![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Trabeculae carnae are features of ...
|
Both ventricles
|
|
|
Before birth, blood from the right atrium passes to the left atrium via the
|
Foramen ovale
|
|
|
Parasympathetic nerves to the heart travel with which cranial nerve?
|
Vagus Nerve
|
|
|
The crista terminalis and pectinate muscle are features of
|
The right atrium
|
|
|
The middle layer of the heart wall is the
|
Myocardium
|
|
|
Coronary arteries are branches of the
|
Ascending aorta
|
|
|
What is secreted by the adrenal cortex so that salt & water can be retained in the body?
|
Aldosterone
|
|
|
Pulmonary circulation
|
1)r.ventricle
2)pulm. artery(r/l)<lungs> 3)pulm. veins (4) 4)lf atrium |
|
|
Systemic Circulation
|
1)lf ventricle
2)aorta(head,neck,trunk,limbs)internal organs 3)IVC & SVC 4)rt atrium |
|
|
Artery
|
carries blood away from heart
1)thick wall 2)high pressure 3)no valves |
|
|
Veins
|
carries blood towards heart
1)thin wall 2)low pressure 3)no valves above heart level except gi venous system 4)valves below heart level except portal system |
|
|
Capillary
|
smallest bv
1)walls have holes for exchange 2)low pressure 3)gas,nutrients,hormones,electrolytes,fluids |
|
|
Body priority
|
1)digestive system
2)brain |
|
|
The volume of blood in adult circulation is about
|
6 liters
|
|
|
The heart pumps about ___ of blood per minute (resting)
|
5 liters
|
|
|
At any given time the majority of blood stay in
|
the vein
|
|
|
Blood pressure
|
bp=p@systole/p@ diastole
bp=p@vent cont/p@vent relax bp=120mmHg/80 p=force/cm2 |
|
|
Blood flow
|
volume of blood flowing thru a vessel
|
|
|
Resistance
|
opposition to flow & is a measure of the amount of friction blood encounters as it passes thru vessels
|
|
|
Pressure gradient
|
blood flows from high pressure to low pressure
|
|
|
Pressure,resistance, flow relations
|
1. bp high=bf high
2. bp low=bf low 3. r high= bf low |
|
|
Laminar flow vs. turbulent flow
|
Laminar flow
1) smooth,straight,silent Turbulent flow 1) spiral,noisy (vascular bruit),related to aneurysm |
|
|
Murmur
|
Cadiac abnormal sound
|
|
|
r/l coronary arteries
|
branches of ascending aorta. related to ischemia,angina pectoris
|
|
|
coronary sinus
|
receives blood from all veins except 2 ant.cardiac veins. empties blood to right atrium.
|
|
|
r/l auricles
|
connected to atrium, pouch shaped.
|
|
|
great vessels of the heart
|
1)svc & ivc (to right atrium)
2)pulm.trunk (from r vent) 3)ascending aorta (from l vent) |
|
|
right atrium
|
1)seperated from l.atrium by interatrial septum.
2)formen ovale- b goes from r.atrium to l.atrium (before birth) 3)foramen ovalis-pulm.circ |
|
|
right ventricle
|
1)seperates r.atrium by tricuspid valve (av valve).
