![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
243 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
23% of deaths from leading chronic diseases attribute in part to
|
Sedentary lifestyle
|
|
|
|
What does not change in cardiovascular system?
What increases? |
Resting HR
Plasma volume, hematocrit Left vent mass (blood volume dec) Valve thickening Epicardial fat HR + BP response to submax exercise peripheral vascular resistance Total Cholesterol, LDL |
|
|
|
Does heart size Dec or Inc with aging?
|
Dec
|
|
|
|
Does speed of RBC production in response to stress of illness change with aging?
|
Yes it decreases
So does: HDL lipoprotein lipase activity End diastolic filling |
|
|
|
What happens to HR max with aging?
CO ? SV? |
Dec
Dec Dec |
|
|
|
What happens to BP with aging?
|
Inc
|
|
|
|
What pulmonary thing stays the same with aging?
What decreases? |
TLC
VA, Tv Respiratory muscle strength Lung expansion Elastic recoil Alveolar surface area Cilia Alveoli tend to collapse sooner on expiration |
|
|
|
What pulmonary things increase
|
Chest wall stiffness
Mucus producing cells Rv FRC RR |
|
|
|
Type 1 fibers
Type 2 |
Slow, oxidative, endurance
Fast twitch |
|
|
|
Does muscle connective tissue Inc or decrease with age?
|
Increase
But muscle mass decreases |
|
|
|
Diagnosis for sarcopenia
|
Low muscle mass +
Low strength Or Low physical performance |
|
|
|
Literally define sarcopenia
Who suffers from this most men or women? |
Skeletal mass less than 2 SD below healthy young adult mean
Natural aging is 10% loss per Decade- Dec loss by exercise Men! Almost x2! |
|
|
|
What causes sarcopenia?
|
Dec activity!!
Dec aloha MN input Dec testosterone Dec GH Dec protein |
|
|
|
What happens to attention span in aging?
Cognitive processing speed? Cognitive accuracy? |
All decrease
|
|
|
|
What happens to SNS response to stress?
|
Inc
|
|
|
|
What eye issue is from too much pressure?
Degenerative opacity? Pigmentary change of retina? |
Glaucoma
Cataract Macula degeneration |
|
|
|
What happens to estrogen with age?
|
Dec
So does progesterone and testosterone and GH |
|
|
|
What happens to insulin concentration with age?
|
Inc!
Also hormonal response to stress increases too |
|
|
|
Urinary changes with age
|
Bladder Dec volume able to hold but also retains more after peeing
Dec strength of urinary sphincter Dec GFR Dec vasopressin Inc a natriuretic peptide |
|
|
|
What % of people are independent but rapidly progress to frailty if activity levels were decreased
|
70%
Also 5%are elite- will remain great unless ill |
|
|

|
367meteres are required to complete a community errand
|
|
|
|
What gait speed is needed for community ambulation?
|
1.2 m/s
|
|
|
|
Community dwellers need to carry what poundage?
|
6.7 lbs
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Each year what percent of community dwelling adults over 75 development a disability
Depending on degree of fitness, for every week of bed rest how much time needed to recover? |
10%
3 months! |
|
|
|
What is a geriatric syndrome
|
Multifactorial health conditions that occur when the accumulated effects of impairment in multiple systems that render an older person vulnerable to situation changes
Ex) frailty |
|
|
|
What is considered low grip. Strength?
|
Average best of 2 from both sides under 20th percentile for sex and BMI
|
|
|
|
Predictor of successful aging
|
Physical function
Absence of hearing issues No arthritis No disability Good cognitive function Lower systolic BP Dec depression Satisfaction |
|
|
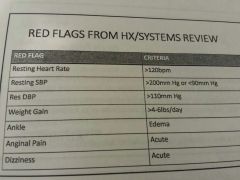
|
Yep
|
|
|
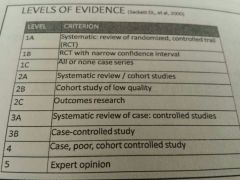
|
Great!
|
|
|
|
Borg scale (6-20) easy way to relate to HR
|

