![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is triangular in shape and comprises the anterior aspect of the Left Ventricle? |
Interventricular Septum |
|
|
What is the Interventricular Septum also known as? |
Anterior Left Ventricular Wall |
|
|
What are the 4 parts of the Interventricular Septum? |
|
|
|
What is the Mitral Valve also known as? |
Bicuspid Valve |
|
|
Which Valve has unequally sized leaflets that are thicker than the Tricuspid Valve? |
Mitral Valve (Bicuspid Valve) |
|
|
Name the leaflets of the Mitral Valve. |
Anterior (anteromedial) Posterior (posterolateral) |
|
|
Which Mitral Valve leaflet is the largest? |
Posterior (posterolateral) |
|
|
Which Valve is trapezoidal in shape and is continuous with the fibrous annular skeleton? |
Mitral Valve (Bicuspid Valve) |
|
|
Which Valve is anchored to paired Left Ventricle papillary muscles by the chordae tenidineae? |
Mitral Valve (Bicuspid Valve) |
|
|
What is another word used for tracing? |
Planimetry |
|
|
What is the the normal Left Atrial Pressure? |
2-12 mmHg (10 mmHg -according to Steph) |
|
|
The 2-4 mm overlapping of the leaflets as they close is called the? |
Zona Coapta |
|
|
Which Valve lies at the Aortic Root? |
Aortic Valve |
|
|
Which Valve has 3 equally sized leaflets? |
Aortic Valve |
|
|
Name the 3 equally sized leaflets of the Aortic Valve. |
|
|
|
The walls of the Aortic Root bulge outward adjacent to the the Aortic Cusps forming what? |
Sinuses of Valsalva |
|
|
What protects the Coronary Arteries when the Heart is in Left Ventricular Systole? |
Aortic Valve Leaflets (cusps) |
|
|
Which area of the Heart houses the Coronary Arteries? |
Aortic Root |
|
|
The center of the free edge of each cusp that ensures closure of the Aortic Valve, is called? |
Arantius' Nodule *not seen on an echo |
|
|
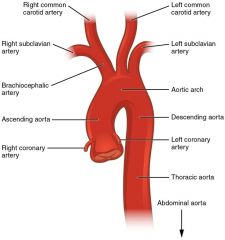
Where does the Ascending Aorta come off from? |
Left Ventricle |
|
|
Name the 3 branches of the Aortic Arch in ascending order. |
|
|
|
Name the 3 areas of the Aorta. |
Asceding Aorta Aortic Arch Descending Aorta |
|
|
Which part of the Heart acts as a reservoir for the potential energy produced by the Left Ventricle to aid in diastolic perfusion? |
Aorta |
|
|
What is the normal diameter range of the Aorta? |
2.5 - 3 cm |
|
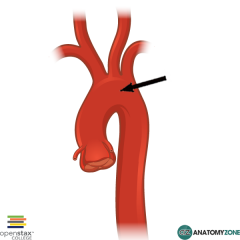
Label the Aorta |
|
|
|
Left and Right Coronary Arteries arise from the _____________________? |
Aortic Sinuses of Valsalva |
|
|
Which artery provides for 90% of the Left Ventricle? |
Left Main Coronary Artery |
|
|
Which Artery is considered the "Widow Maker"? |
Left Main Coronary Artery |
|
|
A blockage in which ARTERY can destroy the Left Ventricle and cause death? |
Left Main Coronary Artery |
|
|
What does the Left Main Coronary Artery branch into? |
Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD) Circumflex Artery (CX) |
|
|
Which branch of the Left Main Coronary Artery extends down the anterior wall to the Left Ventricle Apex via the Anterior Interventricular sulcus (groove)? |
Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD) |
|
|
Which branch of the Left Main Coronary Artery continues laterally in the Atrioventricular groove? |
Circumflex Artery |
|
|
Which artery arises from the superior aspect of the Left Coronary Sinus of Valsalva? |
Left Main Coronary Artery |
|
|
Which ARTERY supplies most of the Left Ventricle? |
Left Coronary Artery |
|
|
What 3 areas of the Heart does the Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD) mainly feed? |
Anterior LV Wall Anterior Septum LV Apex |
|
|
What 2 areas of the Heart does the Circumflex Artery feed? |
Lateral Wall (anterolateral+inferolateral) Posterior Wall |
|
|
Which artery arises form the superior aspect of the Right Coronary Sinus of Valsalva and extends inferomedially following the Atrioventricular groove (sulcus)? |
Right Coronary Artery |
|
|
What 5 areas of the Heart does the Right Coronary Artery supply blood to? |
Inferior Wall Inferior Ventricular Septum RV (RVOT, lateral RV, Anterior RV, Inferior) SA Node AV Node |
|
|
Which ARTERY supplies most of the Right Ventricle? |
Right Coronary Artery |
|
|
Which ARTERY branches into the Posterior Descending Artery (PDA)? |
Right Coronary Artery |
|
|
Which ARTERY supplies blood to the Inferior Left Ventricular Wall and Inferior Interventricular Septum? |
Posterior Descending Artery (PDA) |
|
|
Which ARTERY branches off of the Right Coronary Artery? |
Posterior Descending Artery (PDA) |
|
|
What is the Coronary Sinus also known as? |
Great Coronary Vein |
|
|
True/False: The Left Ventricle is drained mainly by the Great Cardiac Vein. |
TRUE |
|
|
