![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
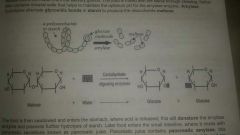
Carb Digestion:Mouth |
●Saliva enters mouth from the salivary glands ●Food is mixed with the saliva through chewing ●saliva contains mineral salts which help to maintain the optimum pH for amylase enzyme ●●Amylase hydrolyses alternate glycosidic bonds in starch to produce the disaccharide maltose |
|
|
|
Carb Digestion:Stomach |
●food enters stomach ●acid is released ●this will denature amylase enzyme to prevent further hydrolysis of starch |
|
|
|
Carb Digestion:Small Intestine |
●food enters small intestine ●mixes with pancreatic juice which contains pancreatic amylase ●this continues hydrolysis of any remaining starch into maltose ●Alkaline salts are present in bile and are released by the walls of the small intestine,help to neutralise acidic contents from stomach and maintain a neutral optimum pH for amylase enzyme ●muscle contractions in the walls of the S.Intestine result in peristalsis, causes food to be pushed along by *rhythmic contraction of muscle in wall can also happen In Oesophagus) |
|
|
|
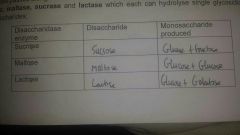
Production of monosaccharides in carb digestion |
As food passes along S.Intestine it encounters 3 diff membrane bound disaccharide enzyme MALTASE,SUCRASE & LACTASE which each can hydrolyse single glycoside bonds to produce Monosaccharides |
|