Add 0 to each number
|
|
|
|
Acsm dyspnea scale
|

|
|
|
|
Acsm anginal Scale
|

|
|
|
|
Claudication scale
|

|
|
|
|
Ankle brachial index
|

Compares posterior tib to brachial systolic
Normally ankle is equal.or greater than brachial (test in supine!) Norm= above. 90 (to 1.2) |
|
|

|
Yes
|
|
|
|
6MWT is used with what populations
|

Also used in phase 2-3 of cardiac rehab
|
|
|
|
Conversion for meters to feet
|
X 3.28
|
|
|
|
Can you do the 6mwt if the diastolic BP is over 100
MDC |
Yes exercise caution
|

|
|
|
When would you use the 2MWT??
|
Mod to severe COPD
Amputations Frail Stroke To measure exercise capacity Set up 50ft between cones |
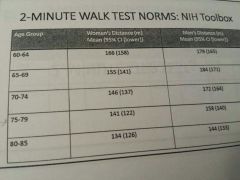
|
|
|
Reasons for termination of 400MWT
|
Hr under 40 or above 135
Chest pain Sob Faint /dizzy Leg pain |
|
|
|
400MWT cut off time
|
Slower than 5:30 may be at risk for functional difficulty
Less than 7min may have difficulty crossing the street **for each additional minute risk of death Inc by 35% |
|
|
|
2 min step test
|
Must lift knee midway between iliac Crest and patella
Count times R knee reaches this height |

|
|
|
What test is based on principal cardiopulm fitness is based on the sooner HR returns to baseline?
|
3min step test
Not graded so easier for fit individuals Does not estimate max capacity Too many confounding variables |
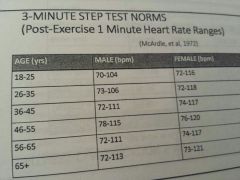
|
|
|
Total body recumbent stepper exercise test good for
|
Chronic stroke or balance issues
|
|
|
|
Geriatric depression scale scores
|

|
|
|
|
15 question geriatric depression scale to be used with those..
|

Medically ill
Mild-mod cog issues Adults with hemodialysis |
|
|
|
SLUMS exam
|

Mental test to detect dementia and mild neuro cognitive disorder (may be better then mmse)
|
|
|
|
MOCA
|
montreal cog assessment to detect mild cog impairment
Free online, many languages Excellent to detect mild alzheimers |
|
|
|
MMSE norms
|

|
|
|
|
Trail making test is for
|
Diagnostic tool for brain impairment especially frontal lobe lesions
Can correct during test Stop test if it's taking longer than 5 minutes |
|
|
|
3 cognitive screens by Medicare
|
GPCOG
MINI COG MIS (memory impairment screen ) |
|
|
|
Is TUG good for dementia?
|

Yes
|
|
|
|
TUG cut off scores
|
Community dwellers >13.5 sec fall risk
Olders with stroke >14sec fall risk |
|
|
|
TUG MDC
|

|
|
|
|
TUG dual task
|
For frail older adults in Institute settings
TUG with water cup If carrying a cup slowed them down over 4 sec more risk of falls in next 6 months |
|
|
|
Does gait speed have ceiling effect?
|
No
|
|
|
|
Gait speed needed to cross street
|
1.2m/s
|
|
|
|
Narrow corridor walk
|
Measure dynamic balance
6.meters c tape guidelines |
|
|
|
Four square step test is used with who
|
Geriatric
Vestibular Parkinsons |
|
|
|
4 square step test cut off scores
|

|
|
|
|
Dynamic gait index
|

To assess likelihood of falling in aging adults or vestibular or stroke
Also a short form (4 things instead of 8) long form has stairs though |
|
|
|
Dynamic gait index cut off scores
|
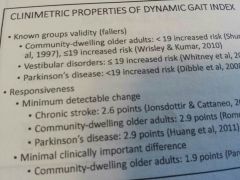
Under 12 balance deficits
Under ten fall risk |
|
|
|
Functional gait assessment FGA
|
Gait and stairs
Forward and backwards walking MDC : 4.2 stroke, 8 vestibular |
|
|

Functional reach test
|

Cut off under 6: 4x likelihood to fall, can't safely use reciprocal stair climbing
6-10 : 2xlikly to fall Can be modified in sitting |
|
|

