![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
231 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
cardiovascular system (CV)
|
consists of the pump and vessels that distribute blood to all areas of the body. This system allows for the delivery of needed substances to the cells of the body as well as for the removal of waste
|
|
|
|
cardiovascular system organs
|
heart
blood vessels arteries capillaries veins |
|
|
|
angi/o
|
vessel
|
|
|
|
aort/o
|
aorta
|
|
|
|
arteri/o
|
artery
|
|
|
|
arti/o
|
atrium
|
|
|
|
ather/o
|
fatty substance
|
|
|
|
cardi/o
|
heart
|
|
|
|
coron/o
|
heart
|
|
|
|
corpor/o
|
body
|
|
|
|
emboi/o
|
plug
|
|
|
|
isch/o
|
to hold back
|
|
|
|
myocardi/o
|
heart muscle
|
|
|
|
pect/o
|
chest
|
|
|
|
phleb/o
|
vein
|
|
|
|
sphygm/o
|
pulse
|
|
|
|
steth/o
|
chest
|
|
|
|
thromb/o
|
clot
|
|
|
|
valv/o
|
valve
|
|
|
|
valvul/o
|
valve
|
|
|
|
varic/o
|
dilated vein
|
|
|
|
vascul/o
|
blood vessel
|
|
|
|
vas/o
|
vessel/duct
|
|
|
|
ven/o
|
vein
|
|
|
|
ventricul/o
|
ventricle
|
|
|
|
-manometer
|
instrument to measure pressure
|
|
|
|
-ole
|
small
|
|
|
|
-tension
|
pressure
|
|
|
|
-tonic
|
pertaining to tone
|
|
|
|
-ule
|
small
|
|
|
|
arteries
|
blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart
|
|
|
|
blood vessels
|
closed system of tubes that conducts blood throughout body: consists of arteries, veins and capillaries
|
|
|
|
capillaries
|
smallest blood or lymphatic vessels, blood capillaries are very thin to allow gas, nutrients and waste exchange between blood and tissues; lymph capillaries collect lymph fluid from tissues and carry it to large lymph vessels
|
|
|
|
carbon dioxide(CO2)
|
waste product of cellular energy production; is removed from cells by blood and eliminated from body by lungs
|
|
|
|
circulatory system
|
also called cardiovascular sulystem. system that transports blood to all areas of the body: organs of the circulatory system include: heart and blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries,
|
|
|
|
de oxygenated
|
blood in veins that are low in oxygen content
|
|
|
|
heart
|
organ of cardiovascular system that contracts to pump blood through blood vessels. located in the mediastinum in center of chest cavity. more toward the left.
|
|
|
|
oxygen (02)
|
gaseous element absorbed by blood from air sacs in lungs; necessary for cells to make energy
|
|
|
|
oxygenated
|
term for blood with a high oxygen level
|
|
|
|
pulmonary circulation
|
pulmonary circulation transports deoxygenated blood from right side of heart to lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged; then it carries oxygenated blood back to left side of heart
|
|
|
|
systemic circulation
|
systemic circulation transports oxygenated blood from left side of heart to cells of body and then back to right side of heart
|
|
|
|
veins
|
blood vessels of cardiovascular system that carry blood toward heart
|
|
|
|
apex
|
directional term meaning tip or summit; am area of lungs and heart
|
|
|
|
cardiac muscle
|
involuntary muscle found in the heart
|
|
|
|
mediastinum
|
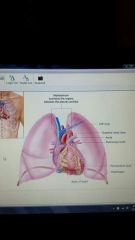
|
|
|
|
endocardium
|
inner layer of heart which is very smooth and lines chambers of heart. smooth and thin. reduces friction as the blood passes through the heart chambers
|
|
|
|
epicardium
|
outer layer of heart; forms part of pericardium
|
|
|
|
myocardium
|
middle layer of muscle, thick and composed of cardiac muscle; layer produces heart contractions. contracts to develop pressure required to pump blood through the vessels
|
|
|
|
parietal pericardium
|
outer layer of pericardium surrounding heart.