2)attached to chordae tendinae attached to papillary muscle 3)seperated by l.vent by interventricular septum (has bundle of his) |
|
|
left atrium
|
1)seperated from left ventricle by mitral valve (av)
|
|
|
left ventricle
|
1) contains myocardial layer
2)trabeculae carnae |
|
|
intrinsic nerve supply
|
1)regulates heart rate, cardiac rhythm & cardiac contractility (cc)
2)sensitive to chemical stimuli, blood ph or pCO2 |
|
|
SA Node
|
1)pacemaker of heart
2)located near opening of SVC |
|
|
Interatrial bundles
|
fibers along r/l atrium walls
|
|
|
AV Node
|
Near right AV opening
|
|
|
Bundle of His (AV bundle)
|
1)inside intervent. septum
2)divides in l/r bundles 3)turns into purkinje fibers (in myocardium) |
|
|
Extrinsic innervation
|
1)associated w/ ANS and sensory fibers of heart
2) ANS controls & regulates heart rate, cardiac contractility & cardiac ouput of BP |
|
|
Sympathetic innervation
|
O-spinal chord (t1-t4)
T-cardiac tissue |
|
|
Parasympathetic innervation
|
O-medulla oblongata
partially form Vagus nerve T-cardiac tissue |
|
|
Sensory nerves
|
O-heart
travel to the CNS with autonomic fibers. |
|
|
Sympathetic stimulation (heart)
|
1)↑ heart rate (tachycardia)
2)↑ bp (hypertension) 3)↑ bf 4)↑ co 5)↑ cc 6)↑ pp |
|
|
Parasympathetic stimulation (heart)
|
1)↓ heart rate (bradycardia)
2)↓ bp (hypotension) 3)↓ bf 4)↓ co 5)↓ cc 6)↓ pp |
|
|
Coronary occlusion
|
tissue of ♥ dies
↓ isoelectric potential changes (♥ will not cont.in sync) ↓ ventricular fibrilation= cardiac arrest or death (most common side=lf.ant.branch of l. coronary artery) |
|
|
Angina pectoris
|
chest pain
|
|
|
Arteriosclerosis
|
hardening of artery caused by fat deposit. causes:
1.fatty diet 2.smoking 3.chronic anxiety |
|
|
Tachycardia
|
fast ♥ rate. causes:
1.↑ bt (fever) 2. stimulates sympathetic system (fear, anxiety) 3.toxin in ♥(bacterial endotoxin) |
|
|
Bradycardia
|
slow ♥ rate. causes:
1.↓bt (hypothermia) 2. stimulates parasympathetic system (sleep) 3.relaxation 4.myocardial weakening (disease of ♥) 5.well trained athlete |
|
|
High blood pressure factors (hypertension)
|
1.co
2.ANS activity 3.peripheral resistance 4.blood volume 5.stroke volume |
|
|
Hypertension
|
1.essential (primary) 80% ?
2.renal ht:renin-angiotensin cycle 15% 3.secondary:ht due to another disease/condition |
|
|
Renal hypertension
|
1.kidney→renin/liver→angiotensinogen
2.meet up in blood=angiotensin 1 3.goes to lungs turns into angiotensin 2 4.goes to adrenal gland→aldosterone 5.goes to kidney 6. retains salt and water 7.hypervolumia & ↑ osmolality 8.renal hypertension |
|
|
Electrocardiogram
|
1.p wave=depolarization of atria
2.QRS=depolarization of vent. 3.T=repolarization of vent. |
|
|
Heart sounds:Lub
|
1st heart sound:systolic
1.av valve closing (sound) 2.aortic & pulmonic valve opening 3.vent.cont. 4.↑ bp 5.atria ↑ |
|
|
Heart sounds:Dup
|
2nd heart sound:diastolic
1.aortic & pulmonic valve (sound) closing 2.av valve opening 3.vent. relax 4.vent. ↑ 5.atria cont. |
|
|
Separation of blood
|
1.plasma 55%
2.buffy coat:wbc& platelets 1% 3.rbc 44% |
|
|
Blood types
|
1.O→O most com. uni.donor,both A B
2.A→AA or AO B antib.only 3.B→BB or BO A antib.only 4.AB→AB uni.receiver,neither A B |
|
|
Rhesus factor
|
when rh- woman has rh+ fetus, she produces rh antibodies against the next fetus.
|
|
|
Microcytic hypochromic anemia
|
iron deficiency. most common worldwide. mostly in children. rbc-small
|
|
|
Macrocytic normochromic anemia
|
(aka marcocytosis)-liver disease & alcoholism. deficient in VB12 & folic acid. rbc-big.
|
|
|
Normocytic normochromic anemia
|
severe blood loss. rbc-normal
|
|
|
Anemia of chronic disease
|
alcholism,RA,cancer,TB,SLE
|
|
|
Leukocytosis
|
1.↑ WBC w/ infection
2.acute infection= ↑ neutrophil 3.chronic infection=all ↑ esp.monocyte |
|
|
Leukemia
|
cancer in kids. ↑ WBC in b.marow,makes rbc starve.
