![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is ventilation |
movement of air exchanged in the pulmonary system |
|
|
what is tidal volume |
amount of air that is inhaled and exhaled during normal breathing |
|
|
what is residual volume (RV)? |
volume of air remaining in the lungs following a full or maximal expiration |
|
|
what is expiratory reserve volume? |
volume of air that can be forcefully expelled following a normal expiration |
|
|
what is inspiratory reserve volume |
volume of air that can be forcefully breathed in following a normal inspiration |
|
|
what is forced vital capacity? |
the amount of air that is under volitional control FVC = IRV + TV+ ERV |
|
|
What is forced expiratory volume? |
FEV1: volume of air that can be forcefully expelled in 1 sec following a full inspiration Normally at least 75% FVC is exhaled within 1st second |
|
|
what is total lung capacity? |
the sum of the residual volume and the forced vital capacity (TV + IRV +ERV + RV) |
|
|
WHAT IS functional residual capacity? |
the volume of air remaining in the lungs following a normal expiration (ERV + RV) |
|
|
draw graph of lung volumes |
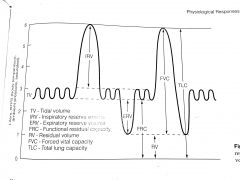
|
|
|
What is atelectasis? |
-shrunken and airless state of part of the lung, acute or chronic, complete or partial -often associated with infection
|
|
|
what are symptoms of atelectasis? |
1. pain on affected side 2. dyspnea 3. cyanosis 4. drop in BP 5. tachycardia 6. diminished or absent breath sounds 7. dull or flat to percussion 8. fever 9. reduced chest excursion on affected side |
|
|
what is auscultation? |
listening to the respiration for breath sounds using a stethoscope |
|
|
Describe normal breath sounds and how can they be abnormal |
-Normal sounds are called vesicular = soft rustling sounds heard throughout all inspiration and at beginning of expiration -breath sounds can be decreased or adventitious (extra sounds) such as crackles, wheezes, rhonchi |
|
|
what is deconditioning? |
decrease in aerobic fitness, VC, muscle strenght, and ROM as a result of prolonged bed rest or inactivity -occasionally accompanied by orthostatic hypotension |
|
|
what is hyperventilation? |
-increased inspiration and expiration of air as a result of an increase in rate and/or depth of respiration -results in depletion of carbon dioxide -->respiratory alkalosis with accompanying symptoms: -fall in BP -vasoconstriction -sometimes syncope -marked anxiety -wrist cramping
|
|
|
WHAT IS TREATMENT FOR HYPERVENTILATION |
-have pt breathe into a paper bag until the CO2 content of the blood returns to normal -pt also needs to be reassured and calmed |
|
|
what is orthopnea? |
difficulty breathing except in the sitting or standing position |
|
|
What is Percussion? |
-use of fingertips to tap the body lightly but sharply to determine position, size, and consistency of an underlying structure and the presence of fluid or pus in a cavity |
|
|
when using percussion to evaluate what should be noted? |
1. pitch 2. vibration elicited 3. resistance encountered -these determine the possibility of an underlying condition or problem |
|
|
what is percussion also used for (besides evaluating)? |
as treatment of pulmonary conditions -force is rhythmically applied with the therapist's cupped hands to the involved segment -used to incr amt of secretion cleared from the tracheobronchial tree |
|
|
what is perfusion? |
-volume of blood that circulates through the lungs -is gravity dependent -if pt has perfusion problem in lungs, tx should occur with the involved side down |
|
|
what is sputum? |
-substance expelled by coughing or clearing the throat -contains variety of material from respiratory tract (e.g. cellular debris, mucus, blood, pus, and microorganisms) -amount, color, and conditions of sputum can be used to differential diagnosis pulmonary conditions |
|
|
what does foul smelling sputum indicate? |
anaerobic infection |
|
|
what does purulent sputum indicate? |
(yellow or green) = infection |
|
|
what does frothy sputum indicate? |
pulmonary edema |
|
|
what does sputum that is mucoid indicate |
(thick, clear) cystic fibrosis or conditions with a chronic cough |
|
|
what does hemoptysis mean? |
blood in sputum |
|
|
what is the valsalva's maneuver? |
attempting to forcibly exhale with the glottis, nose, and mouth closed -causes increased intrathoracic pressure and dec return of blood to the heart |
|
|
what is the norm for PaO2? |
80-100 mmHg |
|
|
what is the norm for PaCO2? |
35-45 mm Hg incr CO2, decr pH (more acidic) |
|
|
what is the norm for pH of body? |
7.35-7.45 incr pH = incr alkalinity |
|
|
what is the adult norm for TV? |
500 mL |
|
|
what is norm for bicarbonate? |
HCO^3- = 22-28 mEq/mL |
|
|
what are lab values for respiratory alkalosis? |
pH : incr PaCO2: decr HCO3-: WNL
|
|
|
what are causes of respiratory alkalosis and signs and symptoms? |
