.
In animal cells, a contractile ring pinches the cytoplasm in two. In plant cells, a cell plate that forms midway between the spindle poles partitions the cytoplasm when it reaches and connects to the parent cell wall. |
|
|
______ protect eukaryotic chromosomes from losing genetic information at their ends.
|
Telomeres
|
|
|
_____ telomeres are associated with aging.
|
Shortening
|
|
|
Telomeres
|
Noncoding, repetitive DNA sequence at the end of chromosomes; protects the coding sequences from degradation.
|
|
|
The chromosomes of a normal eukaryotic body cell _____ by about 100 bases with each replication
|
shorten
|
|
|
Why can cells only divide a certain number of times?
|
When telomeres get too short, checkpoint gene products come into play to halt the cell cycle. The cell stops dividing, and it dies shortly thereafter.
|
|
|
What types of cells retain the ability to divide indefinitely in adults?
|
Stem cells
|
|
|
Why are stem cells immortal?
|
Stem cells are immortal because they continue to make telomerase, a molecule that consists of a non-coding RNA and a replication enzyme.
|
|
|
What is the function of telomeres?
|
Telomeres at the ends of chromosomes provide a buffer against loss of genetic information.
Telomeres shorten with every cell division in normal body cells. When they get too short, the cell stops dividing and dies. |
|
|
On rare occasions, controls over cell division are lost and a ____ forms.
|
neoplasm
|
|
|
Cancer develops as cells of a neoplasm become _____.
|
malignant
|
|
|
_____ is a nuclear division process that occurs only in cells set aside for sexual reproduction.
|
Meoisis
|
|
|
Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by sorting chromosomes into ___ new nuclei.
|
4
|
|
|
During ____, homologous chromosomes swap segments, then are randomly sorted into separate nuclei. Both processes lead to novel combinations of ___ among offspring.
|
meoisis; alleles
|
|
|
Gametes form by different mechanisms in males and females, but____ is part of both processes.
|
meoisis
|
|
|
In most plants, ____ occur between meiosis and gamete formation.
|
spores
|
|
|
Nuclear division process that halves the chromosome number. Basis of sexual reproduction.
|
Meiosis
|
|
|
Sexual reproduction mixes up _____ from two parents.
|
alleles
|
|
|
Meiosis, the basis of sexual reproduction, is a nuclear division mechanism that occurs in____ _______ ______ of eukaryotes.
|
immature reproductive cells
|
|
|
Except for a pairing of nonidentical sex chromosomes, _____ chromosomes carry the same set of genes
|
homologous
|
|
|
Different forms of a gene are called _____.
|
Alleles
|
|
|
The two chromosomes of a homologous pair are typically not identical. Why not?
|
Mutations that inevitably occur in chromosomes change their DNA sequence. Over time, unique mutations accumulate in separate lines of descent, and some of those mutations occur in gene regions. Thus, any gene may differ a bit in sequence from the corresponding gene on the homologous chromosome.
|
|
|
Alleles
|
Forms of a gene with slightly different DNA sequences; may encode slightly different versions of the gene's product.
|
|
|
Gamete
|
Mature, haploid reproductive cell; e.g., an egg or a sperm.
|
|
|
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of _____reproductive cells—gametes —from two parents.
|
haploid
|
|
|
Immature reproductive cell that gives rise to haploid gametes when it divides.
|
Germ cells
|
|
|
Gametes have a single set of chromosomes, so they are ____
|
haploid (n)
|
|
|
Haploid
|
Having one of each type of chromosome characteristic of the species.
|
|
|
The diploid chromosome number is restored at ______ , when two haploid gametes (one egg and one sperm, for example) fuse to form a _____ , the first cell of a new individual.
|
fertilization; zygote
|
|
|
Fusion of two gametes to form a zygote
|
Fertilization
|
|
|
Zygote
|
Diploid cell formed by fusion of two gametes; the first cell of a new individual.
|
|
|
Meiosis ____ the chromosome number.
|
halves
|
|
|
During meiosis, chromosomes of a _____ nucleus become distributed into four ____ nuclei.
|
diploid; haploid
|
|
|
____and the ___ ___ of chromosomes into gametes result in new combinations of traits among offspring of sexual reproducers.
|
Crossovers; random sorting
|
|
|
Crossing over
|
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange corresponding segments during prophase I of meiosis.
|
|
|
Two kinds of multicelled bodies form during the life cycle of a plant:
|
sporophytes and gametophytes
|
|
|
Sporophyte
|
Diploid, spore-producing stage of a plant life cycle.
|
|
|
Gametophyte
|
A haploid, multicelled body in which gametes form during the life cycle of land plants and some algae.