|
|
|
Leukopenia
|
very ↓ WBC. associated w/viral disease.
|
|
|
Plasma contents
|
1.albumin
2.globulin 3.fibrinogen 4.blood glucose 5.electrolytes 6.enzymes,hormones,wast material, blood gases..etc TOTPROTEIN=ALBUMIN+GLOBULIN |
|
|
Albumin
|
made in liver. maintains osmotic pressure. smallest plasma protein
|
|
|
Globulin
|
essential protein for formation of rbc. immunity
|
|
|
Fibrinogen
|
have the greatest molecular weight & involved w/ blood clots (coagulation)
|
|
|
Glucose
|
for formation of energy.
not > 200mg=diabetes |
|
|
Erethropoietin
|
1.kidney→erethropoietin
2.goes to b.marrow→rbc erethropoietin released when body does not have oxygen. people w/ kidney disease have anemia. |
|
|
Lymphatic system
|
Thoracic duct (highway)always green.(main lymph duct)
1.cisterna chyli (ant.lum.spien)-drains lymph via thoracic duct. ends between lf. int.jugular vein & lf. subclavian nerve. joins venous blood. |
|
|
Lymph node locations
|
1.axillary
2.inguinal 3.neck/throat |
|
|
Lymph node disease (lymphadenopathy)
|
rule-can't palpate normal lymyh node.
criteria: 1.size 2.consistency-mushy(infection),rubbery(viral),hard(cancer) 3.painful or painless(diseased) |
|
|
Acquired Immunity
|
1.Active-produced by andtibodies developed in body in response to antigen
|
|
|
Natural Acquired Immunity
|
exposure
|
|
|
Induced Active immunity
|
immunization or vaccine
|
|
|
Passive immunity
|
produced by transfer of antibodies from another source
|
|
|
Natural passive immunity
|
breastfed
|
|
|
Artificial passive
|
administered antibodies
|
|
|
Innate immunity
|
Born with antibodies
|
|
|
T cell
|
1.cell mediated immunity
2.t=thymus 3.direct PHYSICAL attack on infected cells |
|
|
B Cell
|
1.antibody mediated imm/humoral imm
2.b=bursa(lymph node) 3.CHEMICAL attack by secreted antibodies. "Y" |
|
|
Nasal Cavity
|
1.hair-sensory
2.nasal epithelium-warms and moistens air. |
|
|
Pharynx
|
1.nasopharynx
2.oropharynx 3.larynogopharynx-behind thryroid cartilage. between vocal chords. |
|
|
Trachea
|
made of cartilaginous rings. c-shaped.
1.Carina-bottom of trachea a. rt main bronchus b. lf main bronchus |
|
|
Bronchial tree
|
1.lobar bronchus
2.segmental bronchus 3.bronchiole 4.respiratory bronchiole 5.alveolar duct-->atria (access > 1 alveolar sac) |
|
|
Hilus
|
1)main bronchus(biggest hole)
2)Pul.artery(always on top)↑CO2 3)Pul.vein (2 or more)↑CO2 ↑O2 4)lymph vessels 5)nerves(sympathetic,parasympathetic,sensory....has touch and pressure but NO PAIN FIBERS) |
|
|
Sympathetic Stimulation to the Lung
|
1)↑ br (tachypnea)
2)↑ ventilation 3)↑ circulation 4)condensation of mucous or ↓ in mucous secretion |
|
|
Parasympathetic Stimulation to the lung
|
1)↓ br (bradypnea)
2)↓ ventilation 3)↓ circulation 4)↑ mucous secretion |
|
|
Asthma
|
triggered by bt changes or by increased parasympathetic stimulation.
|
|
|
Pancoast tumors
|
cancer in apex of lung.associated with smokers. 40+. cancer spreads to neck and damages sympathetic chain of neck. leads to Horner's syndrome.
|
|
|
Horner's syndrome
|
1)ptosis-drooping eyelid
2)lack of facial sweating 3)dry,warm skin 4)sunrise sign indicates 4-6months to live |
|
|
COPD (chronic obstructed pulmonary disease)
|
1.emphysema-formation of cavities in lungs from smoking.ability to brieath in but not out.
