![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where the cardiovascular system is located in general |
The mediastinum, which is between the lungs. Along with the trachea, esophagus, thymus and vessels. Interpleural space.
|
|
|
Where the cardiovascular system is located in dogs and cats |
3rd and 7th ribs |
|
|
Where the cardiovascular system in bovine and equine |
2nd and 6th ribs |
|
|
Base |
The widest part ,the cranial part of the cardiovascular system. Where the vessels enter and exit. |
|
|
Apex |
Rounded, caudal point of the cardiovascular system. The left ventricle. |
|
|
Thymus |
Main area of immunity in young animals. As animal matures the thymic tissue atrophies. |
|
|
Pericardium |
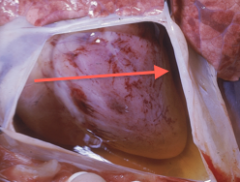
Around the heart. Invaginated sac in the heart's base. Fibrous layer and serous layer. Partially inflated balloon if the heart is the rock pushing on it. |
|
|
Pericardial space |
Between parietal and visceral layers of the serous layer, and is filled with a small amount of fluid. Cushion for protection and reduces friction so the heart can move. |
|
|
Fibrous layer |

Outermost layer of the pericardium. |
|
|
Location of attachment of fibrous layer in dogs and cats. |
The diaphragm, the phrenicopericardial ligament. |
|
|
Location of attachment of fibrous layer in equine and bovine |
The sternum, sternopericardial ligament. Elongated chest cavity. Heart sits more ventral. |
|
|
Serous layer |
Inner layer of the pericardium that consists of the parietal layer, visceral layer, and the pericardial space. |
|
|
Parietal layer |
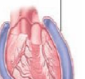
Most superficial of the serous layer, closest to the fibrous layer. |
|
|
Visceral layer |
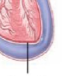
Also called the epicardium. Most inner serous layer, stuck to the heart. |
|
|
Myocardium |

Located in the heart wall, and is the main muscle of the heart.Bulk of the heart. Striated, branched and involuntary. Outer lining is the epicardium and the inner lining is the endocardium. |
|
|
Endocardium |
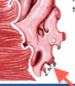
Inner part of the myocardium of the heart wall. Simple squamous epithelium that covers valves and continues with the endothelium |
|
|
Endothelium |

