![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PNS |
- Peripheral Nervous System - when nerves exit the spinal cord/brainstem they are part of the PNS + both motor and sensory nerves |
|
|
Menengies |
- Outer cover of CNS - Layers of tissue for protection + cushion btwn brain & skull - Contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) |
|
|
3 Layers of Menengies |
- Dura mater (outermost) - Arachnoid mater (middle) - Pia mater (inner) |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage |
Burst blood vessel w/in subarachnoid space - Caused by head trauma OR spontaneous rupture - Can result in cog impairments due to cerebral edema or interruption of normal blood supply |
|
|
Epidural Hematoma |
Collection of blood btwn dura mater and skull - Typically caused by rupture of middle menengial artery secondary to fracture of temporal bone - Can be life threatening due to increased cranial pressure |
|
|
Subdural Hematoma |
Collection of blood btwn dura mater and arachnoid mater - Caused by rupture of veins due to displaced dural layers + displacement can be due to trauma or brain shrinkage in old age |
|
|
Menengioma |
Brain tumor originating in the menengies - Reps about 1/3 of tumors originating in the brain - Slow growing, 5-10% are malignant |
|
|
3 parts of Ventricular System |
- Lateral (2) - Third - Fourth |
|
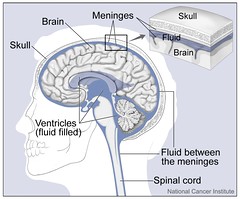
Ventricles |

|
|
|
Cerbrospinal Fluid (CSF) |
- Made by choroid plexi (group of spngey blood vessels) - Small amounts continuously made and reabsorbed by body + absorbed by arachnoid villi then transported back into venous blood flow |
|
|
Purposes of CSF |
- Cushion btwn brain and skull - Regulate intracranial pressure - Provides nourishment to nervous tissue - Removes waste from CNS |
|
|
Hydrochephalus |
Condition involving abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in ventricles of brain - Causes: + Congenital + Mass lesions + Swelling of adj blood tissue + Bits of floating tissue in CNF - Can cause cog impairments and even death + dysarthria |