alveolar hyperventilation 1. dizziness 2. syncope 3. tingling 4. numbness 5. early tetany |
|
|
what are lab value changes for respiratory acidosis? |
pH: decr PaCO2: incr HCO3-: WNL |
|
|
what are causes of respiratory acidosis and signs and symptoms? |
causes: alveolar hypoventilation EARLY 1. anxiety 2. restless 3. dyspnea 4. HA LATE 1. confusion 2. somnolence 3. coma |
|
|
what are lab value changes for metabolic alkalosis? |
pH incr PaCO2: WNL HCO3-: incr |
|
|
what are causes of metabolic alkalosis and signs and symptoms? |
CAUSES bicarbonate ingestion vomiting diuretics steroids adrenal disease SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS vague symptoms weakness mental dullness possibly early tetany |
|
|
What are lab value changes for metabolic acidosis? |
pH decr PaCO2: WNL HCO3-: decr |
|
|
what are causes of metabolic acidosis and signs and symptoms? |
CAUSES diabetic lactic or uremic acidosis prolonged diarrhea SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS secondary hyperventilation (kussmaul breathing) nausea lethargy coma
|
|
|
what could be reason for hemoptysis during percussion? |
if pt is on anticoagulant (coumadin or heparin)
|
|
|
what do bronchodilators do and side effects? |
bronchodilation = open airways to assist in breathing (alupent, ventolin [albuterol], proventil, epinephrine) -used prior to exercise to reduce negative effects of disease process (e.g. asthma) -can incr HR and BP |
|
|
how are corticosteroids used to treat pulmonary conditions? |
ex: prednisone and cortisol -decr edema and inflammation associated with COPD -side effects 1. osteoporosis 2. muscle wasting 3. impaired/slowed wound healing |
|
|
Where do you auscultate lung lobes anteriorly? |
RIGHT Upper lobe: between ribs 2 and ribs 4 Middle: between 4th and 6th ribs Lower: below 6th rib] LEFT Upper: between 2nd and 4th Lingula (still upper lobe bc no middle lobe on L side): between 4th and 6th Lower: below 6th |
|
|
Where do you auscultate lung lobes posteriorly? |
Above spine of scapula = upper lobes below spine = lower lobes Cannot ausc. below 10th rib posteriorly |
|
|
What are Rales? |
aka Crackles sound like rice-krispies discontinuous and heard primarily during inspiration -could be result of air bubbles in secretions or movement of fibrotic tissue during breathing -associated with pulmonary edema -basilar rales often accompany Left ventricular CHF |
|
|
what are Rhonchi? |
-continuous, low pitched, sonorous breath sounds that are most prominent during expiration -could be result of air passing through airways narrowed by inflammation, bronchospasm or secretions -present with asthma and chronic bronchitis |
|
|
what is stridor? |
continuous adventitous sound of inspiration associated with upper airway obstruction |
|
|
what are wheezes? |
continuous breath sounds that are high pitched, sibilant, and musical -associated with asthma |
|
|
What is friction rub? |
caused by rubbing of pleural surfaces against one another, usually as a result of inflammation or neoplastic processes -may be accompanied by pain during inspiration |
|
|
what are signs and symptoms of COPD? |
1. increased resistance to airflow 2. often hx of smoking 3. abnormal breath sounds 4. use of accessory breathing muscles 5. increased chest size 6. dry or productive cough |
|
|
what is asthma? |
increased reactivity of trachea and bronchi to various stimuli (allergens, exercise, cold) causing widespread narrowing of the airways due to inflammation, smooth muscle constriction, and increased secretions |
|
|
what are signs and symptoms of asthma? |
1. wheezing cough 2. dry or productive mucoid sputum with plugs 3. anxiety with severe bronchospasm may restrict airflow to the extent that no wheezing is heard 4. chest wall symmetrically decreased |
|
|
what are PT considerations with asthma? |
1. Use of bronchodilators prior to exercise or exposure to cold |
|
|
What is cystic fibrosis |
-genetically inherited disease -characterized by thickening of secretions of all exocrine glands, leading to obstruction -CF may present as an obstructive, restrictive or mixed disease |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of CF? |
1. Frequent respiratory infections, especially Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
what is the treatment (PT) for CF? |
1. Percussion, vibration, shaking, and postural drainage may have to be performed many times per day if in acute stage or pneumonia develops |
|
|
what is emphysema? |
-permanent abnormal enlargement and destruction of dead air spaces distal to terminal bronchioles -associated with hx of smoking with cough and sputnum production (chronic bronchitis) |
|
|
what are signs and symptoms of emphysema? |
1. barrel chest 2. dyspnea 3. decreased breath sounds with/without wheezing 4. use of accessory mm of ventilation |
|
|
