![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is electrolysis?
|
Electrolysis is the breaking down of a substance using electricity. |
|
|
Describe electrolysis. |
1) Electric current is passed through a molten or dissolved ionic compound, causing it to decompose. 2) This creates a flow of charge through the electrolyte. 3) The positive ions move towards the cathode and gain electrons. 4) The negative ions move towards the anode and lose electrons. 5) As ions gain or lose electrons they become atoms or molecules and are discharged from the solution at the electrodes. |
|
|
What is there in aqueous solutions as well as the ions from the solute? |
Hydrogen ions (H+) Hydroxide ions (OH-) |
|
|
When would hydrogen and oxygen ions be discharged in electrolysis as opposed to the ions in the solute? |
Sometimes it's easier to discharge the ions from the water instead of the ones from the solute.
|
|
|
Which is produced at the cathode/ anode out of: >Hydrogen >Oxygen |
Cathode= hydrogen Anode= oxygen |
|
|
What are the equations at the cathode/ anode in the electrolysis of: 1) Sulfuric Acid (aq) (H2SO4) 2) Sodium Hydroxide (aq) (NaOH) 3) Copper (II) Sulfate (aq) |
Sulfuric Acid Cathode: 2H+ + 2e- --> H2 Anode: 4OH- - 4e- --> O2 + 2H2O Sodium Hydroxide Cathode: 2H+ + 2e- --> H2 Anode: 4OH- - 4e- --> O2 + 2H2O Copper (II) Sulfate Cathode: Cu2+ + 2e- --> Cu Anode: 4OH- - 4e- --> O2 + 2H2O |
|
|
Why are the copper ions discharged at the cathode in the electrolysis of copper (II) sulfate and not the hydrogen ions from the solution? |
Because it's easier for the copper ions to discharge from the solution than the H+ ions. |
|
|
How can you increase the amount of product made during electrolysis? |
> increasing the time > increasing the current |
|
|
What is the equation lining amount of product made during electrolysis, current and time? |
Amount of charge= current x time Q= It |
|
|
Why can't an ionic solid be electrolysed? |
Because the ions are in a fixed position. |
|
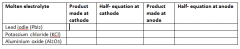
Complete this table. |
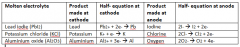
|
|
|
What is the symbol equation for the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen?
|
2H2O + O2 --> 2H2O |
|
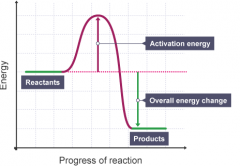
Does this energy level diagram show an exothermic or endothermic reaction? |
Exothermic, because the loss of energy when bonds are made shows more energy was given out so it is exothermic i.e. when hydrogen reacts with oxygen. |
|
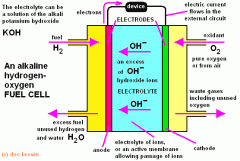
Describe the electrolysis of hydrogen and oxygen to produce water and heat. |
1) Hydrogen goes into the anode compartment and oxygen goes into the cathode compartment. 2) At the cathode, oxygen gains electrons and reacts with water (from the electrolyte) to make OH- ions. 3) O2 + 4e- + 2H2O --> 4OH- 4)These move in the electrolyte to the anode where they combine with the hydrogen to produce water and electrons. 5) 2H2 + 4OH- --> 4H2O + 4e- 6) The electrons flow through an external circuit from the anode to the cathode- this is the electrical current. |
|
|
What are the advantages to Hydrogen- Oxygen fuel cells? |
Advantages - much more efficient - direct energy transfer (no turbines, generators) - fewer places for energy to be lost as heat - no moving parts so energy isn't lost as friction - no pollution |
|
|
What are the two ways pollution is still made when using hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells? |
1) Producing the hydrogen requires a lot of energy which comes from burning non-renewable fossil fuels- which causes pollution. 2) They often contain a poisonous catalyst which, to be disposed of, takes a lot of time, money and may cause environmental problems. |
|
|
Why are hydrogen- oxygen fuel cells used in spacecraft? |
- they provide water that can be used by astronauts - lightweight -compact - no moving parts |
|
|
Why are hydrogen- oxygen fuel cells used in the car industry? |
- no carbon dioxide emissions from the car - fossil fuels such as petrol are non-renewable - large source of hydrogen is available by decomposing water. |
|
|
What is a REDOX reaction? |
Reduction and Oxidation can happen at the same time- this is a REDOX reaction. |
|
|
What is the difference between an oxidising agent and a reducing agent?
