![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the prime functions of the cardiovascular & respiratory systems?
|
Cardiovascular: Transports O2 & nutrition to the cells.
Respiratory: Provides O2 to the bloodstream. |
|
|
What is the basic respiration reaction?
|
sugar + oxygen --> energy + carbon dioxide + water
|
|
|
Broadly, what does the cardiovascular system consist of & how is it regulated?
|
Transport medium (blood), pump (heart), transport network (arteries, capillaries, veins). Regulated by feedback mechanisms.
|
|
|
What ensures a unidirectional blood flow?
|
Valves
|
|
|
How are organs perfused by the arterial tree?
|
The arterial tree branches so that all organs are perfused in PARALLEL
|
|
|
Describe key differences between arteries & veins.
|
Arteries have thicker, muscular walls that are relatively indistensible, decreasing diameter, & lead blood to the capillary network. Veins are the opposite.
|
|
|
Describe the BASIC cardiovascular system arrangement.
|
PUMP --> ARTERIAL TREE --> CAPILLARY NETWORK --> VENOUS SYSTEM --> PUMP
|
|
|
What are the only 2 ways to increase oxygen carrying capacity?
|
Increasing haemoglobin levels &/or increasing heart output.
|
|
|
Define systemic circulation.
|
The general circulation carrying deoxygenated blood from capillaries to R heart & oxygenated blood from L heart to capillaries in all organs of the body including the lungs EXCEPT the alveoli (where gaseous exchange takes place). Pump = left heart.
|
|
|
Define pulmonary circulation.
|
Carries deoxygenated blood from R side of heart to lungs & oxygenated blood from the alveoli in the lungs to the L side of heart. Pump = right heart.
|
|
|
What are the 4 heart valves & where are they located?
|
Tricuspid (between R atrium & ventricle)
Pulmonary (between R ventricle & pulmonary artery) Mitral/Bicuspid (between L atrium & ventricle) Aortic (between L ventricle & aorta) |
|
|
Circulation of the blood DIAGRAM
|
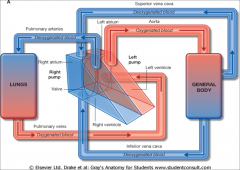
|
|
|
Where does gaseous exchange take place?
|
Alveolar-capillary membrane
|
|
|
What forms the supporting framework & bellows to give tidal flow in of the respiratory system?
|
Supporting framework = thorax (spine, ribs, sternum)
Bellows to give tidal flow = muscles |
|
|
How many lobes does each lung have?
|
Left lung - 2: superior & inferior
Right lung - 3: superior, middle, inferior |
|
|
What 5 structures make up the airway?
|
mouth/nose/pharynx, larynx, trachea & bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
|
|
|
What makes up the intra-pulmonary airway?
|
Main bronchi enter lung & divide into lobar & inter-lobar bronchi, bronchioles, broncho-alveolar airways, alveoli
|
|
|
Name the respiratory muscles
|
Diaphragm, External intercostals, Internal intercostals, Accessory muscles (sterno-cleido-mastoid, trapezius, scalenes)
|
|
|
What happens when the respiratory muscles contract?
|
- thorax volume increases
- air drawn in |
|
|
What surface anatomy would you use in CPR?
|
xiphisternum - where to carry out chest compressions
|
|
|
What can be found at the manubrio-sternal angle/'Angle of Louis'?
|
- second costal cartilage
- apex of R atrium - bifurcation of trachea - root of aorta & aortic arch - superior/inferior mediastinum T4 - 4th thoracic spinous process |
|
|
Surface anatomy of lungs DIAGRAM
|
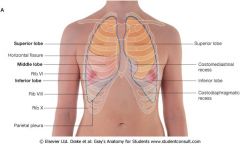
|
|
|
Surface anatomy of heart DIAGRAM
|
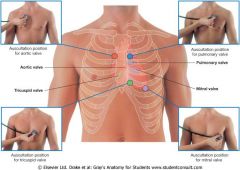
|

