![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does tonicity change in salivary/pancreatic secretion? |
Salivary: isotonic - hypotonic Pancreatic: hypertonic - isotonic |
|
|
What is receptive relaxation? |
Dilation of the gastric fundus as food passes down the oesophagus |
|
|
Stimuli and secretions of gastric mucous cells |
Surface: stimulated by alcohol - produces protective gel Neck: stimulated by vagus - produces lubricant |
|
|
Effects of gastrin, ACh, histamine, somatostatin and PGs on acid secretion |
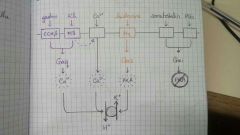
|
|
|
Feedback control of gastric secretion |
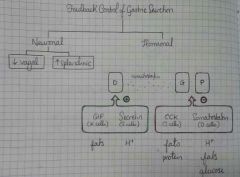
|
|
|
Transporters and enzymes of pancreatic duct cells |
Apical: Cl- / HCO3- exchanger Intracellular: C.A. Basolateral: Na+ / H+ exchanger |
|
|
Regulation of pancreatic secretion at the acinus |
Acinar cells stimulated by... - ACh (+VIP) - CCK Duct cells stimulated by... - Secretin (via Gas) |
|
|
Choleretic v cholagogue |
Choleretic increases bile secretion (e.g. secretin) Cholagogue increases bile flow (e.g. CCK) |
|
|
Why does cimetidine reduce drug metabolism? |
Cimetidine is a CYP450 inhibitor |
|
|
Incidences of gastric / duodenal ulcers due to H. pylori and NSAIDs |
Gastric Ulcers 1) H. pylori 60% 2) NSAIDs 30%
Duodenal Ulcers 1) H. pylori 85% 2) NSAIDs 10-14%
|
|
|
Specificity of H. pylori investigation techniques |
Urea breath test 95% Stool antigen 92% Serology 80% |
|
|
Difference between classical and operant conditioning |
Classical = Pavlov's dogs (involuntary response) Operant = reinforcement and punishment (voluntary response) |
|
|
Structures of the mesolimbic pathway |
VTA, Na, amygdala, hippocampus, PFC |
|
|
Difference between grade and stage |
Grade = pattern and degree of inflammation / cell death Stage = degree of fibrosis |
|
|
Risk of HBV and HCV via sexual and vertical transmission |
HBV Sex 30% Vertical 5-90% HCV Sex rare Vertical <10% |
|
|
Incubation times for viral hepatitis |
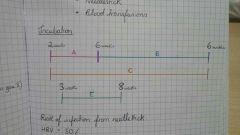
|
|
|
Results for acute infection, chronic infection and resolved / false +ve / low level "chronic" infection / resolving chronic infection |
Acute: all +ve but anti-HBs Chronic: all +ve but anti-HBs and IgM Resolving: only anti-HBc is positive |
|
|
What drugs can cause type A and B reactions? |
Type A - paracetamol - methotrexate Type B - antibiotics - NSAIDs - anti-retrovirals |
|
|
Predisposing factors of hepatocellular carcinoma |
- HBV, HCV and cirrhosis - fungal toxins from contaminated food |
|
|
UK drinking guidelines |
14 units over 3+ days with at least 2 alcohol free days |
|
|
Roles of P1 and P2 enzymes |
P1 - expose chemically reactive group - activates pro-drugs - produces cytotoxic intermediates P2 - add sugar/sulfate to make water-soluble |
|
|
Gilbert and Crigler-Najjar syndrome |
Gilbert: mutated UGT1A1 Crigler-Najjar: deleted UGT1A1 |
|
|
P1 enzyme that deactivates ethinylestradiol |
CYP3A4 |
|
|
What type of hyperbilirubinaemia does Dubin-Johnson disease cause? |
Hepatic conjugated |
|
|
Achalasia |
- problem with oesophageal n. plexus - LOS can't relax - stronger peristalsis |
|
|
Pain caused by stone in common bile duct and sphincter of Oddi |
Common bile duct: colicky pain Sphincter of Oddi: constant pain |