Modified total body rotation test
|

That's all
|
|
|
|
SLS
|
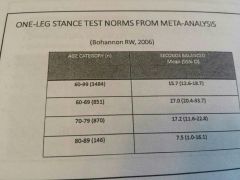
Can predict fall risk but difficult for older people.
But didn't mention cut off scores |
|
|
|
What does equal sway during Romberg with eyes open or. Closed?
|
Proprioceptive or Cerebellar disorder
|
|
|
|
Purpose of sharpened Romberg
|
Cerebellar involvement
MDC Pd: 39 sec eyes open, 19 eyes closed |
|
|
|
CTSIB clinical test for sensory interaction of balance tests for
|
To see what the person is relying on for balance
*** look up |
|
|
|
Modified CTSIB
|

Measures the way balance triad interacts to maintain balance against gravity (eliminates dome)
|
|
|
|
Berg balance is good for?
Weakness es |
Frail population "due to scales emphasis on discrimination when balance is relatively poor
-Ceiling effect with active adults - no external stimulus - no uneven surface - no gait |
|
|
|
Is Berg good enough alone for predicting falls?
|
No, use in conjunction with other tests
64% sensitivity for correctly predicting fallers 90% specificity for correctly predicting non fallers |
|
|
|
Berg cut off
|

48 low fall risk
40 med 39 high Good at identifying people at risk for multiple falls |
|
|
|
Berg balance MDC
|

4pts
|
|
|
|
Fullerton advanced balance scale FAB
|
To identify balance problems in independently higher functioning older adults
Based on systems control :sensory motor and musculoskeletal system contributions to balance Every 1 pt deduction = 8 % Inc in fall risk |
|
|
|
Who should not do thales Fullerton balance test?
|
Osteoporosis because there is a jumping component
Lower body joint pain |
|
|
|
What wii game was correlated statistically to the TUG and 10mwt?
|
Basic step
Generalizability Useful in community dwelling Also balance board is good for PD |
|
|
|
Cut off score for ABC scale
|
Under 67% Inc fall risk
Under 50 is homebound (add up responses decided by total number of items) |
|
|
|
Can you use ABC scale with vestibular patients?
|
Yes
Correlated to the TUG and DGI (but not the best predictor with stroke) |
|
|
|
FES falls efficacy scale
Good for... Weakness... |
Frail elders in/out Institute
Weakness... -Doesn't capture challenges of community mobility - doesn't predict frequently of falls or activity limitations However cut off > 70% = fear of falling |
|
|
|
Since FES can't predict frequently of falls... What version can?
|
FES international
|
|
|

Fear of falling avoidance behavior questionnaire ffabq
|
Measures avoidance behavior instead of fear or self efficacy
|
|
|
|
Muscle performance tests
|

|
|
|
|
Chair rise test correlates to gait speed?
|

Yah
Cut off for falling were 15sec to do 5 MDC : 3.12 sec (it's how long does it take to do like 5) |
|
|
|
Hip extensor test purpose
|

To enable MMT of hip. Extensors without being in prone (lay flat and push down while PT. Lifts limb 90cm)
|
|
|
|
Heel rise test
|

Test terminated if patient pushes on therapists hands
|
|
|
|
Toe tap test
|
To determine speed of ankle (how many taps in ten sec)
|
|
|
|
Getting up. From floor test is a strong independent risk factor for predicting
|
Serious fall related injury
|
|
|
|
Do cardiologists use grip strength in cardiac rehab?
|
Yes
Phase 2+3 MDC 5.2kg R hand 5.1 L hand |
|
|
|
Is low grip strength associated with low bone mineral density?
|
Yes and Inc risk of vert fx
|
|
|
|
Grip. Strength and Cap?
|
Positive correlation with bad outcome. For lower grip. Strength (2 weeks in hospital or death)
|
|
|
|
Grip strength, hospital, death?
|
Death within a year of hospitalization Correlated with low grip. Strength
|
|
|
|
Postural tests
|

|
|
|
|
How do you do flexicurve?
|
Measure standing without shoes
Mark c7 and lumbosacral L5joint space Mold curve from. C7 to L5 interspace Trace mold. On grid 10 X 10 paper Clinical kyphosis is defined as 13 or greater |

|
|
|
Wall to occiput distance test
|
Hand person stand as straight as possible against wall, measure distance from occiput to wall
Unable to touch wall is a + finding Wall occiput distance (WOO) Inc 1.2.cm for every vertebral fx Consider xray if > 4cm |
|
|
|
Rib/pelvis test
|
>2 fingers rules out lumbar compression fx with high degree of certainty
Under two get xray <1 finger rules in fx with high degree of certainty |
|
|
|
What's the point of assessing pes planus?
|
When compensated with orthotics static and dynamic balance immediately improved!
|

|
|
|
ROM tests
|

|
|
|
|
What's the best measure of shoulder flexible
|
Back scratch test
|
|
|
|
Thomas test
|
Tests for hip flexion contracture
|
|
|
|
Sensory tests
|