Inner lining of vessels leaving the heart. |
|
|
Right and left atria |

Right and left auricles of the heart which is what you see of the front, which are extensions of the ______. Where the blood comes into. |
|
|
Right and left ventricle |
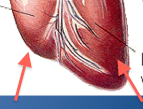
Left is thicker, major pump, and forms the apex of the heart. Right pumps to lungs. Separated by interventricular sulcus. The pumps that move blood through the body. |
|
|
Systematic vessels |
Cranial and caudal vena cava, pulmonary artery and vein, and aorta in the heart. |
|
|
Cranial and caudal vena cava |
Part of the systematic vessel that deals with blood returning from the body to the heart. Enter into the right atrium. |
|
|
Pulmonary artery and vein |
Part of the systematic vessel which takes blood to and from the lungs. |
|
|
Aorta |
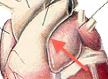
Part of the systematic system. Major artery that takes blood from the heart to the rest of the body. |
|
|
Coronary vein |
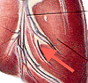
Coronious sinus , part of the cardiac vessels. Find out what it does. |
|
|
Coronary artery |
look up |
|
|
Valves |
Opens and closes to the control the flow in the heart. Chrodae tendinae and papillary muscles. |
|
|
Right and left atrioventricular valves |
Valves that control flow between the atria and ventricles. Include tricuspid (right AV) and mitral (left AV) |
|
|
Pulmonic valve |
Valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk, also referred to as the pulmonary artery. |
|
|
Aortic valve |
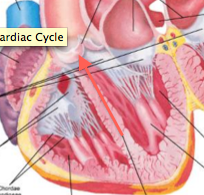
Valve between left ventricle and aorta. Controls flow. |
|
|
Systole |
Part of the cardiac cycle when the muscles contract to push blood. include atrial and ventricular systole. |
|
|
Diastole |
Part of the cardiac cycle when the muscles relax, chambers open and fill with blood. Atrial and ventricular diastole. |
|
|
relaxed; partially; blood |
When the cardiac cycle begins, all four chambers are _________ and the ventricles are ___________ filled with _______ . |
|
|
Review. |
Slides 10 & 11. |
|
|
The conducting system |
Sinoatrial (SA) node, Atrioventricular (AV) node, right and left av bundles and purkinje fibers. |
|
|
Sinoatrial (SA) node |
Pacemaker cell in the wall of the right atrium. Part of the conducting system. Automatically depolarizes and repolarizes, |
|
|
Depolarization and repolarization |
causes electrical impulse for muscle contraction. One impulse fired from the SA node causes one heartbeat. |
|
|
AV node (atrioventricular node) |
find |
|
|
S1 |
The "lub". Closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves at the beginning of the ventricular systole. Mitral valve is the loudest on the left, tricuspid is the loudest on the right. |
|
|
S2 |
The "dub". Closure of the semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonic) at the beginning of the ventricular diastole. Easiest to hear on the left side of the chest. |
|
|
S3 and S4 |
Only heard in large animals. sinus arrhythmia is common in dogs. |
|
|
Normal Resting Heart Valves |
|
|
|
Apex |
The strongest beat. Swings and bumps the wall. |
|
|
Aortic valve |
4th intercostal space. Left side auscultation |
|
|
Pulmonic valve |
3rd intercostal space. Left side auscultation. |
|
|
Left Av (mitral valve) |
5th intercostal space. Left side auscultation. |
|
|
Apex beat |
4th and 5th intercostal space. Left side auscultation. |
|
|
Right AV (tricuspid valve) |
4th intercoastal space. Right side auscultation. |
|
|
Left |
_____ side is better for aortic valve. |
|
|
Cardiac output |
Amount of blood ejected from each ventricle in one minute. Stroke volume x heart rate. The measure of how well the heart is functioning. CO = SV x HR |
|
|
Heart rate |
How many beats per section of time, generally bpm. |
|
|
Stroke volume |
The amount of blood pumped out of each ventricle with each heart beat. |
|
|
Things that affect heart rate |
Autonomic nervous system: sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight), parasympathetic nervous system (rest and digest), and hormones. |
|
|
Part of the sympathetic nervous system |
Cardiac nerves |
|
|
Part of the parasympathetic nervous system |
Vagus nerves. |
|
|
Things that affect stroke volume |
preload, contractility, afterload |
|
|
Preload |
How much blood is returned to the ventricles. Frank Starling Law of the heart. |
|
|
Contractility |
+ and - inotropic agents |
|
|
Afterload |
Force needed to push open the valves. How hard to press to open the doors. |
|
|
Lungs |
Most blood in the fetal heart bypasses the _______ during fetal circulation. |
|
|
Oxygen from mom to placenta |
Umbilical vein brings blood to the baby part. Small amount goes to lungs for developmental nutrients. |
|
|
Foramen ovule |

Right --> left atrium --> left ventricle --> body. Helps blood get to the lungs when the baby takes its first breath, causing this to close. Important bypass point. |
|
|
Fossa ovalis |
The foramen ovule after its closed. |
|
|
Ductus arteriosus |
Pulmonary artery --> aorta. Ligamentum arteriosum. Important bypass point. |
|
|
Arteries |
Take blood from heart to body. Thick walls. More smooth muscle to dilate and constrict and regulate systematic blood pressure. |
|
|
Veins |
Return blood to the heart (deoxygenated), thin walls for low pressure, little elastic tissue, little smooth muscle. Valves that prevent backflow. Loose structures |
|
|
veins ; merge |
Smaller venules form larger and larger _____. Eventually _____ and dump into the cranial and caudal vena cava |
|
|
Capillaries |
Make up arterioles that make up arteries. No muscle layer in walls. Where oxygen and nutrients switch for carbon dioxide and waste products.Leak into veins. |
|
|
Jugular vein |
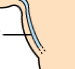
Venipuncture site; commonly used in all types of animals. |
|
|
Cephalic vein |
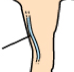
Venipuncture site; Cranialmedial aspect of forelimb. |
|
|
Femoral vein |
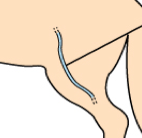
Venipuncture site ; Medial aspect of hind limb. Most commonly used in cats. |
|
|
Saphenous vein |
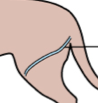
Venipuncture site; Lateral aspect of hind limb. Used commonly in dogs. |
|
|
Coccygeal vein |
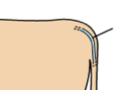
Venipuncture site; Ventral midline of tail. Used in ruminants and rodents |
|
|
Review |
Slides 21-23 |

