![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atoms cannot... |
Be created or destroyed. |
|
|
All atoms of an element are... |
Identical. |
|
|
All Matter is made from... |
Atoms. |
|
|
Different elements contain... |
Different types of atoms. |
|
|
Define atom. |
The smallest particle of a chemical element that can exist. |
|
|
Describe the structure of an atom. |
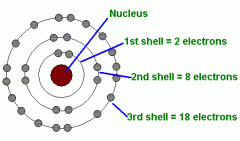
|
|
|
Name the particles in an atom. |
Proton, Neutron, Electron. |
|
|
A term that includes both protons and neutrons is... |
Sub-Atomic particles. |
|
|
What are the charges and relative masses of these particles? |
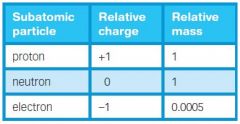
E= 1/1840 |
|
|
How do you calculate the number of electrons? |
Number of protons=Number of Electrons=Atomic Number |
|
|
What is the mass number? |
Number of protons+ Number of Nuetrons |
|
|
Protons are _________ charged sub-atomic particles, found in the ______(_______) of an atom. |
Positively, Centre (Nucleus). |
|
|
Electrons are __________ charged. |
Negatively. |
|
|
They orbit around the _______ of an atom. |
Nucleus. |
|
|
Neutrons are _______, they are neither positively nor negatively charged. |
Neutral. |
|
|
Where are Neutrons found? |
In the nucleus of an atom. |
|
|
What are the 8 things we can use to create a profile for an atom? |
Name, Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, Protons, Electrons, Neutrons, Electron Arrangement and a dot n cross diagram. |
|
|
What do the numbers on an Element in the periodic table mean? |
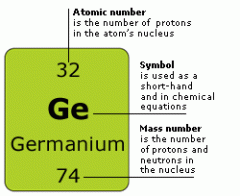
|
|
|
Group= |
Last Number of Electron Arrangement |
|
|
Period= |
Number of shells. |
|
|
Define Ion. |
An Ion is an atom, or group of atoms, that has gained or lost electrons and become electrically charged. |
|
|
Define Isotopes. |
Atoms with added neutrons. |
|
|
Define Ionic Bonding. |
Ionic bonding is the complete transfer of electrons between atoms. It is a type of chemical bond that creates 2 oppositely charged ions. Metal becomes positive by giving away. Non-Metal accepts these electrons and becomes negatively charged. |
|
|
What does Ionic bonding happen between? |
Metals and Non-Metals. |
|
|
Recall a diagram that shows ionic bonding. |
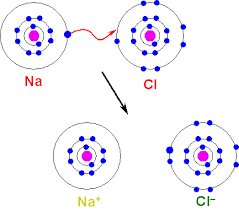
Na => Na+ Cl=> Cl- ADD SQ. BRACKETS AROUND THE IONS. DRAW Na AS CROSSES. |
|
|
Losing Electrons... Gaining Electrons... |
Becomes Positive. (---=+) Becomes Negative. (+-=-) |
|
|
To quickly calculate the number of atoms required in a compound for the charges to cancel each other out,... |
Swap the (small) top numbers and the make them into (small) bottom numbers |
|
|
What does Iron (III) mean? |
Fe +3 |
|
|
Atoms aim to... |
have their outermost shell filled. |
|
|
Define Covalent bonding. |
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. This creates a stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces. |
|
|
What elements does Covalent bonding happen between? |
Non-Metals and other Non-Metals. |
|
|
What does not need to be shown in diagrams of covalent bonding? |
The inner shells as they never change. Only the outermost shell needs to be shown.W |
|
|
What is an alternative way to show Covalent Bonding? |
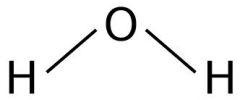
And/or dot n cross diagrams. |
|
|
What if there are several pairs of shared electrons? |

|
|
|
Recall the diagram for Ethane |
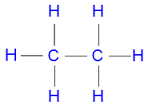
C2H6 |
|
|
When a covalent substance boils, are the covalent bonds broken? |
Nope. |
|
|
What forces are disrupted when a covalent substance boils? |
Intermolecular forces. |
|
|
What Word can be used to describe these forces? |
Weak. |
|
|
What does this mean? |
It doesn't take a lot of energy to disrupt them. |
|
|
Covalent compound generally have ___ boiling and melting points. |
Low. |
|
|
When an ionic substance melts or boils the strong _____________ attractions between ions have to be broken. |
Electrostatic. |
|
|
This takes quite a lot of energy, so ionic compounds generally have ____ melting and boiling points. |
High. |
|
|
Which type of compound conducts electricity when molten? |
Ionic. |
|
|
Why do Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten? |
Because the ions are free to move. |
|
|
Which type of compound dissolves easiest in water? |
Ionic. |
|
|
Atomic Number= |
Number of Protons. |
|
|
Isotopes are... |
Varieties of an element which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. |
|
|
The mass number is always... |
Th bigger number. |
|
|
No 2 elements share the same... |
Atomic Number. |
|
|
Recall the diagram for Ionic Lattice. Why is it called a giant Ionic Lattice? |
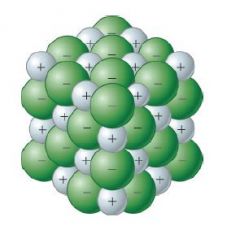
It is called a lattice because it is organised in a regular repetitive way. It is sometimes called giant because it is repeated many times. |