LOP =monofilament scoring, should get all 10 for intact protective sensation
Ipswich-test light touch toes for those at risk of ulceration Up down is for proprioceptive of big toe |
|
|
|
What's the primary reason those over 65 visit doctor?
|
Dizziness
93% bppv vestibular neuritis or menieres |
|
|

|

Good review
|
|
|
|
Semicircular canal. Senses
Otoliths sense |
Angular acceleration
Linear acceleration |
|
|
|
Most common type bppv
|
Canalithiasis free floating otoconia
Latent onset with head movement resolves within a minute |
|
|
|
Immediate onset of nystagmus that doesn't resolve
|
Cupulothiasis
|
|
|
|
Contraindications to dix hallpike
|
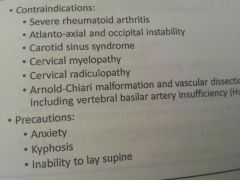
|
|
|
|
Describe central nystagmus
|
-Doesn't fatigue
- Can change direction vs head posistion - can also be vertical |
|
|
|
What direction is...
Posterior canal beat Anterior Horizontal |

|
|
|
|
Physical performance test was developed for
|

Older adults : adl iadl and physical
Two versions 7 and 9 item |
|
|
|
9 item modified physical performance test for
|

Frail
|
|
|
|
Purpose of short performance physical battery
|

LE function aging adults in community
Predict disability mobility and ADL predict need for Institute |
|
|
|
Elderly mobility scale purpose
|

Asses mobility in frail elders to determine post acute placement
TX, gait, times, functional reach |
|
|
|
DE Morton mobility index
|

Measures mobility States acute care hospital patients
But also for any setting Bed mobility, TX, balance, gait, dynamic balance |
|
|
|
Senior fitness test
|

Seven functional assessments of general strength endurance flexible mobility
Assess functional capacity of non frail adults living independently who may be at risk for decline in function Only a general appraisal |
|
|

Senior fitness test contraindications
|

|
|
|
|
Bestest balance evaluation systems test
|

6 components
|
|
|
|
Mini bestest
|

Dynamic balance assessment
4 of the usual 6 components |
|
|
|
Brief bestest
|

|
|
|
|
Grip strength for each sex
Slow walking speed is Low physical activity measured by |
Men under 30kg is frail
Women under 18kg is frail Under. 65 m/s for 15 feet Calories burned |
|
|
|
What two tests can distinguish between frail and nonfrail?
|
Stair climb and chair rise test
|
|
|
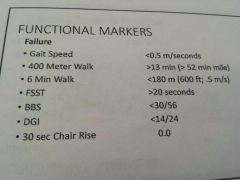
|
Post exercise SBP declines because of venous pooling and should normalize in supine
|
|
|
|
What DBP change after exercise means HF and what means CAD
|
Drops-hf
Inc: cad (labels HTN) |
|
|
|
Doubling exercise volume from 40%1rm to 75% maxmizines
|
Post exercise my fibrillation protein synthesis in aging men
|
|
|
|
Exercise and cognitive function
|
Increased especially executive function via plasticity and also thereby reducing falls
|
|
|
|
Exercise and gh
|
Inc
Also Inc testosterone |
|
|
|
V02max peaks..... years old!
|
15-20
|
|
|
|
Hr max equation in geriatric
|
208-(.7x Age)
The 220-age is low estimate |
|
|
|
What intensity to use for aerobic training when determining target HR
|
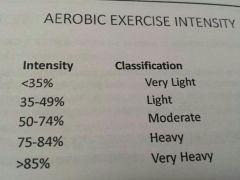
Healthy adult 60-80%
Frail can use as low as 40 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
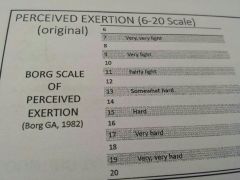
Hr from the borg scale 0-10 scale
|
Number of RPE X 10
12-14 is somewhat hard fyi |
|
|
|
What about predicting HRmax from RPE (6-20) in those on beta blockers?
What's recommendation for exercise |
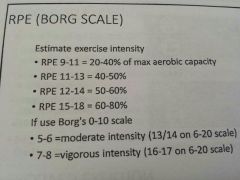
Great with RPE...
RPE of 12-13 is 60 max HR 16 is 85%hrmax 13-15 RPE for those on beta blockers |
|
|
|
Claudication scale
|

