![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Name 6 functions of the Integumentary system
|
1) chemical barrier
2) physical barrier 3) temperature regulation 4) sensory 5) metabolic 6) excretion |
|
|
|
Three layers of canine skin
|
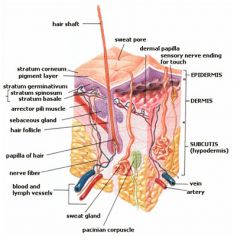
Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis
|
|
|
|
Name 4 cell types of the epidermis and give their purpose
|
1)keratinocytes- make keratin for waterproofing
2)melanocytes- melanin for UV 3) Langerhans cells- help fight invading microorganisms 4) Merkel cells- involved in sense of touch |
|
|
|
Name the 5 layers of Epidermis in dogs
|
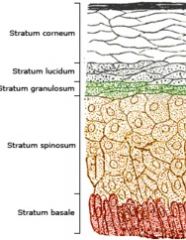
1) Stratum basale
2) Stratum spinosum 3) Stratum granulosum 4) Stratum lucidum 5) Stratum corneum |
"Cher Likes Getting Skin Botoxed" (from superficial to deep)
|
|
|
Which epidermal layer is not found on most of the canine body, and where is it found?
|
Stratum lucidum, found only in thick and hairless skin, such as paw pads.
|
|
|
|
In which stratum do you find Langerhans cells?
|
St. spinosum
|
|
|
|
Which epidermal layer helps prevent deydration?
|
Stratum granulosum
|
|
|
|
Which epidermal layer consists mostly of dead cells?
|
Stratum corneum
|
|
|
|
Which epidermal layer is the home of dividing cells?
|
Stratum basale
|
|
|
|
In which epidermal layers do you find melanocytes?
|
Throughout epidermis
|
|
|
|
What sort of tissue makes up the dermal layer?
|
Connective tissue
|
|
|
|
What are the layers of the dermis?
|
1) papillary- loose connective tissue
2) reticular- dense connective tissue |
|
|
|
The papillary layer is ______ to the epidermis
|
deep to the epidermis
|
|
|
|
The reticular layer is _______ to the papillary layer.
|
deep to the papillary
|
|
|
|
The Hypodermis is also known as
|
Subcutis/ subcutaneous layer/ superficial fascia
|
|
|
|
Name 5 functions of the hypodermis:
|
1) anchors skin to underlying structures
2) Allows skin to slide relatively freely over structures 3) Absorbs shock 4) Insulates 5) Contains Pacinian corpuscles (sensitive to heavier touch) |
|
|
|
Name 4 things that make up the integumentary system
|
skin, hair, nails, glands
|
|
|
|
Which layer anchors skin to underlying structures:
a) epidermis b) dermis c) hypodermis? |
C) hypodermis
|
|
|
|
Which layer contains oil glands and sweat glands?
a) epidermis b) dermis c) hypodermis? |
B) Dermis
|
|
|
|
Which layer absorbs shock and insulates?
a) epidermis b) dermis c) hypodermis? |
c) hypodermis
|
|
|
|
Which layer protects from UV damage?
a) epidermis b) dermis c) hypodermis? |
a) epidermis
|
|
|
|
Which layer contains Pacinian corpuscles?
a) epidermis b) dermis c) hypodermis? |
C) hypodermis
|
|
|
|
Paw pads have how many epidermal layers, and which is the thickest
|
have all 5 epidermal layers, stratum corneum is thickest
|
|
|
|
Paw pads are made up of:
|
insulating fat and connective tissue
|
|
|
|
Where do you find exocrine sweat glands in a dog?
|
paw pads only
|
|
|
|
Which three epidermal layers are found in the Planum Nasale?
|
Str. basale, spinosum, corneum
|
|
|
|
The skin of the Planum Nasale contains no _____
|
glands (also no str. granulosum, or lucidum)
|
|
|
|
Name four types of glands in the dog.
|
1) Sudoriferous (sweat)
2) tail 3) anal 4) sebaceous |
|
|
|
Sebaceous glands are found everywhere but ____
|
on the paw pads
|
|
|
|
Anal glands are normally expressed during ______
|
defecation (or when the dog runs into a plate glass door)
|
|
|
|
Most sebaceous glands have a single gland that empties into ____
|
a hair follicle
|
|
|
|
Name three uses for claws.
|
Predatory/ protective
digging traction/ movement |
|
|
|
Describe the three types of animal hair.
|
1) primary- guard hairs (one in a compound follicle)
2) secondary- several (up to 15 in one follicle) 3) tactile/sinus- surrounded by venous cavity, sensory nerves |
|
|
|
Where do you find tactile/ sinus hairs?
|
found on sides of muzzle and over eyes.
|
|
|
|
Describe a double coat.
|
Long primary hair w/ shorter undercoat
|
|
|
|
Name 5 subtypes of double coat and name a breed that has it.
|
1) Corded- puli, commodor
2) Long- poodle, afgan 3) Broken- terrier 4) Medium- cockers, setters, corgis 5) Curly- port water dogs, irish springer spaniels |
|
|
|
Describe a single coat and name a breed that has it.
|
has just a primary hair, no undercoat, greyhound, dobie, maltese, great dane, papillion
|
|
|
|
What metabolic functions are performed by the skin?
|
stores nutrients, synthesizes Vitamin D
|
|
|
|
What substances are excreted through the integumentary system?
|
sweat, water, salt, organic waste
|
|
|
|
Name 5 benefits of massage on the integumentary system.
|
1) transmits psychological benefits of touch
2) oils (used on furless areas) can protect and nourish skin 3) Increased circulation helps to maintain healthy skin 4) Helps remove dry scaly skin 5) Reduces excessive scar tissue |
|
|
|
How does massage stimulate vasomotor activity in skin?
|
by creating increased circulation and heat
|
|
|
|
What is one benefit of increased circulation in the skin?
|
bringing additional nutrition
|
|
|
|
Stimulating the sudiferous glands would cause increased _________.
|
Insensible perspiration
|
|
|
|
hyperemic
|
reddish pink
|
|
|
|
Stimulated sebaceous glands produce _____.
This helps improve: |
sebum
improves skin's condition, texture and tone |
|
|
|
How does skin help regulate temperature?
|
sweat glands eliminate excess body heat.
|
|
|
|
Tail glands are most active during _________ and _______.
|
Puberty and estrus
|
|
|
|
Tail glands are used for:
|
scent marking and ID
|
|