|
|
|
|
pericardium
|
double walled outer sac around heart, inner layer of pericardium is called epicardium, outer layer is the heart itself; this sac contains pericardial fluid that reduces friction caused by heart beating
|
|
|
|
visceral pericardium
|
inner layer of pericardium surrounding heart
|
|
|
|
internal view of heart
|
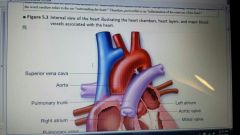
|
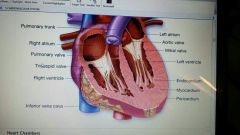
|
|
|
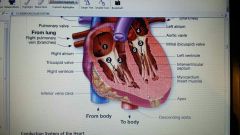
atria
|
3 upper chambers of heart, left atrium receives blood retuning from lungs and right atrium receives blood retuning from body
|
|
|
|
interatrial septum
|
wall or septum that divides left and right atria
|
|
|
|
ventricles
|
2 lower chambers of heart that receive blood from atria and pump it back out of heart; left ventricle pumps blood to body, and right ventricle pumps blood to lungs; also fluid filled spaces within cerebrum: certain cerebrospinal fluid, which is watery, clear fluid that provides protection from shock or sudden motion to brain.
|
|
|
|
interventricular septum
|
wall or septum that divides left and right ventricles
|
|
|
|
aortic valve
|
semilunar valve between left ventricle of heart and aorta in heart; prevents blood from flowing backwards into ventricles
|
|
|
|
atrioventricular valve (AV or A-V)
|
heart valves located between atrium and ventricle; includes tricuspid valve in right side of heart and bicuspid or mitral valve in left side of heart
|
|
|
|
bicuspid valve
|
valve between left atrium and ventricle; prevents blood from flowing backwards into atrium: has 2 cusps or flaps; also called mitral valve
|
|
|
|
cusps
|
leaflets or flaps of heart valve
|
|
|
|
mitral valve
|
valve between left atrium and ventricle in heart; prevents blood from flowing backwards into atrium: also called bicuspid valve because it has 2 cusps or flaps
|
|
|
|
pulmonary valve
|
semilunar valve between right ventricle and pulmonary artery in heart; prevents blood from flowing backwards into ventricles
|
|
|
|
semilunar valve
|
heart valves located between ventricles and great arteries leaving heart; pulmonary valve is located between right ventricle, and pulmonary artery and aortic valve are located between left ventricle abd aorta
|
|
|
|
tricuspid valve
|
valve between right atrium and ventricles of heart; prevents blood from flowing backwards into atrium, has 3 cusps or flaps
|
|
|
|
4 valves that control blood flow
|
1) tricuspid valve
2) pulmonary valve 3) mitral valve 4) aortic valve |
|
|
|
aorta
|
largest artery in body; located in mediastinum and carries oxygenated blood away from left side of heart
|
|
|
|
diastole
|
period of time during which heart chamber is relaxed
|
|
|
|
inferior vena cava
|
branch of vena cava that drains blood from abdomen and lower body
|
|
|
|
pulmonary artery
|
large artery that carries deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lung
|
|
|
|
superior vena cava
|
branch of vena cava that drains blood from chest and upper body
|
|
|
|
systole
|
period of time during which heart chamber is contracting
|
|
|
|
path of blood flow through heart chambers
|
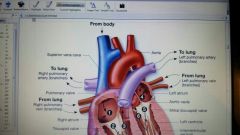
|
|
|
|
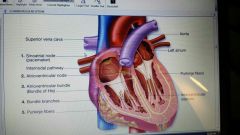
atrioventricular bundle
|
In heart, conducts electrical impulse from atrioventricular node into ventricles formally called bundle of His
|
|
|
|
atrioventricular node
|
This area at junction of right atrium and ventricle receives stimulus from sinoatrial node and sends impulse to ventricles through bundle of His
|
|
|
|
autoimmune nervous system (ANS)
|
portion of nervous system consisting of nerves to internal organs that function involuntary; regulates functions of glands (especially salivary, gastric and sweat glands) , adrenal medulla, heart and smooth muscle tissue; system is divided into 2 parts: sympathetic and parasympathetic
|
|
|
|
bundle branches
|
part of conduction system of heart; electrical signal travels down interventricular septum
|
|
|
|
bundle of His
|
bundle of His is located in interventricular septum; receives electrical impulse from atrioventricular node and distributes it through ventricular walls, causing them to contract simultaneously