|
|
|
|
Normal and abnormal response to exercise
|

|
|
|
|
Does hrmax rise as high in geriatric patient?
|
No
|
|
|
|
Spinal mobility may Dec up to.... By the time we r 70
|
50%
|
|
|
|
Single most important predictor for need for eventual nursing home
|
Leg strength
|
|
|

Older adults gain strength similar to young people
|

Early hypertrophy is from neuro factors not effected by age
|
|
|
|
Strength training intensity
|

Doms should not occur at 80% 1rm
|
|
|
|
How do you assess 70-80% 1rm
|

And they should have muscle fatigue around 8-12 rep
|
|
|
|
Gold standard for knee extension testing for strength
|
Isokinetic dynamometer and this is Correlated well with the 8rep test (that test also determines 80% of 1rm
|
|
|
|
When should you use 30-60%1rm instead of 70-80%?
|

mi (wait 3-6 weeks to start)
MS RA Extremely frail (should be between fairly light and somewhat hard) |
|
|
|
Who should not be strength training
|
Advanced CHf.
Cancer tumor in target area Recent unstable MI |
|
|
|
How to progress from 30-60%1rm
70-80%? |
Once 25 reps can be reached Inc intensity by 10%
If 12 reps can be reached Inc by 5% |
|
|
|
How long is the recommended resistance training session for sub acute MI
|
20-30min
|
|
|
|
3 sets?
|
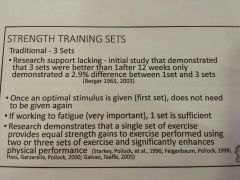
Research shows 1 is equally as good if reps to fatigue!
|
|
|
|
High % +Low reps =
Low % + high reps = |
Strength
Power! Some say power is better than strength for older adults. But a meta analysis said only small. Advantage And also might be a better predictor |
|
|
|
Acsm recommendations for strength training, hypertrophy, power
|

|
|
|
|
Lab values hgb, hematocrit and WBC normal levels and exercise recommendations
|

|
|
|
|
Clotting time INR values/exercise
|

|
|
|
|
PaCO2 <35 =
PaCO2 > 45= |
Hyperventilation so teach PLB
Hypoventilation so teach deep breathing and sit up right to improve CO2 removal |
|
|
|
Acsm flexibility recommendations
|
2d/week
10 min |
|
|
|
Does acsm recommend muscle or single join therex?
|
Both
Free weights and machines 1-3 sets 60-80% 8-12 reps 1-3 min rest |
|
|
|
Acsm aerobic recommendations
|
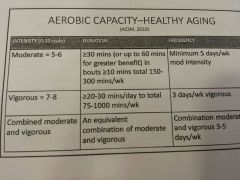
|
|
|
|
How does CO change with age effect drugs
|
Dec output = Dec absorption and distribution
Dec blood flow = Dec absorption and distribution |
|
|
|
How does GI change with age effect drugs
Liver |
Inc PH and Dec peristalsis = delayed gastric emptying and breakdown of coating of capsules* but absorption in the gut remains normal. Into the tenth decade and beyond!
Dec drug metabolism, does usually effect aging adult unless alcoholism |
|
|
|
How does lean body mass decrease with age effect distribution
Inc fat? |
Water soluble drugs reach higher unit concentration, easily toxic
Half life increases so last longer |
|
|
|
Warfarin is a med that competes for protein binding sites so...
|
May potentiate another drug, compete for binding sites
|
|
|
|
Renal. Function with age and pharmokinetics
|
Decreased so drugs have prolonged half life
|
|
|
|
Can nsaids cause irreversible damage to aging adult?
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
Can beta blockers cause confusion?
|

