![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name some vasculitis of small vessels.
|
- hypersensitivity angiitis
- HS purpura - cryoglobulinemia - Bechet's syndrome |
|
|
Name some vasculitis of small-to-medium vessels.
|
- PAN
- microscopic polyangiitis - Churg-Strauss syndrome |
|
|
Name some vasculitis of medium vessels.
|
- Wegener's granulomatosis
- Kawasaki syndrome |
|
|
Name some vasculitis of large vessels.
|
- Giant cell arteritis
- polymyalgia rheumatica - Takayasu arteritis |
|
|
Name some vasculitis of capillaries.
|
- goodpasture disease
|
|
|
The following patients being treated for their diseases all developed palpable purpura. What is the cause?
- gout patient treated with allopurinol - rheumatoid arthritis patient treated with gold salts - HTN patient treated with thiazide - seizure patient treated with phenytoin - strep pharyngitis patient treated with penicillin |
hypersensitivity angiitis (drug hypersensitivity)
- serum sickness like - localized to skin |
|
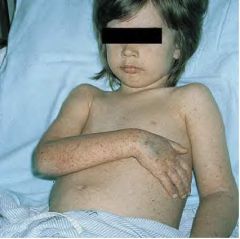
Name this disease and the type of vasculitis.
|
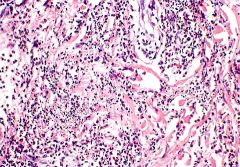
RMSF- rash on upper extremity extensors
hypersensitivity vasculitis - neutrophilic and eosinophilic infiltrate, nuclear dust around vessels (fragments of neutrophil nuclei) |
|
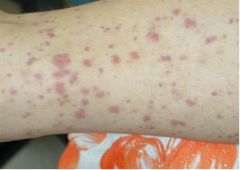
What is this? and in what diseases you see this?
|
palpable purpura
- hypersensitivity angiitis - HS purpura - cryoglobulinemia |
|
|
Name some causes of hypersensitivity angiitis.
|
- infectious disease: eg RMSF
- neoplasms: hyperinflammatory state - SLE: connective tissue disease - drug reactions - HS purpura - cryoglobulinemia |
|
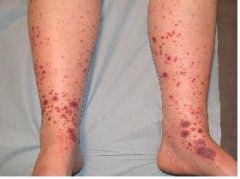
What is this disease?
- skin lesion (see figure) - arthritis - abdominal pain, may see bloody diarrhea - IgA deposits and complement in vessel walls - preceded by URI, immunizations, drugs, food, insect bites. |
HS purpura (hypersensitivity vasculitis)
- triad of purpura, arthritis, and abdominal pain - other symptoms: renal (glomerulonephritis, RBC casts) |
|
|
Treatment for HS purpura.
|
- usually self-limited
- steroid if needed |
|
|
What is this disease?
- recurrent episodes of palpable purpura - hepatomegaly, lymphadenopathy - polyarthralgia, weakness - proliferative glomerulonephritis - associated with HepC virus - IgM and IgG precipitate at cool temps, can be detected in serum. |
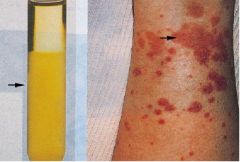
cryoglobulinemia (hypersensitivity vasculitis)
|
|
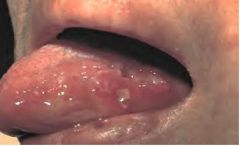
What is this disease?
- recurrent aphthous ulcer (see figure) - positive pathergy test - eye lesion (may go blind) - genital ulcer - |
Bechet's syndrome
- pathergy test: scratchy skin |
|
|
Pathogenesis of PAN.
|
- systemic vasculitis with transmural necrotizing inflammation y neutrophils -> intimal proliferation and wall degeneration
- all organ except lungs and venules |
|
|
What is this disease?
- p-ANCA - high ESR - anemia - HepB positive |
PAN
- p-ANCA: antibodies to MPO - anemia due to renal failure and blood loss |
|
|
Renal sequelae of PAN.
|
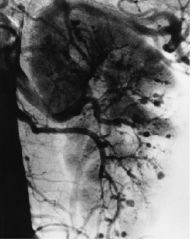
- segmental aneurysm (see picture)-> rupture -> retroperitoneal hemorrhage
- rapid necrotizing glomerular ischemia -> sudden severe HTN, nephrotic syndrome, renal failure |
|
|
CV sequelae of PAN.
|
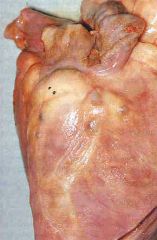
- angina pectoris
- MI: coronary arteries lesions with microaneurysms (see picture) - pericarditis |
|
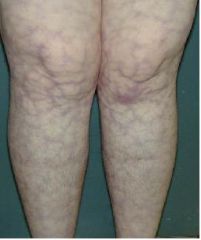
What is this and What diease is this?
|
- livedo reticularis
- caused by PAN |
|
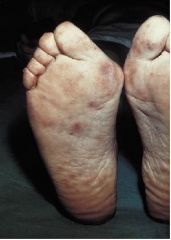
What is this called and what can caues this?
|
- subcutaneous nodule
- caused by PAN |
|
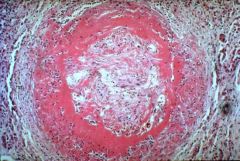
What is this disease?