|
|
|
|
purkinje fibers
|
part of conduction system of heart: found in ventricular myocardium
|
|
|
|
sinoatrial node (SA)
|
Also called pacemaker of heart. area of right atria that indicates electrical pulse that causes heart to contact
|
|
|
|
condution system of heart
|
|
|
|
|
electrocardiogram (EKG) wave
|
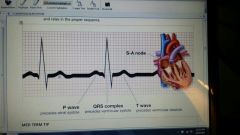
|
|
|
|
3 types of blood vessels
|
1) arteries
2) capillaries 3) veins |
|
|
|
lumen
|
space, cavity or channel within tube or tubular organ or structure in body such as vessels
|
|
|
|
s
comparative structure of blood vessels |
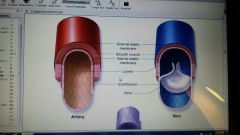
|
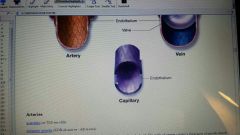
|
|
|
arterioles
|
smallest branch of arteries; carries blood to capillaries
|
|
|
|
coronary arteries
|
group of 3 arteries that branch off aorta and carry blood to myocardium
|
|
|
|
arteries
|
large thick walled vessels that carry blood away from the heart. walls contain smooth muscle that contract or relax to change the size of the arterial lumen.
|
|
|
|
major arteries of body
|
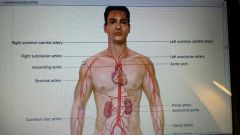
|
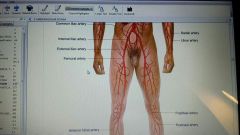
|
|
|
capillary bed
|
network of capillaries found in a given tissue or organ. arterial blood flows into a capillary bed and venous blood flows back out.
|
|
|
|
venules
|
smallest veins; receive deoxygenated blood leaving capillaries. then merge into larger veins
|
|
|
|
blood pressure (BP)
|
measurement of pressure that is exerted by blood against walls of a blood vessel
|
|
|
|
diastolic pressure
|
lower pressure within blood vessels during relaxation: phase of heart beat. lower number of BP
|
|
|
|
pulse (P)
|
expansion and contraction produced by blood as it moves throug artery. pulse can be taken at several pulse points throughout the body where artery is close to surface
|
|
|
|
systolic pressure
|
maximum pressure within blood vessels during heart contraction. upper number of BP
|
|
|
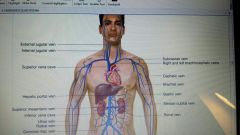
major veins of body
|
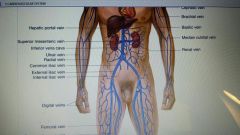
|
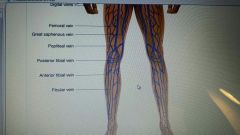
|
|
|
angitits
|
inflammation of vessel
|
|
|
|
angiospasm
|
involuntary muscle contraction of the smooth muscle in the wall if a vessel. narrows the vessel
|
|
|
|
angiostenosis
|
narrowing of a vessel
|
|
|
|
embolus
|
The obstruction of a blood vessel by a blood clot that has broken off from a thrombus somewhere else in the body and traveled to the point of obstruction. If it occurs in a coronary artery it may result in a myocardial infraction
|
|
|
|
infract
|
an area of tissue within an organ or part that undergoes necrosis following the loss of its blood supply
|
|
|
|
ischemia
|
The localized and temporary deficiency of blood supply due to an obstruction to the circulation
|
|
|
|
murmur
|
a sound in addition to the normal heart sounds arising from blood flowing through the heart. This extra sound may or may not indicate heart abnormality
|
|
|
|
ortho static hypotension
|
The sudden drop in blood pressure a person experiences when standing straight up suddenly
|
|
|
|
palpitations
|
pounding racing heartbeat
|
|
|
|
plaque
|
a yellow, fatty deposit in an artery that is the hallmark of arthrostenosis also called an atheroma
|
|
|
|
atheroma
|
tumor like collection of fatty substances
|
|
|
|
regurgitation
|
to flow backwards. In the cardiovascular system this refers to the back flow of blood through a valve
|
|
|
|
thrombus
|
a blood clot forming within a blood vessel. may partially or completely occlude the blood vessel
|
|
|
|
angina pectoris
|
condition in which there is severe pain with a sensation of constriction around the heart. caused by a deficiency of oxygen to the heart muscle
|
|
|
|
arrhythmia
|
irregularity in the heartbeat or action. cones in many different forms: some are not serious while others are life threatening
|
|
|
|
bundle branch block (BBB)
|
occurs when the electrical impulse is blocked from traveling down the bundle of His or bundle branches. results in the ventricles beating at a different rate than the atria also called heart block
