![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
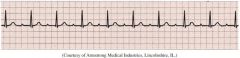
1st Degree AV Block
|
|
|
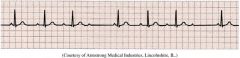
2nd Degree AV Block
Wenchebach Mobitz I PR interval increasing until P wave drops |
|
|
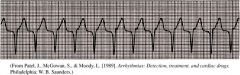
Accelerated Idioventricular
|
|
|
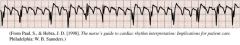
Atrial Flutter with Various Blocks
|
|
|
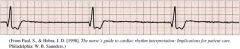
Idioventricular
|
|
|
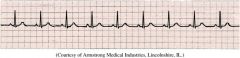
Normal Sinus Rhythm
|
|
|
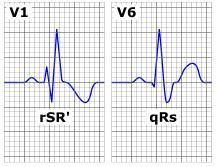
Right Bundle Branch Block
|
|
|
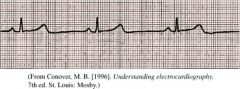
Sinus Bradycardia
|
|
|
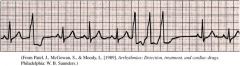
Sinus Rhythm with 1 PVC and 3 runs of Vtach
|
|
|
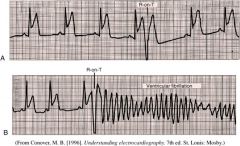
Sinus Rhythm with ST Elevation
|
|
|
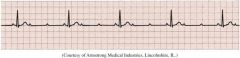
2nd Degree AV Block
Mobitz II PR Interval is constant P wave caused QRS b/c constant PR interval time |
|
|
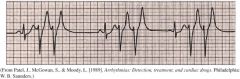
A Fib
|
|
|
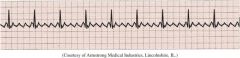
A flutter
|
|
|
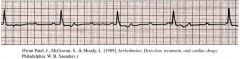
3rd Degree Heart Block
Complete Heart Block P-P same R-R same QRS identical PR interval different |
|
|
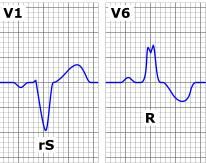
Left Bundle Branch Block
|
|
|
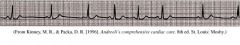
PVC
|
|
|
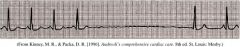
Sinus Arrhythmia
|
|
|
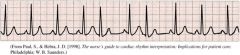
Sinus Pause
|
|
|
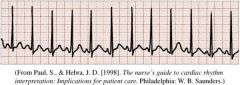
Sinus Rhythm with PAC
Doesn't hemodynamically change you |
|
|
Sinus Tachycardia
|
|
|
Describe lead placement: for a 12 lead EKG:
|
V1 & V2: fourth intercostal space
V3: in between V2 & V4 V4: mid clavicular line, 5th intercostal V5: anterior axillary line, in line with V4 V6: in line with V4 |
|
|
What does the SA node pace at?
|
60-100 beats per minute
|
|
|
What does the Av node pace at?
|
40-60 BPM
|
|
|
What do the ventricles pace at?
|
20-40 BPM
|
|
|
Normal PR interval
|
0.12-0.20 s
|
|
|
Normal QRS Interval
|
0.04 - 0.10 s
|
|
|
ST segment elevation = ?
|
myocardial injury
|
|
|
St segment depression = ?
|
ischemia
|
|
|
T wave represents ?
|
ventricular repolarization
|
|
|
QT interval normal?
|
0.32 - 0.50 s
|
|
|
U waves ?
|
Prominent waves seen in hypokalemia; sometimes seen after T wave
|
|
|
Causes of Bundle Branch Blocks
|
Tumor, dead cells, genetics
|
|
|
Symptoms of Bundle Branch Blocks
|
Bradycardia, syncopy
|
|
|
Which of the BBB has a greater risk of sudden death?
|
Left Bundle Branch Block
|
|
|
Types of temporary pacemakers
|
Transcutaneous: inserted via thoracic chest
Transvenous: placed via catheter Epicardial: outside of heart |
|
|
Indications for permanent pacemaker
|
Complete heart block
Symptomatic bradycardia Wolfe-Parkinson-White Syndrome |

