![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are 4 main functions of the cardiovascular system?
|
To:
transport respiratory gases Remove waste products of metabolism Transport hormones Control temperature |
|
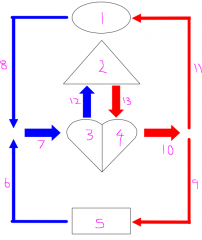
Labels of circulation
|
1 - brain
2 - lungs 3 - right side of heart 4 - left side of heart 5 - body 6 - caudal vena cava 7 - vena cava 8 - cranial vena cava 9-11 - aorta 12 - pulmonary artery 13 - pulmonary vein |
|
|
What is the definition of cardiac output?
|
The volume of blood ejected by one ventricle in one minute
|
|
|
What is the major determinant of the magnitude of the C.O.?
|
Oxygen requirement of body e.g. during exercise cardiac output increases to lungs
|
|
|
How may the distribution of C.O. be affected?
|
During exercise, cardiac output to skeletal muscle can increase to over 80% at expense of other areas
|
|
|
What is systole?
|
Period of ventricular contraction
|
|
|
What is diastole?
|
Period of ventricular relaxation
|
|
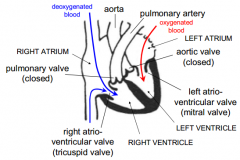
Is the heart in systole or diastole?
|
Diastole
|
|
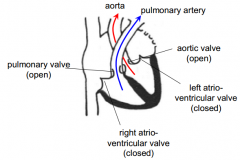
Is the heart in systole or diastole?
|
Systole
|
|
|
Which valves are open during systole?
|
Pulmonary and aortic valve
|
|
|
Which valves are open during diastole?
|
Right AV (tricuspid) and left AV valve (mitral)
|
|
|
How do you calculate cardiac output?
|
C.O. (l/min) = heart rate (bpm) x stroke volume (l)
|
|
|
What is stroke volume?
|
The volume of blood pumped from one ventricle in one beat
|
|
|
What is the effect of an increased heart rate on diastole?
|
Diastole usually longer than systole at resting heart rate, at strenuous heart rate diastole is hugely reduced and shorter than systole
|
|
|
What accounts for most of the ventricular filling during diastole?
|
The pressure in the ventricles is less than
|