|
|
|
|
cardiac arrest
|
complete stopping of heart activity
|
|
|
|
cardiomegaly
|
enlarged heart
|
|
|
|
cardiomyopathy
|
General term for a disease of the myocardium. can be caused by alcohol abuse, patasites, viral infection and congestive heart failure. One of the most common reasons a patient may require a heart transplant
|
|
|
|
congenital septal defect (CSD)
|
a hole, present at birth, in the septum between 2 heart chambers. results in a mixture of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. There can be an atrial septal defect (ASD) and a ventricular septal defect ( VSD)
|
|
|
|
congestive heart failure (CHF)
|
pathological condition of the heart in which there is a reduced outflow of blood from the left side of the heart because the left ventricle myocardium has become too weak to efficiently pump blood. results in weakness, breathlessness and edema
|
|
|
|
coronary artery disease (CAD)
|
insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle due to an obstruction of one or more coronary arteries. may be caused by atherosclerosis and may cause angina pectoris and myocardial infraction
|
|
|
|
endocarditis
|
inflammation of the lining membranes of the heart. may be due to bacteria or to an abnormal immunological response. In bacterial endocarditis the mass of bacteria that forms is referred to as vegetation
|
|
|
|
fibrillation
|
am extremely serious arrhythmia characterized by am abnormal quivering or contraction of heart fibers. When this occurs in the ventricles, cardiac arrest and death can occur. emergency equipment to defibrillate or convert the heart to a normal beat is necessary
|
|
|
|
flutter
|
an arrhythmia in which the atria beat too rapidly but in a regular pattern
|
|
|
|
heart valve prolapse
|
condition in which the cusps or flaps of the heart valve are too loose and fail to shut tightly, allowing blood to flow backward through the valve when the heart chamber contracts. Most commonly occurs in the mitral valve but may affect any of the heart valves
|
|
|
|
heart valve stenosis
|
The cusps or flaps of the heart valve are too stiff. Therefore they are unable to open fully, making it difficult for blood to flow throw shut tightly , allowing blood to flow backward. This condition may affect any of the heart valves
|
|
|
|
myocardial infraction
|
condition caused by the partial or complete occlusion or closing of one or more of the coronary arteries. symptoms include a squeezing pain or heavy pressure in the middle of the chest. A delay in treatment could result in death. Also referred to as a heart attack
|
|
|
|
myocarditis
|
inflammation of the muscle layer of the heart wall
|
|
|
|
pericarditis
|
inflammation of the pericardial sac around the heart
|
|
|
|
tetralogy of Fallot
|
combination of 4 congenital anomalies: pulmonary stenosis, an interventricular septal defect, improper placement of the aorta and hypertrophy of the right ventricle. needs immediate surgery to correct
|
|
|
|
valvulitis
|
inflammation of a heart valve
|
|
|
|
aneurysm
|
weakness in the wall of an artery resulting in localized widening of the artery. Although an aneurysm may develop in any artery, common sites include the aorta in the abdomen and the cerebral arteries in the brain
|
|
|
|
arteriorhexis
|
ruptured artery. may occur if an aneurysm ruptures an arterial wall
|
|
|
|
arteriosclerosis
|
thickening, hardening and loss of elasticity of the walls of the arteries. Most often due to atherosclerosis
|
|
|
|
atheroma
|
a deposit of fatty substance on the wall of an artery that bulges into and narrows the lumen of the artery. A characteristic of atherosclerosis. Also called a plaque
|
|
|
|
atherosclerosis
|
The most common form of arteriosclerosis. caused by the formation of yellowish plaques of cholesterol on the inner walls of arteries
|
|
|
|
coarctation of the aorta
|
severe congenital narrowing of the aorta
|
|
|
|
hemorrhoid
|
varicose veins in the anal region
|
|
|
|
hypertension
|
blood pressure above the normal range.
