![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the areas of auscultation |
Aortic area- 2nd R ICS (along sternum border) Pulmonic area- 2nd L ICS (along sternum border) Third location (?)- 3rd ICS (along sternum border) Tricuspid areas- 4th & 5th L ICS (along sternum border) Mitral area- 5th L ICS (7-9cm lateral to the midsternal line) |
|
|
Describe the clinical findings for Acute Arterial Occlusion |
♣ Pain ♣ Pallor ♣ Pulselessness ♣ Paresthesias – feeling of ‘pins and needles’ ♣ Paralysis
|
|
|
Describe the clinical findings for Arterial Insufficiency |
o Skin changes o Prolonged capillary refill o Loss of hair o Thinning of skin o Dependent rubor
|
|
|
Describe the clinical findings for Venous insufficiency |
* Edema (swelling) |
|
|
Describe the clinical findings for Deep Venous Thrombosis |
o warmth, erythema o posterior calf tenderness o Homan’s sign o swelling o measure circumference (are they equal?? |
|
|
Homan’s sign |
A positive sign is present when there is pain in the calf on dorsiflexion of the patient's foot at the ankle while the knee is fully extended |
|
|
Afterload |
Load/resistance, against which the LV must eject its vol of blood during contraction |
|
|
Aneurysm |
a sac formed by localized dilatation of the wall of an artery, a vein, or the heart |
|
|
Allen test |
a test for occlusion of the radial or ulnar artery, in which one of these arteries is compressed after blood, has been forced out of the hand by clenching it into a fist; failure of the blood to diffuse into the hand when opened indicates that the artery not compressed is occluded. |
|
|
Arterial Insufficiency |
inadequate blood flow in arteries. May be caused by occlusive atherosclerotic plaques or emboli; damaged, diseased, or weak vessels; arteriovenous fistulas; aneurysms; hypercoagulability states; or heavy use of tobacco |
|
|
Atrioventricular Node |
Collection of Purkinje fibers beneath the endocardium of the right atrium, continuous with the atrial muscle fibers and atrioventricular bundle; it receives the cardiac impulses from the SA node and passes them on to ventricles. |
|
|
Brawny Edema |
Change typical of chronic venous insufficiency, characterized by thickening, induration, liposclerosis and non-pitting edema; brawny color is due to hemosiderin from lysed RBCs |
|
|
Claudication |
limping; lameness |
|
|
Coarctation |
narrowing |
|
|
Dextrocardia |
location of the heart in the right side of the thorax, the apex pointing to the right. |
|
|
Embolism |
Obstruction in a blood vessel due to a clot or other matter that gets stuck while traveling through the bloodstream |
|
|
Gangrene |
Decay or death of an organ or tissue caused by a lack of blood supply |
|
|
Homan’s Sign |
Present when passive dorsiflexion of the ankle by the examiner elicits sharp pain in the calf. Caused by a thrombosis of the deep veins of the leg |
|
|
Jugular Venous Pressure |
blood pressure in the jugular vein, which reflects the volume and pressure of venous blood. JVP is estimated by positioning the head of a supine patient at a 30- to 45-degree angle and observing the neck veins |
|
|
Lymphedema |
blockage of the lymph vessels, with a resulting accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the interstitial tissues of the body |
|
|
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dsypnea |
respiratory distress that awakens patients from sleep, related to posture (especially reclining at night), attributed to CHF w/ pulmonary edema or sometimes to chronic pulmonary disease |
|
|
Patent Ductus Arterious |
(PDA) a heart defect that occurs when the ductus arteriosus does not close at birth |
|
|
Pericardial Friction Rub |
scraping or grating friction rub heard with the heart beat, usually a to-and-fro sound, associated with pericarditis or other pathological condition of the pericardium |
|
|
Phlebitis |
inflammation of a vein |
|
|
Preload |
pressure stretching the ventricle of the heart, after passive filling and atrial contraction |
|
|
Sinus Node |
impulse generating (pacemaker) tissue located in the right atrium of the heart |
|
|
Sphygmomanometer |
BP meter is a device used to measure BP, comprising an inflatable cuff to restrict blood flow, and a mercury or mechanical manometer to measure the pressure |
|
|
Stenosis |
abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure |
|
|
Stroke Volume |
the volume of blood pumped by the R/L ventricle of the heart in one contraction |
|
|
Thrill |
abnormal tremor or vibration, as in the respiratory or vascular system. |
|
|
Thrombophlebitis |
vein inflammation related to a blood clot |
|
|
Thrombosis |
formation of clot or thrombus inside a blood vessel, obstructing flow of blood through the circulatory system |