Yes!
|
|
|
|
Can nonsteriodals or salicylate cause falls?
|

Yes
|
|
|
|
Can beta blockers cause depression?
|

Yes!
|
|
|
|
Can Calcium channel blockers cause incontinence?
|

|
|
|
|
ACE
Can be combined with |

Dec sympathetic hormones and aldosterone release (same as angiotensin 2)
Antihypertensive! HCT can cause Oh or cramps |
|
|
|
Two anti arrythmics that promote dilation, stabilize HR and Dec contractibility force
Side effects |

BB and CC
Swelling in ankles Brochoconstriction |
|
|
|
Beta blockers as antiarryrhmic
Side effects Effects on exercise |
Mask hypoglycemia
Reduce heat tolerance Premature fatigue Reduce time to claudication Inc exercise with angina Blunts HR response Base exercise on target HR |
Antenolol
Metoprolol/lopressor Inderal/propranlol |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker as antiarryrhmic
Effect on exercise |
May in or Dec capacity
Usually doesn't effect capacity with those with HTN |
Dilatiazem/cardizem
Verapamil Nifedipine |
|
|
Digitalis effect on exercise
|
Used for CHf /improves left vent function
Improves exercise only in people with afib or CHf Adrs: gi, blurred vision, depression, arrythmics, fatigue, confusion |
|
|
|
Nitrates effect on exercise
|
Helps those with angina at submax work load
Exaggerated response to systemic heat ** vasodilation after exercise! |
Nitroglycerin
Isosorbide Dinitrate |
|
|
Two classes of bronchodilators
|
Anticholinergic and short acting beta 2 sympathomimetics
- beta adrenergic agonists (albuteral) - xanthine derivative (theophylline) Reduce doe and improve exercise with COPD |

|
|
|
Can you exercise with BG over 300 without ketosis?
|
With caution yes if person is feeling well and hydrated
|
|
|
|
Glipizide
|
Sulfonylureas (insulin secretagogues)
|
|
|
|
Action times. Of insulin
|
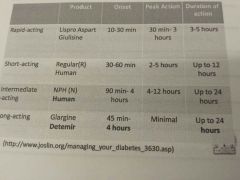
|
|
|
|
Classes of anti dementia drugs
|
Cholinesterase inhibitors :aricept, rivastigmine (for psychotic symptoms lewy body dementia, alzheimers, PD)
NMDA receptor antagonist (namenda) Dec aggression |
|
|
|
Urinary incontinence meds adrs
|
Dry mouth
Worse glaucoma Heart burn Dec. Memory Fatigue |
|
|
|
Meds for urge incontinence
|
Antispasmodic :Enabled, Ditropan, Detrol
Stress: cymbalta Overflow : proscar, fiomax |
|
|
|
Suggested calories for low activity level.. Moderate... Active
|
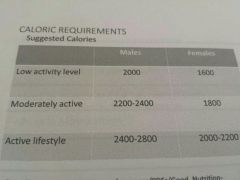
|
|
|
|
Cyrene recommended protein
Carbs.. |
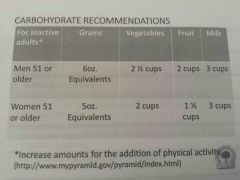
80g may be greater In older adults
|
|
|
|
What interferes with calcium in diet
|

|
|
|
|
Best indicator vit D status
|

Serum 25OHD
Recommended Dailey value 600-4000 |

|
|
|
Cancer facts of exercise
|
Resistance helped them complete chemo on schedule, Inc efficacy and Dec anxiety
No AdRs with aerobic Good response post breast cancer Inc peak 02 consumption, Dec fatigue 3-5 hours walk per week 50%less likely to die from breast cancer then those with 1hr per week Reduced colon cancer recurrence 42-49% Dec depression in all those except breast cancer |
|
|
|
Acsm guidelines for cancer
Free, intensity, duration, type |
Freq:
*aerobic 3-5dys (20-60min), *resistance 2-3dys (1-3 sets 8-12 reps or 15 if frail) * flex 2-7 days (4 reps) Intensity : aerobic 40-60%HRR resistance 40-60%1rm |
|
|
|
Acsm guidelines for cardiac disorders who have not undergone a stress test even if you told them too
|
Closely supervise
Continuous ECG Regular bp HR rest + 20 2-4 METS (progress 1-2 increments) 11-14 RPE |
|
|
|
Cardiac rehab
|

|

|
|
|
With Coronary heart disease which is better high calorie expenditure or standard cardiac rehab
|
High calorie expenditure
|
|
|
|
Absolute contraindications to resistive training
|