|
|
|
|
hypotension
|
decrease in blood pressure. cam occur in shock, infection, cancer, anemia and as death approaches
|
|
|
|
patent ductus arteriosus (PVD)
|
congenital heart anomaly in which the fetal connection between the pulmonary artery and the aorta fails to close at birth. This condition may be treated with medication and resolve with time. In some cases surgery is required
|
|
|
|
peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
|
Any abnormal condition affecting blood vessels outside the heart. symptoms may include pain, pallor, numbness and loss of circulation and pulses.
|
|
|
|
phlebitis
|
inflammation of vein
|
|
|
|
polyarteritis
|
inflammation of several arteries
|
|
|
|
Raynaud ' s phenomenon
|
periodic ischemic attacks affecting the extremities of the body, especially the fingers, toes, ears and nose. The affected extremities become cyanotic and very painful. These attacks are brought on by arterial constriction due to extreme cold or emotional stress
|
|
|
|
thrombophlebitis
|
inflammation of a vein resulting in the formation of blood clots within the vein
|
|
|
|
varicose veins
|
swollen and distended veins. usually in the legs
|
|
|
|
auscultation
|
process of listening to the sounds within the body by using stethoscope
|
|
|
|
sphygmomanometer
|
instrument for measuring blood pressure. Also referred to as blood pressure cuff
|
|
|
|
stethoscope
|
instrument for listening to body sounds such as chest, heart and intestines
|
|
|
|
cardiac enzymes
|
blood test to determine the level of enzymes specific to heart muscles in the blood. an increase of enzymes may indicate heart muscle damage such as myocardial infraction. The enzymes include: creatine phosphokinase (CPK) , lactate dehydroge-nase (LDH) and glutamic oxaloacetoc transaminase (GOT)
|
|
|
|
serum lipoprotein level
|
blood test to measure the amount if cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. an indicator of atherosclerosis risk
|
|
|
|
angiogram
|
X ray of a vessel taken during angiography
|
|
|
|
angiography
|
X rays taken after the injection of am opaque material into blood vessel. can be performed on the aorta as an aortic angiography. on the heart as angiocardiography. and on the brain as cerebral angiography
|
|
|
|
cardiac scan
|
patient is given radioactive thallium intravenously and then scanning equipment is used to visualize the heart. It is especially useful in determining myocardial damage
|
|
|
|
doppler ultrasonography
|
measurement of sound wave echoes as they bounce off tissue and organs to produce an image. In this system used to measure velocity of blood moving through blood vessels to look for blood clots or deep vein thromoses
|
|
|
|
echocardiography
|
noninvasive diagnostic method using ultrasound to visualize internal cardiac structure, cardiac valve activity can be evaluated using this method
|
|
|
|
catheter
|
flexible tube inserted into the body for the purpose of moving fluids into or out of the body. . In the cardiovascular system a catheter is used to place dye into blood vessels so they may be visualized on X rays
|
|
|
|
cardiac catherization
|
passage of a thin tube catheter through a blood vessel leading to the heart. done to detect abnormalities to collect cardiac blood samples, and to determine the blood pressure within the heart
|
|
|
|
electrocardiogram
|
hard copy record produced by electrocardiography
|
|
|
|
Holter monitor stress testing
|
portable EGG monitor worn by a patient for a period of a few hours to a few days to assess the heart and pulse activity as the person goes through the activities of daily living. used to assess a patient who experiences chest pain and unusual heart activity during exercise and normal activities
|
|
|
|
stress testing
|
method for evaluating cardiovascular fitness. The patient us placed on a treadmill or a bicycle and then subjected to steadily increasing levels of work. an EKG and oxygen levels are taken while the patient exercises. tge test us stopped if abnormalities occur on the EKG. Also called an exercise test or a treadmill test
|
|
|
|
cardiopulmonary resuscitation
|
procedure to restore cardiac output and oxygenated air to the lungs f I r a person in cardiac arrest. A combination of chest compressions and respiration performed by one or 2 CPR trained rescuers
|
|
|
|
defibrillation
|
procedure that converts serious irregular heartbeats by giving electric shocks to the heart using instrument called a defibrilator. Also called cardioversion. automated external defibrillators (AED) are portable devices that automatically detect life threatening arrhythmias. abd deliver the appropriate electrical shock. they are designed to be used by non medical persons and are found I'm public places.
