![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Front (Term) |
Junctional rhythm
Originate in AV node |
|
|
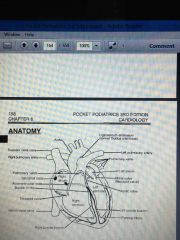
Blood flow through heart |
Superior/inferior vena cava Right atrium Tricuspid Right ventricle Pulmonic valve Pulmonary arteries Lungs Left atrium Bicuspid Left ventricle Aorta |
|
|
Electrical current through heart |
SA node AV node Bundle of HIS Bundle branch fibers Perkinge fibers |
|
|
Heart sound locations |
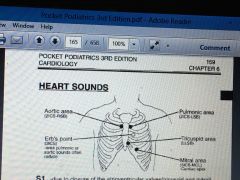
|
|
|
Heart sound due to closure of AV valves |
S1 |
|
|
Heart sound from closure of semilunar valves |
S2 |
|
|
Heart sound from ventricles filling |
S3 |
|
|
Heart sound from ventricles filling |
S3 |
|
|
Heart sound from atria ejection |
S4 |
|
|
S3 and S4 heart sounds are hear loudest at |
Mitral area |
|
|
T/F
Loudness of murmur is proportional to severity of disease |
False |
|
|
Which part of stethoscope is used for high pitch murmurs |
Diaphragm |
|
|
Which part of stethoscope is used for high pitch murmurs |
Diaphragm |
|
|
Which part of the stethoscope is used for low pitch murmurs |
Bell |
|
|
With murmurs the terms regurgitation, insufficiency, and incompetence mean ________ |
The same thing |
|
|
With murmurs the terms regurgitation, insufficiency, and incompetence mean ________ |
The same thing |
|
|
An innocent murmur is systolic or diastolic |
Systolic |
|
|
With murmurs the terms regurgitation, insufficiency, and incompetence mean ________ |
The same thing |
|
|
An innocent murmur is systolic or diastolic |
Systolic |
|
|
A pathological murmur is diastolic/systolic |
Diastolic |
|
|
There is no evidence of cardiac disease with _________ murmurs |
Innocent |
|
|
________ murmurs are more common in children/young adults |
Innocent |
|
|
Innocent murmurs are grade _______ |
3 or less |
|
|
Low frequency cutaneous vibrations associated with loud heart murmurs |
Thrills |
|
|
Low frequency cutaneous vibrations associated with loud heart murmurs |
Thrills |
|
|
At what stage of heart murmurs does a palpable murmur begin |
Stage 4 |
|
|
Murmur that is louder when sitting forward after exhalation |
Aortic regurgitation |
|
|
Murmur that is louder when sitting forward after exhalation |
Aortic regurgitation |
|
|
Pulmonic stenosis and pulmonic regurgitation are louder during |
Inspiration |
|
|
Murmur accentuated by exercises |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
Holosystic murmurs |
Start at S1 and extend to S2
Mostly regurgitation murmurs |
|
|
Murmur with splitting of S2 |
Atrial septal defect |
|
|
Murmur with splitting of S2 |
Atrial septal defect |
|
|
Continuous machine murmur |
Patent ductus ateriosus |
|
|
Ekg paper Little 1 mm box |
.04 seconds |
|
|
Ekg paper 5 mm box |
.20 seconds |
|
|
Ekg paper 5 mm box |
.20 seconds |
|
|
Ekg paper Time between slashes at top of the page |
3 seconds |
|
|
Determining heart rate on EKG |
300/ by number of big boxes between two consecutive QRS |
|
|
Determine an irregular heart rate on EKG |
Count the of QRS between two 3 second black marks and multiply x 10 |
|
|
Describe the different heart rhythms |
Regular Regular irregular Irregular irregular |
|
|
Normal PR interval |
.12-.21 |
|
|
Normal PR interval |
.12-.21 |
|
|
PR interval greater than .21 |
Heart block |
|
|
PR interval less than .12 |
White Levine |
|
|
QRS normal interval |
Less than .12 |
|
|
Lengthening in QRS intervals can occur with |
Pacemakers Bundle branch block Beats initiated in ventricles |
|
|
Hallmark of infarction in EKG |
Abnormal Q wave |
|
|
Hallmark of infarction in EKG |
Abnormal Q wave |
|
|
T/F Most Q waves are permanent |
True |
|
|
Hallmark of infarction in EKG |
Abnormal Q wave |
|
|
T/F Most Q waves are permanent |
True |
|
|
No surgery if infarct occurred within |
6 months |
|
|
Hallmark of myocardial injury |
Elevated ST segment |
|
|
Inverted T wave |
Ischemia |
|
|
Peak T wave |
Hyperkalemia |
|
|
Sometimes a U wave is seen |
Sign of electrolyte disturbance |
|
|
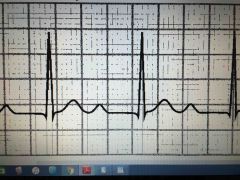
First degree heart block
Prolonged PR interval greater than .20 sec |
|
|
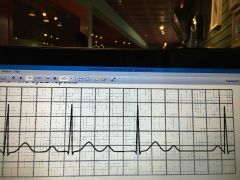
2nd degree heart block type 1 Webcheback Not all atria pulses reach ventricle
P-R interval lengthens until a QRS falls off |
|
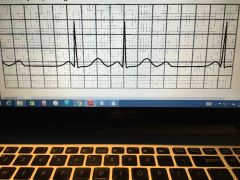
|
2nd degree heart block type 2 Mobitz
Not all atria reach ventricles No prolongation of P-R interval |
|
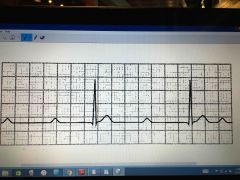
|
Third degree heart block
Atria and ventricles beat independently
No relationship between P and QRS |
|
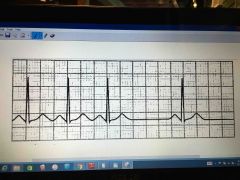
|
Sinus arrhythmia
NSR varies with inspiration
Increase rate with inspiration
Decrease rate with expiration |
|
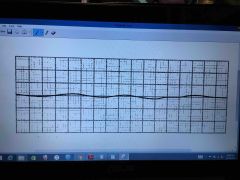
|
Asystole
Flatline
Failure of sinus to produce an impulse |
|
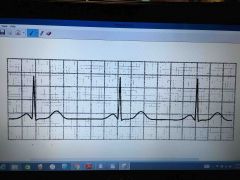
Front (Term) |
Sinus bradycardia
Less than 60 beats per minute |
|
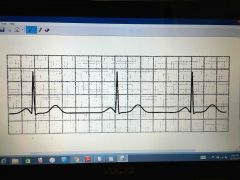
|
Sinus bradycardia
Less than 60 beats per minute |
|
|
|
Sinus tachycardia
More than 100 beats per minute |
|
|
|
Premature atrial contraction (PAC)
P wave appears early or abnormal |
|
|
|
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
Series of rapid beats that begins and ends randomly |
|
|
|
Atrial flutter
Sawtooth pattern |
|
|
|
Atrial fibrillation |
|
|
|
Premature ventricular contraction |
|
|
|
Ventricular tachycardia |
|
|
|
Ventricular fibrillation |
|
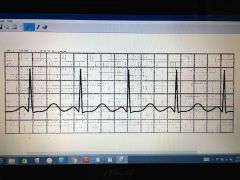
|
Normal sinus rhythm |