- medial smooth muscle destruction - fibrinoid necrosis of intima and media -> obliteration/stenosis of lumen - transmural neutrophils |
PAN
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system sequelae of PAN.
- pain - paresthesia - sensory loss |
mononeuritis multiplex
|
|
|
Central nervous system sequelae of PAN.
|
- seizures
- stroke: ischemic or hemorrhagic - encephalopathy: global cognitive dysfunction |
|
|
GI sequelae of PAN.
|
- abdominal pain, intestinal bleeding, obstruction, perforation
- mesenteric aneurysm -> rupture -> intraperitoneal hemorrhage, shock, death - cholecystitis, hepatic infarction, pancreatic infarction |
|
|
Treatment of PAN.
|
high dose prednisone and cyclophosphamide
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- p-ANCA - also affect pulmonary capillaries and venules - very common |
microscopic polyangiitis (necrotizing vasculitis)
- pulmonary: diffuse alveolar hemorrhage - renal: glomerulonephritis |
|
|
What is this disease?
- p-ANCA - hypereosinophila - allergic rhinitis, asthma, sinusitis - lung: pulmonary infiltrate, fever, malaise, wt loss - heart: cause of death - skin: purpura - GI: ischmia |
Churg-strauss syndrome (systemic necrotizing vasculitis)
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- sinusitis, nasal ulcers, occular inflammation - focal area of necrotizing granulomatous inflammatoin in lungs - proliferative glomerulonephritis - purpura, nodules - mononeuritis multiplex, cranial neuritis |
Wegener's granulomatosis
- "ELK" |
|
|
What is this disease?
- c-ANCA - lung nodule - anemia - high ESR |
Wegener's granulomatosis
|
|
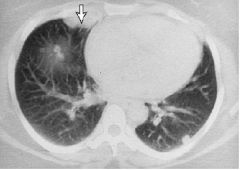
What is this disease?
- lung nodule - glomerular crescents - rhinitis |
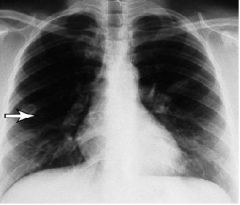
Wegener's granulomatosis
|
|
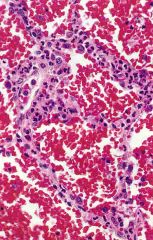
What is this disease?
- lung biopsy |
Wegener's granulomatosis
- necrotizing capillaritis: neutrophils infiltrating alveolar septae |
|
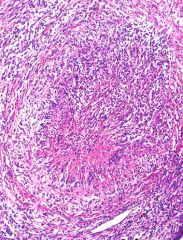
What is this disease?
- lung biopsy |
Wegener's granulomatosis
- transmural necrosis (lumen obliterated |
|
|
What is this disease?
- PAN like arteritis in children under age 4 - associated with S. aureus - can be prevented with ASA, IV gamma-globulin |
Kawasaki syndrome
|
|
|
What is the #1 cause if acquired heart disease in US?
|
Kawasaki syndrome
|
|
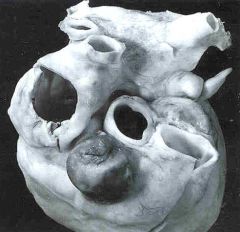
What is this disease?
|
Kawasaki syndrome
- RCA aneurysm ruptured with pericardial temponade |
|
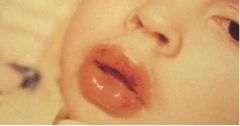
What is this disease?
- fever - above skin lesions - coronary artery aneurysm - conjuctivitis - segmental aneurysm |
Kawasaki syndrome (mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome)
|
|
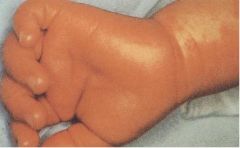
What is this disease?
- above lesion - associated with s. aureus - coronary artery aneurysm |
Kawasaki syndrome (mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome)
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- headache, fever, anemia - jaw claudication - scalp tenderness, diplopia - high ESR: 90 |
giant cell arteritis
|
|
|
What is the most common vasculitis in the US?
|
giant cell arteritis
|
|
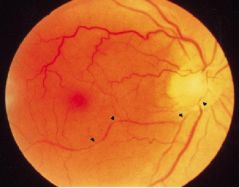
What is this? what disease could this be associated with?
|
- vasospasm if retinal arteries
- associated with giant cell arteritis |
|
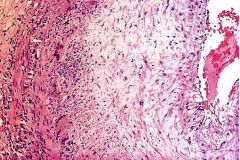
What is this disease?
|
giant cell arteritis
- granulomatous infiltrate of inner media with giant cells |
|
|
What should you do when someone is diagnosed with giant cell arteritis?
|
treat it right away with high dose prednisone, do not wait for biopsy because patients can become blind.
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- myalgia, but no muscle weakness or atrophy - aching AM stiffness - wt loss, fever, anorexia - high ESR - scalp tenderness |
polymyalgia rheumatica
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- women under 40 - cold/numb fingers - weak pulse in upper extremity than lower extremity - arterial bruit |
Takayasu arteritis (pulseless disease)
|