Which VEIN runs parallel to the Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD) joining the Posterior Cardiac Vein? |
Great Cardiac Vein |
|
|
Which 2 veins create the Coronary Sinus? |
Great Cardiac Vein Posterior Cardiac Vein |
|
|
What is the term used to describe... The body/system of names or terms in a particular field; terms referring to a similar subject. |
Nomenclature |
|
|
What are the standardized nomenclature (terminology) for tomographic planes? |
Short axis Vertical long axis (2 chamber) Horizontal long axis (4 chamber) |
|
|
From base to apex, the Left Ventricle is divided into 3 segments, which are? |
Basal (proximal) Mid-cavity (middle) Apical |
|
|
A term used to describe sedentary movement/thickening of a wall segment(s). |
Hypokinetic |
|
|
A term used to describe the loss of movement/thickening of a wall segment(s). |
Akinetic |
|
|
A term used to describe a wall segment(s) of the Heart that does not thicken and is instead pushed away by the opposing wall. |
Dyskinetic |
|
|
What is the AnteroLateral Wall of the LV fed by? |
Cx LAD |
|
|
What is the Apex of the Heart fed by? |
LAD |
|
|
What is the IVS fed by? |
LAD RCA |
|
|
What is the Lateral wall of the RV fed by? |
RCA |
|
|
What is the Anterior RVOT fed by? |
RCA |
|
|
What is the Anterior Septum (anterior LV wall) fed by? |
LAD |
|
|
What is the InferoLateral (Posterior Inferior) LV wall fed by? |
RCA Cx |
|
|
What is the AnteroSeptal LV wall fed by? |
LAD
|
|
|
What is the Anterior LV wall fed by? |
LAD |
|
|
What is the AnteroLateral LV wall fed by? |
LAD Cx |
|
|
What is the InferoLateral LV wall fed by? |
RCA Cx |
|
|
What is the Inferior LV wall fed by? |
PDA |
|
|
What is the InferoSeptal LV wall fed by? |
PDA LAD |
|
|
What is the ONLY Bicuspid Valve in the Heart? |
Mitral Valve |
|
|
The Mitral Valve exists to separate _____________ for the greatest ________________________. |
High Pressure Pressure Gradient (difference) |
|
|
What is the measurement of the Mitral Valve Orifice? |
4 - 6 cm sqd |
|
|
What is the Mitral Valve's normal VELOCITY? |
0.6 - 1.3 m/s |
|
|
What is the BEST METHOD to measure the Mitral Valve area (PSAX)? |
Planimetry |
|
|
True/False: E Wave is always higher than A Wave. |
TRUE |
|
|
Measuring the tips of the Mitral Valve leaflets in PW Doppler gives you the Velocity of which 2 waves? |
E and A
|
|
|
What are the Aortic Valve leaflets named after? |
Coronary Arteries |
|
|
What does the Aortic root house? |
Aortic Valve |
|
|
What is the normal Aortic Root measurement at End Diastole? |
2.0 - 3.7 cm |
|
|
What is the normal ACS? When should it be measured? |
1.5 - 2.6 cm Early Systole |
|
|
What is the normal measurement of the Aortic Valve Orifice? |
> 2 cm sqd |
|
|
What is the normal Doppler measurement of the Aortic Valve? |
1.0 - 1.7 m/s |
|
|
Which area of the Heart does Coarchtation usually occur? |
Below (posterior) the Left Subclavian Coronary Artery in the Descending Aorta. |
|
|
If a patient presents with a Bicuspid Aortic Valve, which view is the BEST view to evaluate it? |
SupraSternal |
|
|
Name the Coronary Arteries in the Aortic Arch. |
BrachialCephalic (Innominate) Artery Common Carotid (Right,Left) Subclavian Artery (Right,Left) |
|
|
Which view do we evaluate for CoArchtation? |
SupraSternal |
|
|
If a patient presents with a Bicuspid Aortic Valve, what should they also be evaluated for? |
CoArchtation |
|
|
What is the closure position called of a Bicuspid Aortic Valve in M-Mode? |
Eccentric Closure (not centered/off axis) |
|
|
What is the RVOT fed by? |
RCA |
|
|
What acts as a reservoir for the potential energy briefly produced by the LV to aid in DIASTOLIC perfusion? |
Aorta (Large pressure gradient) |
|
|
What is considered the HEARTS circulatory system? |
Coronary Circulatory System |
|
|
What feeds the SA node and AV node? |
RCA |
|
|
Which arteries come off of the Left Main Coronary Artery? |
Left Cx and LAD *Left Main Coronary Artery branches into the LCx and LAD |
|
|
Which Coronary Arteries arise from the Sinuses of Valsalva? |
Left Coronary Artery Right Coronary Artery |
|
|
What is the Apex (left) of the LV fed by? |
LAD |
|
|
In which 2 views do we see the Anterior LV wall, which is fed by the LAD. |
2 chamber 3 chamber |
|
|
In which view do we see the Anterior Septum, which is fed by the LAD? |
4 chamber |
|
|
In which view do we see the AnteroLateral LV wall, which is fed by the Cx? |
4 chamber |
|
|
In which view do we see the InferoLateral wall, which is fed by the Cx? |
3 chamber |
|
|
Which artery branches off of the RCA? |
PDA |
|
|
Which artery feeds the Inferior LV wall? |
PDA |
|
|
Which is the ONLY view we see the Inferior LV wall, which is fed by the PDA? |
2 chamber |