what are PT treatments for emphysema? |
1. pursed lip breathing with expiration 2. endurance exercises 3. pt education regarding disease |
|
|
what is Restrictive lung disease due to alterations in lung parenchyma and pleura |
Fibrotic changes within the pulmonary parenchyma or pleura resulting in decr lung compliance & due to: 1. idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis 2. asbestosis 3. radiation pneumonitis 4. oxygen toxicity |
|
|
What are Restrictive lung disease due to alterations in the chest wall? |
Restricted motion of bony thorax, with diseases such as: 1. ankylosing spondylitis 2. arthritis 3. scoliosis 4. pectus excavatum (caves in), 5.chest wall skin burns 6. scleroderma |
|
|
What are Restrictive Lung disease due to alterations in the neuromuscular apparatus: |
Decreased muscular strength results in an inability to expand the rib cage, seen in disease states such as: 1. multiple sclerosis 2. muscular dystrophy 3. Parkinson's disease 4. spinal cord injury 5. cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
|
|
|
what is flail chest and symptoms? |
two or more fractures in two or more adjacent ribs 1. shallow breathing 2. crepitation during ventilation over fracture site 3. paradoxical movement of flail section during ventilation Inspiration: flail section is pulled inward Expiration: flail section moves outward |
|
|
what is treatment for flail chest? |
1. gentle breathing exercises 2. splinting 3. pain management 4. proper positioning |
|
|
what is pneumothorax? |
Air enters the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse due to loss of negative pressure
|
|
|
what are signs and symptoms of pneumothorax? |
1. dry cough 2. decreased or absent breath sounds 3. trachea deviation away from affected site 4. local or referred pain 5. hyperresonant and tympanic percussion sound |
|
|
what is treatment for pneumothorax? |
Chest tube |
|
|
what is tuberculosis facts? |
infection spread by aerosolized droplets from an untreated infected host -after 2 weeks, meds make host noninfectious -incr incidence of TB in HIV population
|
|
|
what are signs and symptoms of TB? |
1. slight non productive cough 2. slight fever 3. hemoptysis 4. dyspnea 5. chest wall pain 6. possible chest x-ray changes |
|
|
what is pulmonary edema |
Excessive seepage of fluid from the pulmonary vascular system into the interstitial space; Due to: 1. Left ventricular failure 2. aortic valvular disease 3. mitral valvular disease 4. inhalation of toxic fumes 5. narcotic overdose |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of Pulmonary edema: |
1. Dyspnea on exertion or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea |
|
|
Treatment of Pulmonary edema: |
1. Medication, including oxygen and diuretics |
|
|
what is Pulmonary emboli? |
A thrombus from the peripheral venous circulation lodges in the pulmonary artery leading to obstruction of blood flow to the lungs |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of Pulmonary emboli |
Without infarction: 1. tachypnea 2. anxiety 3. restlessness 4. rales (crackles) 5. wheezing, 6. decreased breath sounds 1.chest pain 2. hemoptysis 3. pleural friction rub 4. fever 5. positive chest x-ray |
|
|
Treatment of Pulmonary emboli: |
1. Low-dose heparin |
|
|
what is a normal hematocrit? |
Male: 40-54% Female: 37-47% Newborn:50-62% |
|
|
what are hemoglobin norms |
12-16 g/100 mm |
|
|
what is obstructive pulmonary disease characterized by? |
reductions in airflow with or without reductions in vital capacity |
|
|
what are restrictive lung disorders characterized by? |
decreased VC with normal expiratory airflows |
|
|
What is the TLC FRC RV VC PaCO2 FEV1 for both Obstructive and Restrictive diseases |
OBSTRUCTIVE TLC: incr FRC: incr RV: incr VC: decr PaCO2: incr FEV1: sharp decr
RESTRICTIVE TLC: decr FRC: decr RV: decr VC: decr PaCO2: decr FEV1: normal |
|
|
How is obstructive lung disorder categorized? |
mild moderate severe based on VC, FEV1, and FEV1/FVC |
|
|
what is VC FEV1 FEV1/FVC normally? |
VC: >80% FEV1>80% FEV1/FVC > 70% |
|
|
what is VC FEV1 FEV1/FVC for mild obstructive pulmonary disease? |
VC 66-80% FEV1: 66-80% FEV1/FVC 60-70% |
|
|
what is VC FEV1 FEV1/FVC for moderate obstructive pulmonary disease? |
VC: 50-65% FEV1: 50-65% FEV1/FVC: 45-59% |
|
|
what is VC FEV1 FEV1/FVC for severe obstructive pulmonary disease? |
VC: <50% FEV1: <50% FEV1/FVC: <45%
|
|
|
what is arterial oxygen saturation? |
SaO2 ratio of amount of oxygen in a known volume of blood to the amount of oxygen that could be carried by that volume of blood -measured using a pulse oximeter |
|
|
what SaO2 indicates poor gas exchange and a need for supplemental O2? what PaO2 does this correspond to? |
<88% PaO2 58 mmHg (assuming arterial pH is in normal range -supplemental O2 needs a medical doctor's prescription before it can be given to a patient |