|
|
|
|
extra corporeal circulation (ECC)
|
During open heart surgery, the routing of blood to a heart lung machine so it can be oxygenated and pumped to the rest of body.
|
|
|
|
implantable cardioverter defibrilator (ICD)
|
device implanted in the heart that delivers an electrical shock to restore a normal heart rhythm. particularly useful for persons who experience ventricular fibrillation
|
|
|
|
pacemaker implantation
|
electrical device that substitutes for the pacemaker of the heart. It controls the beating of the heart by a series of rhythmic electrical impulses. an external pacemaker has the electrodes on the outside of the body. am internal pacemaker has the electrodes surgically implanted within the chest wall.
|
|
|
|
thrombolytic therapy
|
process in which drugs; such as streptokinase (SK)or tissue type plasminogen activator (tpa) are injected into a blood vessel to dissolve clots and restore blood flow
|
|
|
|
aneurysm ectomy
|
surgical removal of sac of an aneurysm
|
|
|
|
arterial anastomosis
|
surgical joining together of 2 arteries. performed if an artery is severed or it is damaged section of an artery is removed
|
|
|
|
atherectomy
|
surgical procedure to remove a deposit of fatty substance. an atheroma from an artery
|
|
|
|
coronary artery bypass graft
|
Open heart surgery in which a blood vessel from another location in the body (often leg vein) is grafted to route blood around a blocked coronary artery
|
|
|
|
embolectomy
|
removal of an embolus or clot from blood vessel
|
|
|
|
endarterectomy
|
removal of the diseased or damaged inner lining of an artery. usually performed to remove atherosclerosis plaques
|
|
|
|
heart transplantation
|
replacement of a diseased or malfunctioning heart with a donors heart
|
|
|
|
intracoronary artery stent
|
placement of a stent within a coronary artery to treat coronary ischemia due to atherosclerosis
|
|
|
|
ligation and stripping
|
surgical treatment for varicose veins. The damaged vein is tied off (ligation) and removed (stripping)
|
|
|
|
percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
|
method for treating localized coronary artery narrowing. A balloon catheter is inserted through the skin into the coronary artery and inflated to dilate the narrow blood vessel
|
|
|
|
stent
|
stainless steel tube placed within a blood vessel or a duct to widen the lumen
|
|
|
|
valve replacement
|
removal of a diseased heart valve abd replaced with an artificial valve
|
|
|
|
valvoplasty
|
surgical procedure to repair a heart valve
|
|
|
|
ACE Inhibitor drugs
|
produce vasodilation and decrease blood pressure. ex: benazeptil, lotensin, catopril, capoten
|
|
|
|
antiarrhythmic
|
reduces or prevents cardiac arrhythmia
ex: flecainide, tambocor, ibutilide, corvert |
|
|
|
anticoagulant
|
prevents blood clot formation.