|
|
|
Animal gametes arise by meiosis of __ __ __
|
diploid germ cells
|
|
|
Sperm formation
|
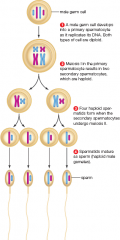
|
|
|
Egg formation (image)
|
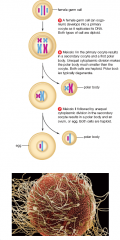
|
|
|
What is a chromosome?
|
A structure that consists of DNA and associated proteins
Carries part or all of a cell’s genetic information |
|
|
Chromosome structure
|
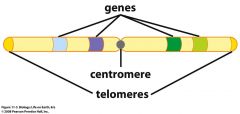
|
|
|
Each duplicated chromosome has two DNA strands (sister chromatids) attached to one another at the ______
|
centromere
|
|
|
Division of a eukaryotic cell typically occurs in two steps:
|
nuclear division followed by cytoplasmic division
|
|
|
What are the three stages of the cell cycle?
|
Interphase, mitosis, and cytoplasmic division
|
|
|
Describe interphase
|
Interphase consists of three stages, during which a cell increases in size, doubles the number of cytoplasmic components, and replicates its DNA
G1: Interval of cell growth and activity S: Interval of DNA replication (synthesis) G2: Interval when the cell prepares for division |
|
|
____ is a nuclear division mechanism that maintains the chromosome number.
|
Mitosis
|
|
|
What is the function of mitosis?
|
In multicelled species, mitosis and cytoplasmic division increase cell number during development and replace damaged or dead cells later in life
|
|
|
During ______, a cell’s chromosomes are loosened to allow transcription and DNA replication
|
interphase
|
|
|
Why do chromosome condense to prepare for nuclear division?
|
Tight condensation keeps the chromosomes from getting tangled and breaking during nuclear division
|
|
|
What happens in prophase?
|
Chromosomes condense
Microtubules form a bipolar spindle Nuclear envelope breaks up Microtubules attach to the chromosomes |
|
|
What is a centrosome?
|
A region near the nucleus that organizes spindle microtubules; usually includes two centrioles
|
|
|
What is a spindle?
|
A dynamic network of microtubules that forms during nuclear division
Grows into the cytoplasm from opposite poles of the cell and attaches to duplicated chromosomes Microtubules from opposite poles attach to different sister chromatids and separate them |
|
|
What happens in metaphase?
|
All duplicated chromosomes line up midway between the spindle poles
|
|
|
What happens in anaphase?
|
Microtubules separate the sister chromatids of each chromosome and pull them to opposite spindle poles
|
|
|
What happens in telophase?
|
Two clusters of chromosomes reach the spindle poles
A new nuclear envelope forms around each cluster Two new nuclei are formed, each with the same chromosome number as the parent cell |
|
|
What is cytokenisis?
|
The process of cytoplasmic division
|
|
|
Describe cytokensis in animal and plant cells?
|
Animal cells
A cleavage furrow partitions the cytoplasm A band of actin filaments rings the cell midsection, contracts, and pinches the cytoplasm in two Plant cells A cell plate forms midway between the spindle poles; it partitions the cytoplasm when it reaches and connects to the parent cell wall |
|
|
What is the cell cycle?
|
The sequence of stages through which a cell passes during its lifetime (interphase, mitosis, and cytoplasmic division) is called the cell cycle
|
|
|
Mitosis is the basis of body size _____ and tissue ____ in multicelled eukaryotes; it is also the basis of asexual reproduction in single-celled and some multicelled eukaryotes
|
increases; repair
|
|
|
Most differentiated human cells are in ___– some types never progress past that stage
|
G1
|
|
|
When a cell divides is determined by ___ ___ ___; some cause the cell cycle to advance, others stop the cycle from proceeding
|
gene expression controls
|
|
|
There are three major checkpoints in the eukaryotic cell cycle, each regulated by protein complexes. What are they?
|
G1 to S:
G2 to mitosis Metaphase to anaphase |
|
|
_____ occurs in immature germ cells to create mature reproductive structures called gametes.
|
Meiosis
|
|
|
In asexual reproduction, there is no variation in offspring unless there is a ______.
|
mutation
|
|
|
A nuclear division mechanism that precedes cytoplasmic division of immature reproductive cells in sexually-reproducing eukaryotic species
|
Meiosis
|
|
|
In meiosis, DNA is replicated ___ and divided ___.
|
once; twice
|
|
|
Name 9 differences between meiosis and mitosis
|
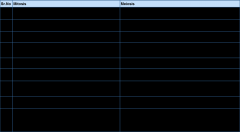
|

