![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood pressure of 140/90 or higher.. stays elevated
|
hypertension
|
|
|
a systolic blood pressure of 120-139, and a diastolic pressure of 80-89
|
prehypertension
|
|
|
for many older adults .... pressure gives the most accurate diagnosis of hypertension
|
systolic
|
|
|
hypertension that has no known cause: also known as essential or idiopathic
|
primary hypertension
|
|
|
hypertension with a known cause
|
secondary hypertension
|
|
|
primary causes of secondary hypertension
|
kidney disease, tumors, abnormal adrenal glands
|
|
|
DASH diet
|
|
|
|
hypertension algorithm
|
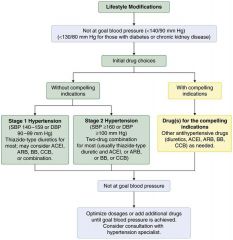
|
|
|
An increase in the diameter of blood vessels, which increases blood flow and lowers blood pressure.
|
vasodilation
|
|
|
Produced or originating from within a cell or organism.
|
endogenous (angiotension 1 and ACE )
|
|
|
Any severe elevation in blood pressure (usually a diastolic pressure greater than 130 mm Hg) with or without damage to internal organs or other structures, e.g., brain, heart, aorta, kidneys.
|
hypertensive emergency
|
|
|
Agents used in hypertensive emergencies include
|
sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerin, labetalol, and enalaprilat.
|
|
|
Hypotension occurring when a person assumes an upright position after getting up from a bed or chair. (systolic drop of 10 or more)
|
orthostatic hypotension
|
|
|
risk of hip fracture increase by .......... for elderly when ....... where started
|
50%...... antihypertensives (falling due to orthostatic hypotension)
|
|
|
Calcium channel blockers (CCB) |
|
|
|
Beta blockers
|
|
|
|
angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor (ACE inhibitor)
|
|
|
|
Angiotensin II receptor antagonist
|
|

