![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Modern Cell Theory - How many criterions?
|
1.Every living organism is made up of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the structural and functional unit of living
organisms. The smallest living organisms are single cells, and cells comprise the functional units of multicellular organisms. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells ensuring the continuity of life. 4. Cells contains hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division 5. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition. |
|
|
Basic Features to All Cells?
What are some examples of exceptions ? |
1. Plasma (cell) membrane
2. Genetic material: nucleus or nucleoid 3. Cytoplasm 4. Cell Organization and Cell Dimensions A. The yolk of a bird is a single cell. B. Some nerve cells in mammals. C. Some algae are multinucleate. |
|
|
The Domains of Prokaryotes
|
1. Bacteria
2. Archaea |
|
|
Three Common Shapes of Bacteria
|
1. Spherical
2. Rod-shaped 3. Spiral |
|
|
Features of Prokaryotes
|
• Generally very small and relatively simple
• Boundary is the plasma membrane • Rigid wall composed of a unique substance, Peptidoglycan • May have motile structures called flagella • Single DNA molecule (circular) • May have plasmids. • Cytoplasm • Ribosomes • NO internal membrane-bounded structures (organelles) |
|
|
THE EUCARYOTIC CELL
|
• The Nucleus Is the Information Store of the Cell
• Mitochondria Generate Usable Energy from Food to Power the Cell • Chloroplasts Capture Energy from Sunlight • Internal Membranes Create Intracellular Compartments with Different Functions • The Cytosol Is a Concentrated Aqueous Gel of Large and Small Molecules • The Cytoskeleton Is Responsible for Directed Cell Movements • The Cytoplasm Is Far from Static • Eucaryotic Cells May Have Originated as Predators |
|
|
Features of the Eukaryotic Cell:
|
• Eukaryotic cells have a system of internal membrane- bounded structures, called organelles.
• Nucleus bounded by the nuclear envelope (Eukaryotic means true nucleus) • Cytoplasm of cytosol in which specialized organelles are suspended • Greater efficiency for cell activities • Organelles physically separate different types of cell activities in the cytoplasm space • Organelles also allow for separation of cell activities in time, to provide for sequential cell activities • May or may not (animals) secrete an external cell wall |
|
|
Main functions of organelles in eukaryotic cell
• Nucleus: • ER: • Golgi apparatus: • Lysosomes: • Endosome: • Peroxisome: • Mitochondria: • Chloroplast: |
• Nucleus: double membrane with nuclear pores, contains main genome, site of DNA and RNA synthesis.
• ER: interconnected sacks and tubes of membrane, site of membrane synthesis. With ribosome = rER and site of TM and secreted protein synthesis. sER: more rare, steroid synthesis in some cells and organic molecules detoxified here. Ca2+ can be stored here. • Golgi apparatus: receives proteins and lipids from ER, modifies them, and sends on their way. • Lysosomes: degrade worn-out organelles, macromolecules, and endocytosed particles. • Endosome: early vesicle involved in endocytosis. • Peroxisome: oxidize toxic molecules. • Mitochondria: ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation. Chloroplast: in plants, site of photosynthesis. |
|
|
Pyrimidines VS Purines
|
Pure - As - Gold
Pyrimidines - T- C - U |
|
|
3 Subunits of Macromol
|
1. Sugars
2. AA 3. Nucleotides |
|
|
Catabolic Vs Metabolic Pathways
|
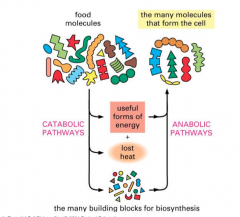
|
|
|
Laws of Thermodynamics
|
1st - Energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only transformed.
2nd - Within a closed system entropy exists and tends to increase. 3rd - |