|
|
|
|
Relative contraindications to resistive training
|

|
|
|
|
When can you start RT with...
Mi Revascularzation |
5weeks after MI or cabg and within 4 weeks of supervision rehab
3weeks post |
|
|
|
%rm vs load
60, 70, 80, 90 |
17, 12, 8, 5
|
|
|
|
CHf benefits of exercise
|
-Increase cardiac output
- Skeletal muscle metabolism improvement -peak blood flow increase to the exercising limb because of the vascular resistance reduction - arterial function improve |
|
|
|
Acsm guidelines CHf
|

3 Mets or more
THR of 40 to 75% vo2max 3 to 7 days a week 20 to 40 minutes but start with 10 to 20 with interval training : of 2 to 6 minutes of exercise and 1 to 2 minutes of rest RPE of 11 to 14 |
|
|
|
Acsm guidelines HF
|
They should first have exercise testing then it should be initially supervised with a goal of 30 minutes of moderate activity 5 days a week
|
|
|
|
Is it ok to exercise with hypertension in a pool
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
Under how many steps a day is considered sedentary
What is considered active |
Under 5000
over 10,000 |
|
|
|
What happens to blood pressure after resistance training in older adults with high to normal blood pressure
|
Reduction in resting blood pressure and the benefit remained unchanged for a month without exercise
3mmhg change for SBP and DBP this has been associated with reduced cardiac morbidity by 5 to 9 percent and reduce stroke by 8 to 14 percent and all-cause mortality by 4% |
|
|
|
Acsm guidelines HTN
|

|
|
|
|
Acsm guidelines PVD
|

|
|
|
|
What minimum gait speed must be accomplished for sub acute stroke with severe gate impairment to experience a meaningful improvement and disability level
|
0.16 m/s this is the MCID
|
|
|
|
Ahaaa stroke guidelines
|
Any large muscle activity
40 to 50 percent peak oxygen uptake 40 to 70 percent heart rate reserve 11 to 14 or 6 to 20 RPE 3 to 7 days a week 20 to 60 minute sessions or multiple 10 minute session |
|
|
|
Aha stroke guidelines strength
|
Circuit training, weight machines, free weights, isometric exercises
1 to 3 sets of 10 to 15 repetitions 8 to 10 exercises involving major muscle group 2 to 3 days a week |
|
|
|
What exercise is most effective in improving glucose intolerance and a risk reduction of diabetes
|
Resistance may be more effective than aerobic exercise
|

|
|
|
Is physical activity advice alone associated with a1c changes
|
No need structure exercise
|
|
|
|
What met intensity made a significant improvement and glycine at control with older adults at risk
|
Short intermittent bouts 15 minutes three METS ( barely moderate intensity) was equally as effective as 45 minutes of sustained morning walking at 3 METS
this improved 24-hour glycemic control post meal exercise is significant lowering three hour post-dinner glucose levels |
|
|
|
Is high intensity interval training effective and safe for type 2 diabetes
|
Yes one study did 5 series of three minute brisk walking at 70% heart rate reserve interspersed with three minutes at 30 percent heart rate reserve
|
|
|
|
How should intensity be measured with diabetes
|
RPE should be used as an adjunct
exercise intensity should be based on target heart rate using the karvonen formula (40-90%) the heart rate max should be determined by a stress test Resistance intensity should be measured by no more than 8 max they should not be able to lift a weight more than eight to ten times |
|
|
|
Does moderate walking with peripheral neuropathy and diabetes increase risk of foot ulcer or re ulceration
|
No
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Does decreased proprioception contribute to development of OA
Decreased and hip abductor strength will increase load on what side of the knee |
Yes
Medial, strengthening will decrease knee pain and physical function but it will not improve knee ad duction moment |

|
|
|
Can you exercise with OA with acute inflammation
|

Yes
|

Patients with weakness strengths could still maintain high levels of dynamic balance with strong ankles
|
|
|
Are runners at increased risk for OA
|
No there is no evidence
older age is a strong risk factor as well as obesity and also serious knee injury |
|
|
|
Just tia chi training help with OA pain control and function
|
Yes but improvements disappear after detraining
|
|
|
|
Oa modalities
|