|
An oxidising agent accepts electrons and gets reduced. A reducing agent donates electrons and gets oxidised. |
|
|
What does OIL RIG stand for? |
Oxidation Is Loss Reduction Is Gain (Of electrons) |
|
|
What is the word equation for rusting?
|
iron + water + oxygen --> hydrated iron (III) oxide |
|
|
What methods can be used to prevent rusting? |
> alloys > oil, grease and paint > tin plating > sacrificial method (galvanising) - a coat of zinc is put onto the object- it's more reactive so will lose electrons in preference to the iron. |
|
|
What is the problem with tin plating?
|
If there is a scratch, the iron will rust even faster than on its own. |
|
|
What are displacement reactions? |
Displacement reactions are also REDOX reactions. They involve a more reactive metal displacing a less reactive metal from its compound. |
|
|
What is the functional group for an alcohol and what do they always end in? |
Alcohols have an '-OH' functional group and end in 'ol'. |
|
|
What is the general formula of an alcohol? |
CnH2n+1OH |
|
|
What is fermentation and what is the word/ symbol equation? |
Fermentation is the process of converting sugars (usually a glucose solution) into ethanol, with the reaction being bought about by enzymes in yeast: glucose --> ethanol + carbon dioxide C6H12O6 --> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 |
|
|
Why does the temperature in a fermentation reaction need to be controlled and what is the optimum temperature? |
Because it is controlled by enzymes: too cold and the yeast is too inactive and the reaction's really slow- but too hot and the enzymes denature. The optimum temperature is between 25°C and 50°C. |
|
|
Why must oxygen be prevented from getting at the alcohol during fermentation? |
Because it converts the ethanol into ethanoic acid (vinegar). |
|
|
How is pure ethanol extracted once the fermentation reaction stops. |
It can be distilled using fractional distillation to give pure ethanol. |
|
|
What is the symbol/ word equation for the hydration of ethene and how is this reaction sped up. |
ethene + water (steam) --> ethanol C2H4 + H2O --> C2H5OH To speed this up, the ethene and steam are passed over a heated phospheric acid catalyst. |
|
|
Compare fermentation and hydration in terms of: 1) Manufacture 2) Sustainability 3) Purity 4) Atom economy 5) Percentage yield |
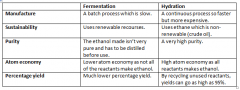
|
|
|
Why were CFC's originally thought to be great? |
They are non-toxic, non- flammable and chemically inert (unreactive). |
|
|
How are free radicals made? |
By evenly breaking covalent bonds so each atom gets one of the shared electrons e.g. H-H --> H. + H. The H. is a free radical ( the unpaired electron is shown by a dot). The unpaired electron makes the free radical very reactive. |
|
|
How do CFC's deplete the ozone layer? |
1) CFC molecules are broken down by the stratosphere by UV light to give highly reactive free radicals: CCl2F2 --> CCLF2. + Cl. 2) Chlorine free radicals react with ozone to form ordinary oxygen and chlorine oxide: O3 + Cl. --> O2 + ClO. 3) The chlorine oxide molecule is very reactive and reacts with ozone to make two oxygen molecules and another Cl. free radical: ClO. + O3 --> 2O2 + Cl. |
|
|
Why do CFC's stay in the atmosphere a long time? |
The chlorine atoms aren't used up, so they stay in the stratosphere for ages and carry on breaking down ozone. |
|
|
Why are CFC's so dangerous? |
Ozone absorbs UV light from the Sun. CFC's reducing the amount of ozone in the stratosphere results in more UV light reaching us. This causes medical problems like increased risk of sunburn and skin cancer. |
|
|
What can CFC's be replaced with? |
Alkanes or hydrofluorocarbons (HCFs) that provide a safe alternative and will not damage the ozone layer. |
|
|
What will hard water form with soap instead of a lather? |
It will form limescale (calcium carbonate) instead which can eventually block the pipes. |
|
|
What is the origin of hard water? |
The origin of water hardness is from when water flows over rocks and through soils containing calcium and magnesium compounds that dissolve in the water. |
|
|
Which of the following substances do dissolve in water: 1) Magnesium sulfate 2) Calcium sulfate 3) Calcium carbonate |
1) Magnesium sulfate and calcium sulfate dissolve in water. 2) Calcium carbonate doesn't dissolve in water. |
|
|
How is rainwater slightly acidic? |
Calcium carbonate exists as limestone, chalk or marble. It doesn't dissolve in water but it will react with acids. And since CO2 from the air dissolves in rainwater forming carbonic acids, rainwater is slightly acidic. So that means: carbon dioxide + water + calcium carbonate --> calcium hydrogencarbonate |
|
|
What is temporary and permanent hardness caused by?
