![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the 3 main problems that occur when not using STP in a LAN with redundant links.
|
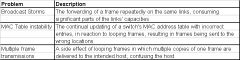
|
|
|
List the reasons why a switch chooses to place an interface into Forwarding or Blocking State.
|
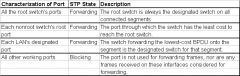
|
|
|
List the most important fields in Hello BPDU messages.
|

|
|
|
Default Port Costs According to IEEE
|
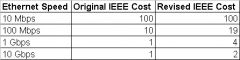
|
|
|
Summary description of steady-state STP operations
|
1. The root creates and sends a Hello BPDU, w/ a cost of 0, out all its working interfaces (those in a forwarding state).
2. The nonroot switches receive the Hello on their root ports. After changing the Hello to list their own bridge ID as the sender’s BID, and listing that switch’s root cost, the switch forwards the Hello out all designated ports. 3. Steps 1 and 2 repeat until something changes. |
|
|
STP timers
|

|
|
|
Define what happens during the Listening State
|
Like the Blocking State, the interface does not forward frames. Old, now-incorrect MAC table entries are timed out during htis state, because the old incorrect MAC table entries would be the root cause of the temporary loops.
|
|
|
Define what happens during the Learning State
|
Interfaces in this state still do not forward frames, but the switch begins to learn the MAC addresses of frames received on the interface.
|
|
|
IEEE 802.1d Spanning-Tree States
|
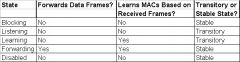
|
|
|
How are RSTP (802.1w) and STP (802.1d) similar?
|
• It elects the root switch using the same parameter and tiebreakers.
• It elects the root port on nonroot switches with the same rules. • It elects designated ports on each LAN segment with the same rules. • It places each port in either Forwarding or Blocking State, although RSTP calls the Blacking State the Discarding State. |
|
|
RSTP and STP Port States
|
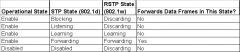
|
|
|
RSTP and STP Port Roles
|

|
|
|
Compare 3 Options for Multiple Spanning Trees
|
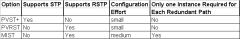
|
|
|
STP Defaults and Configuration Options
|
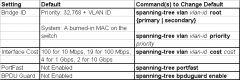
|
|
|
2 branches of logic in how the "spanning-tree root primary" command picks a new base STP priority
|
• 24,576 if the current root has a base priority higher than 24,576
• 4096 less than the current root’s base priority if the current root’s priority is 24,576 or lower |
|
|
Strategy for solving STP problems on the exams
|
1. Determine the root switch.
2. For each nonroot switch, determine its one root port (RP) and cost to reach the root switch through that RP. 3. For each segment, determine the designated port (DP) and the cost advertised by the DP onto that segment. |
|
|
Alternate port
|
In RSTP 802.1w, a port role used to denote an interface that is currently receiving an inferior Hello BPDU, making it a possible replacement for the root port. Also used in the Cisco 802.1d STP implementation.
|
|
|
backup port
|
In RSTP 802.1w, a port role used when multiple interfaces on 1 switch connect to a single collision domain. this makes 1 interface the designated port (DP), and 1 or more others become available to replace the DP (backup role).
|
|
|
Blocking State
|
In 802.1d STP, a port state in which no received frames are processed, and the switch forwards no frames out the interface, with the exception of STP messages.
|
|
|
BPDU Guard
|
A cisco switch feature that listens for incoming STP BPDU messages, disabling the interface if any are received. The goal is to prevent loops when a switch connects to a port expected to only have a host connected to it.
|
|
|
bridge ID (BID)
|
An 8-byte identifier for bridges and switches used by STP and RSTP. It is composed of a 2-byte priority field followed by a 6-byte System ID field that is usually filled with a MAC address.
|
|
|
BPDU
|
Bridge protocol data unit. The generic name for Spanning Tree Protocol messages.
|
|
|
designated port
|
In both STP and RSTP, a port role used to determine which of multiple interfaces, each connected to the same segment or collision domain, should forward frames to the segment. The switch advertising the lowest-cost Hello BPDU onto the segment becomes the DP.
|
|
|
disabled port
|
In STP, a port role for nonworking interfaces -- in other words, interfaces taht are not in a connect or up/up interface state.
|
|
|
Discarding State
|
An RSTP interface state in which no received frames are processed, and the switch forwards no frames out the interface, with the exception of RSTP messages.
|
|
|
EtherChannel
|
A Cisco-proprietary feature in which up to 8 parallel Ethernet segments between the same 2 devices, each using the same speed, can be combined to act as a single link for forwarding and Spanning Tree Protocol logic.
|
|
|
forward delay
|
An STP timer, defaulting to 15 seconds, used to dictate how long an interface stays in both the Listening state and Learning state. Also called the forward delay timer.
|
|
|
Forwarding State
|
An STP and RSTP port state in which an interface operates unrestricted by STP.
|
|
|
Hello BPDU
|
The STP & RSTP message used for the majority of STP communications, listing the root's Bridge ID, the sending device's Bridge ID, and the sending device's cost w/ which to reach the root.
|
|
|
IEEE 802.1d
|
The IEEE standard for the original Spanning Tree Protocol.
|
|
|
IEEE 802.1s
|
The IEEE standard for Multiple Instances of Spanning Tree (MIST), which allows for load balancing of traffic among different VLANs.
|
|
|
IEEE 802.1w
|
The IEEE standard for enhanced version of STP, called Rapid STP, which speeds convergence.
|
|
|
Inferior Hello
|
When comparing 2 or more received Hello BPDUs, a Hello that lists a numerically larger root Bridge ID than another Hello, or a Hello that lists the same root Bridge ID but w/ a larger cost.
|
|
|
Learning State
|
In STP, a temporary port state in which the interface does not forward frames, but it can begin to learn MAC addresses from frames received on the interface.
|
|
|
Listening State
|
A temporary STP port state that occurs immediately when a blocking interface must be moved to a Forwarding state. The switch times out MAC table entries during this state. It also ignores frames received on the interface & doesn't forward any frames out the interface.
|
|
|
MaxAge
|
In STP, a timer that states how long a switch should wait when it no longer receives Hellos from the root switch before acting to reconverge the STP topology. Also called the MaxAge timer.
|
|
|
PortFast
|
A switch STP feature in which a port is placed in an STP Forwarding state as soon as the interface comes up, bypassing the Listening and Learning states. This feature is meant for ports connected to end-user devices.
|
|
|
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
|
Defined in IEEE 802.1w. Defines an imporved versions of STP that converges much more quickly & consistently than STP (802.1d).
|
|
|
root port
|
In STP, the 1 port on a nonroot switch in which the least-cost Hello is received. Switches put root ports in a Forwarding state.
|
|
|
root switch
|
In STP, the switch that wins the election by virtue of having the lowest Bridge ID, and, as a result, sends periodic Hello BPDUs (the default in 2 seconds).
|
|
|
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
|
A protocol defined by IEEE standard 802.1d. Allows switches and bridges to create a redundant LAN, w/ the protocol dynamically causing some ports to block traffic, so that the bridge/switch forwarding logic will not cause frames to loop indefinitely around the LAN.
|