|
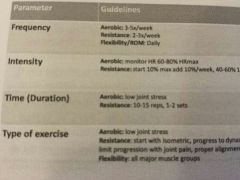
|
|
|
What intensity should people with arthritis workout
|
60 to 80 percent heart rate max for aerobic
and 40 to 60 percent in one rep max for intensity |
|
|
|
Can high intensity weight bearing exercise retard progression of rheumatoid arthritis
|
Yes also less use of glucocorticoids activation of bone remodeling
feet were more protected then hands |
|
|
|
A change in what is the strongest predictor for observing improvements in all of the assessed cardiovascular disease risk factors and disease characteristics
|
Vo2 max
|
|
|
|
What percent intensity is good for rheumatoid arthritis
|
The goal should eventually be 60 to 85 percent of heart rate max
|
Water or land base is good
|
|
|
What is the angle for thoracic hyperkyphosis
|
Cobb angle of 50 to 65 degrees this also is a risk of falls
|
|
|
|
Risk factors for severe vertebral fractures
|
More previous non vertebral fractures
low serum albumin levels prednisone |
|
|
|
What muscles with osteoporosis are significantly less compared to women without osteoporosis
|
Back extensors
isometric contractions of back extensors can decrease post fracture pain and edema |
|
|
|
Would you have increased time on the tug test just because of hyperkyphosis
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
ACSM guidelines for patients who are at risk of osteoporosis
|
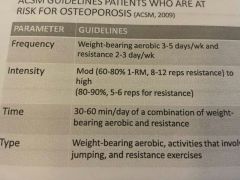
|
|
|
|
Acsm guidelines who have osteoporosis
|
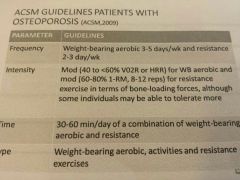
|
|
|
|
Risk factors for fracture risk for osteoporosis according to FRAX - The Who
|

|
|
|
|
Physical signs that should make you want to screen for osteoporosis
|

|
FYI marginal evidence for hip protectors
|
|
|
Is golf allowed after a total hip replacement
Jogging? |
Yes (Bowling is too with experience)
No |
|
|
|
Is horseback riding allowed after a total knee replacement
swimming? |
Yes and yes, so is doubles tennis with experience but not singles
And so is low impact aerobics |
|
|
|
Should people with fibromyalgia exercise at a high intensity
|

Moderate is good and low intensity if that's all they can tolerate
|
|
|
|
4 point Hopkins fall grading scale
|

|

|
|
|
Is gender a predictor of fall
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
MMSE under what indicates fall risk
|
17
|
|
|
|
Exercise recommendations from multiple sclerosis
|

|
|
|
|
What about heart rate with multiple sclerosis for blood pressure
|
They may be dulled because of cardiovascular disautonomia
|
|
|
|
What program can help people with Parkinson's delay mobility disability
|
Sensorimotor agility programs which includes resistance training and coordination with progressive challenges
|
|
|
|
Can aerobic training increase gray matter volume in the frontal and superior temporal lobe
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
What functional tests are good for people with dementia
|
Figure 8 walk test
tug grip dynamometer six minute walk test 30 second chair rise |

|
|
|
Standard cardiac rehab program burns how many calories per week
|
700 to 800
it also recommends a deficit of 3500 calories via dietary deficit |
|
|
|
How much exercise is required to maintain substantial weight loss
|

80 minutes of moderate activity every day or
35 minutes of vigorous activity Fyi: it takes 45 to 60 minutes to prevent transition from overweight and obesity |
|
|
|
When intensity is appropriate for COPD
|
When intensity is appropriate for COPD426 on the Borg dyspnea scale and at least greater than 60% peak exercise capacity
|
|
|
|
Patients with COPD and significant muscle atrophy could do resistance training at what level
|
50-80% % one rep max for 6 to 12 reps and 2-4sets
|
|
|
|
Acsm guidelines from moderate to severe COPD
|
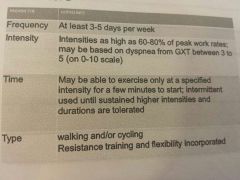
|

|
|
|
Acsm guidelines for well controlled asthma and mild COPD
|
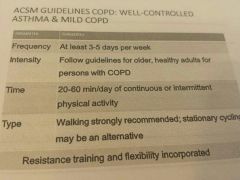
|
|