ex: warfarin sodium, coumadin, warfarin |
|
|
|
antipidemic
|
reduces amount of cholesterol and lipids in the bloodstream. treats hyperlipidemia.
ex: atorvastin, lipitor, simvastin, zocor |
|
|
|
antiplatelet agents
|
inhibits the ability of platelets to clump together as part of a blood clot
ex: clopidogrel, plavix, aspirin, ticlopidine, ticlid |
|
|
|
beta blocker drugs
|
treats hypertension and angina pectoris by lowering the heart rate.
ex: metopropol, lopressor, propranolol, inderal |
|
|
|
calcium channel blocker drugs
|
treats hypertension, angina pectoris and congestive heart failure by causing the heart to beat less forcefully and less often
ex: diltiazem, cardizem, nifedipine, procardia |
|
|
|
cardiotonic
|
increases the force of cardiac muscle contraction. treats congestive heart failure
ex: digoxin, lanoxin |
|
|
|
diuretic
|
increases urine production by the kidneys which works to reduce plasma and therefore blood volume resulting in lower blood pressure
ex: furosemide, lasix |
|
|
|
thrombolytic
|
dissolves existing blood clots
ex: tissue plasminogen activator (tpa), alteplase, activase |
|
|
|
vasoconstrictor
|
contracts smooth muscle in walls of blood vessels raises blood pressure
ex; metaraminol, aramine |
|
|
|
vasodilator
|
relaxes the smooth muscle in the walls of arteries thereby increasing diameter of the blood vessel. used for 2 main purposes; increasing circulation to an ischemic area and reducing blood pressure
ex: nitroglycerine, nitro-dur, isoxsuprine, vasodilan |
|
|
|
AED
|
automated external defibrillator
|
|
|
|
AF
|
atrial fibrillation
|
|
|
|
AMI
|
acute myocardial infarction
|
|
|
|
AS
|
arteriosclerosis
|
|
|
|
ASD
|
atrial septal defect
|
|
|
|
ASHD
|
arteriosclerotic heart disease
|
|
|
|
AV, A-V
|
atrioventricular
|
|
|
|
BBB
|
bundle branch block
|
|
|
|
CABG
|
coronary artery bypass graft
|
|
|
|
CAD
|
coronary artery disease
|
|
|
|
CC
|
cardiac catherization chief complaint
|
|
|
|
CCU
|
coronary care unit
|
|
|
|
CoA
|
coarctation of the aorta
|
|
|
|
CP
|
chest pain
|
|
|
|
CSD
|
congenital septal resuscitation
|
|
|
|
CV
|
cardiovascular
|
|
|
|
CPR
|
cardiopulmonary resuscitation
|
|
|
|
ECC
|
extra corporeal circulation
|
|
|
|
ECG, EKG
|
electrocardiogram
|
|
|
|
ECHO
|
echocardiogram
|
|
|
|
GOT
|
glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase
|
|
|
|
HTN
|
hypotension
|
|
|
|
ICD
|
implantable cardioverter defibrilator
|
|
|
|
LVAD
|
left ventricular assist device
|
|
|
|
LVH
|
left ventricular hypertrophy
|
|
|
|
MI
|
myocardial infarction, mitral insufficiency
|
|
|
|
mm Hg
|
millimeters of mercury
|
|
|
|
MR
|
mitral regurgitation
|
|
|
|
MS
|
mitral stenosis
|
|
|
|
MVP
|
mitral valve prolapse
|
|
|
|
PAC
|
premature atrial contraction
|
|
|
|
PDA
|
patent ductus arteriosus
|
|
|
|
PTCA
|
percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
|
|
|
|
PVC
|
premature ventricular contraction
|
|
|
|
S1
|
First heart sound
|
|
|
|
S2
|
Second heart sound
|
|
|
|
SA, S-A
|
sinoatrial
|
|
|
|
SK
|
streptokinase
|
|
|
|
tPA
|
tissue type plasminogen activator
|
|
|
|
V fib
|
ventricular fibrillation
|
|
|
|
VSD
|
ventricular septal defect
|
|
|
|
VT
|
ventricular tachycardia
|
|