2)chronic bronchitis 3)pneumonia-acute infection of blood tissue alveoli.usually affects the middle lobe. leads to septicemia. |
|
|
Septicemia
|
infection in the blood.
1)high fever 2)coughing w/ sputum 3)tiredness |
|
|
Inhalation (inspiration)
|
1) chest volume ↑ from vertical and horizontal stance.
2) ribs move ↑(except 1st pair) 3) pleural cavity pressure ↓ 4)lung tissue expands 5)diaphragm goes ↓ 6)abdominal cavity pressure ↑ 7)ant. abd.muscle tense |
|
|
Exhalation (expiration)
|
1)chest volume goes ↓
2)ribs move ↓ 3)pleural cavity pressure ↑ 4)lung tissue shrinks 5)diaphragm ↑ 6)abdominal cavity pressure ↓ 7)ant. abd.muscle relaxed |
|
|
Respiratory centers
|
regulates breathing. located in the pons and the medulla oblongata.
|
|
|
Pons
|
1 pneumotaxic center-suppresses breathing
2 apneustic center-excitement |
|
|
Medulla Oblongata
|
respiratory rhymycity center-allows one to breathe in and out.
|
|
|
Relaxed breathing
|
only the diaphragm works (goes up and down)
|
|
|
Forced respiration
|
body recruits additional accessory respiratory muscles.
1.scm 2.intercostal muscles (external,internal,innermost) 3.scalene muscle(lateral side of neck) |
|
|
Horner's syndrome
|
1)ptosis-drooping eyelid
2)lack of facial sweating 3)dry,warm skin 4)sunrise sign indicates 4-6months to live |
|
|
COPD (chronic obstructed pulmonary disease)
|
1.emphysema-formation of cavities in lungs from smoking.ability to brieath in but not out.
2)chronic bronchitis 3)pneumonia-acute infection of blood tissue alveoli.usually affects the middle lobe. leads to septicemia. |
|
|
Septicemia
|
infection in the blood.
1)high fever 2)coughing w/ sputum 3)tiredness |
|
|
Inhalation (inspiration)
|
1) chest volume ↑ from vertical and horizontal stance.
2) ribs move ↑(except 1st pair) 3) pleural cavity pressure ↓ 4)lung tissue expands 5)diaphragm goes ↓ 6)abdominal cavity pressure ↑ 7)ant. abd.muscle tense |
|
|
Exhalation (expiration)
|
1)chest volume goes ↓
2)ribs move ↓ 3)pleural cavity pressure ↑ 4)lung tissue shrinks 5)diaphragm ↑ 6)abdominal cavity pressure ↓ 7)ant. abd.muscle relaxed |
|
|
A arch of aorta
AB pulmonary trunk AB1 rt pulmonary artery AB2 lf pulmonary artery AC pulmonary veins AD pulmonary valve AE ductus arteriosum B SVC BB thoracic aorta BC rt atrium BD aortic valve BE mitral (bicuspid)valve C brachiocephalic trunk C1 rt.subclavian C2 rt.common carotid artery CA chordae tendineae CB lf ventricle CD papillary muscle CE epicardium or apex D lf common carotid artery DA myocardium DB interventricular septum DC rt ventricle DE tricuspid valve E lf subclavian EB ascending aorta EE IVC |
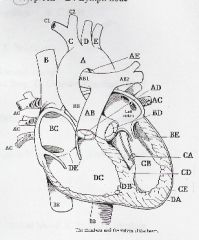
label diagram
|
|
|
A cupola (parietal pleura)
AB thyroid cartilage AC cricoid cartilage AD tracheal ring AE visceral pleura B apex of lung BA carina BC horizontal (minor) fissure BD lower (inferior) lobe BE base C parietal pleura CA mediastinum CB lingual D pleural cavity DA middle lobe |
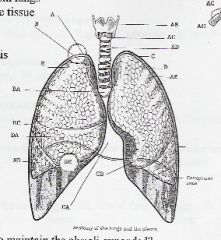
label diagram
|