|
|
Valsalva Maneuver |
performed by forcibly exhaling against a closed glottis (a closed airway). This maneuver with slight modifications can be used as a test of cardiac function and autonomic nervous control of the heart or to ‘clear’ the ears and sinuses (equalize pressure) when ambient pressure changes, as in diving or aviation |
|
|
Venous Hum |
benign medical condition where 20% of the blood flow travels to the brain and back to the heart. Due to the large amount of blood it can move quite fast causing the vein walls to vibrate which can create a humming noise to be heard by the patient |
|
|
CAD |
Coronary Artery Disease |
|
|
CHF |
Congestive Heart Failure |
|
|
CV |
Cardiovascular |
|
|
CVA |
Cerebrovascular Accident; Costovertebral Angle |
|
|
DP |
Dorsalis Pedis |
|
|
DVT |
Deep Venous Thrombosis Signs: - Warmth, erythema - Posterior Calf tenderness - Homans sign Swelling Measure circumference |
|
|
JVD |
Jugular Venous Distention - between 2 heads of SCM |
|
|
JVP |
Jugular Venous Pressure
|
|
|
ICS |
Intercostal Space |
|
|
MI |
Myocardial Infarction |
|
|
PMI |
Point of Maximal Impulse |
|
|
POP |
Popliteal |
|
|
PVD |
Peripheral Vascular Disease |
|
|
PT |
Physical Therapy; Posterior Tibial; Patient; Prothrombin Time |
|
|
RRR |
Regular Rate and Rhythm |
|
|
Describe S1sounds |
closure of the mitral and tricuspid (AV) valves, best heard at the apex, usually heard as one sound, same time or slightly before the carotid pulse palpated |
|
|
Describe S2 |
closure of the aortic and pulmonic (semilunar) valves, heard best at the base. There are 2 components-A2 aortic (loudest) and P2 pulmonic |
|
|
Describe Split S2 |
best heard during inspiration, under 50 yo, 2nd left intercostals space (pulmonic area), fixed splitting |
|
|
Describe S3 |
early diastolic sound, low frequency, caused by rapid ventricular filling, best heard at the apex, normal in children and young adults, older patients may indicate heart failure |
|
|
Describe S4 |
late diastole, confused with split S1, low pitched, caused by increased resistance to ventricular filling, best heard at apex with the bell |
|
|
Describe a murmur |
due to increased flow across normal valve, partially obstructed forward flow (stenosis), backflow-incompetent valve (regurgitation), flow into dilated chamber, shunting through a normal passage. Make sure to note systolic v. diastolic, duration/timing, pitch, quality, radiation, and grade. |
|
|
Describe Ejection clicks |
best heard in the apex, high pitched after S1, forceful ejection, deformed valve |
|
|
Describe the opening snap |
heard in apex, high pitched, diastolic, will arise from opening of mitral or tricuspid valve with pressure (with stenosis) |
|
|
What are the pressures for NORMAL BP |
Systolic <120 Diastolic <80 |
|
|
What are the pressures for Pre-Hypertensive BP |
Systolic 120-139 Diastolic 80-89 |
|
|
What are the pressures for hypertension Stage 1 |
Systolic 140-159 Diastolic 90-99 |
|
|
What are the pressures for hypertension Stage 2 |
Systolic ≥160 Diastolic ≥100 |
|
|
Average Pulse and BP @ birth |
Pulse: 140 Systolic: 70 |
|
|
Average Pulse and BP @ 6 months |
Pulse: 130 Systolic: 90 |
|
|
Average Pulse and BP @ 1 yr |
Pulse: 115 Systolic: 90 |
|
|
Average Pulse and BP @ 2 yr |
Pulse: 110 Systolic: 92 |
|
|
Average Pulse and BP @ 6 yr |
Pulse: 103 Systolic: 95 |
|
|
Average Pulse and BP @ 8 yr |
Pulse: 100 Systolic: 100 |
|
|
Average Pulse and BP @ 10 yr |
Pulse: 95 Systolic: 105 |
|
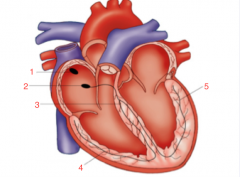
|
1. SA Node 2. AV Node 3. Bundle of HIS 4. Right Bundle Branches 5. Left Bundle Branches |
|
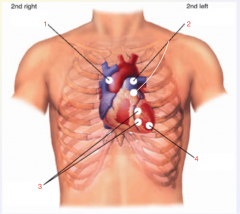
|
1. Aortic Area - 2nd Intercostal Space (Right) 2. Pulmonic Area - 2nd Intercostal Space (Left) 3. Tricuspid Area (Rt Vent) - Left Sternal Border 4. Mitral Area - Apex of Left Ventricle
|
|
|
Define cresendo |
Increasing intensity, |
|
|
Define Decresendo |
decreasing intensity |
|
|
Cresendo-decresendo |
(Diamond shaped) Increase immediately followed by decrease |
|
|
Describe the grading pitting edema |
1+: slight, disappears rapidly (2mm) 2+: Disappears in 10-15 sec (4mm) 3+: >1 minute, (6mm) 4+: deep pit, last 2-5 minutes (8mm) |
|
|
what does postural color changes indicate |
Marked pallor followed by rubor = arterial insufficiency Color should return in <10 sec. |
|
|
Describe the grading of pulses |
4+ = bounding, very increased 3+ = full, increased 2+ = expected 1+ = diminished 0 = absent, not palpable |
|
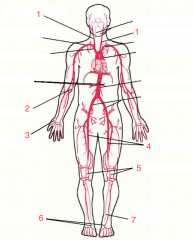
|
1. Carotid 2. Brachial 3. Radial 4. Femoral 5. Popliteal 6. Dorsal Pedis 7. Posterior Tibial |
|
|
Define Thrill |
palpable vibration at site of partial obstruction of valve or artery |