|
Temporary- caused by the hydrogencarbonate ion, HCO3- in Ca(HCO3) Permanent- caused by dissolved calcium sulfate. |
|
|
Describe how boiling removes temporary hardness and state why it doesn't work for permanent hardness. |
The heating of calcium hydrogencarbonate forms insoluble calcium carbonate (limescale), water and carbon dioxide. Ca(HCO3)2 (aq) --> CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) This won't work for permanent hardness though, as heating a sulfate ion does nothing. |
|
|
How does washing soda (sodium carbonate) remove both temporary and permanent hardness? |
The carbonate in washing soda (sodium carbonate, Na2CO3) joins onto the calcium ions and makes an insoluble precipitate of calcium carbonate. This works whether the hardness is due to calcium sulfate or calcium hydrogencarbonate. Ca2+ (aq) + CO3 2- (aq) --> CaCO3 (s) |
|
|
Describe how both types of hardness can be removed by an 'ion exchange resin'. |
An 'ion exchange resin' has lots of sodium or hydrogen ions and 'exchanges them for calcium or magnesium ions. |
|
|
Describe what you have to react together to get an ester and use fats and oils as an example. |
To get an ester you have to react an acid with an alcohol. Fats and oils are esters; they are produced when an alcohol called glycerol reacts with fatty acids. |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats and oils? |
Saturated fats and oils contain only single bonds. Unsaturated contain at least one C=C double bond in their carbon chains. In general, saturated fats are less healthy as they increase cholesterol in the blood. |
|
|
What is the difference between monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats? |
Monounsaturated fats contain one C=C double bond. Polyunsaturated fats contain more than one C=C double bond. |
|
|
Describe how you can use bromine water to test for saturated/ unsaturated fats and oils. |
An unsaturated compound will decolourise bromine water. An addition reaction takes place at the double bond and a colourless dibromo compound is formed. Saturated compounds don't have double bonds so the bromine water stays orange. |
|
|
Describe hydrogenation. |
1) Unsaturated oils are liquid at room temperature. 2) They can be hardened by reacting them wit hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst at around 60°C. This is called hydrogenation. The hydrogen reacts with the double- bonded carbons and opens out the double bonds. 3) Margarine is made from partially hydrogenated vegetable oil which gives it a good, spreadable consistency. |
|
|
What is an emulsion? |
1) Oils and water don't mix- they're immiscible. 2) However, you can mix immiscible liquids like these two to make an emulsion. You have to shake vigorously. They'll break up the oil into very small droplets which disperse through the water. |
|
|
Give an example of an oil-in-water emulsion and a water-in-oil emulsion. |
> Milk is an oil-in-water emulsion (there's less oil than water). > Butter is a water-in-oil emulsion (there's less water than oil). |
|
|
Describe saponification. |
1) Saponification is the process of reacting a fat with an alkali to produce soap and glycerol. 3) The chemical reaction first breaks up the fat and oil to release glycerol and fatty acids. This is called hydrolysis (breaking up with water). Then the fatty acids react with NaOH to make soap. fat + sodium hydroxide --> soap + glycerol |
|
|
Describe a detergent molecule. |
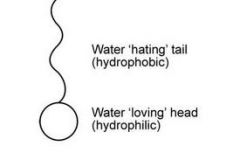
|
|
|
Describe dry cleaning. |
> Dry cleaning uses solvents instead of water. > These solvents are much better than detergents at removing oil and greases and will clean stains that won't dissolve in water. > This is because the solvent can completely dissolve the oil and grease removing the stains. |
|
|
Why is it beneficial to wash clothes at a lower temperature? |
1) Biological detergents contain enzymes which are biological catalysts. They help break down some large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules which can be removed. 2) Most enzymes work best at lower temperatures so biological detergents mean you can do your washing at lower temperatures which saves energy and money. 3) At high temperatures, the enzymes are denatured. 4) Washing at cooler temperatures also means you can wash more delicate clothing. |

