![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Apolipoproteins on the surface of lipoproteins serve as ligands for _____ ______.
|
cellular receptors. (zip code)
|
|
|
Chylomicron remnants have apo-__, marking them for the LPR receptor in the _____.
LDL have apo-___, which b/ to the LDL receptor in ____ and ____ _____. HDL have apo-___ and apo-____, which b/ to the SRB1 receptor in _____ and mediates ______ cholesterol transport. |
ApoE, liver
ApoB-100, liver & peripheral tiss Apo AI and Apo AII; liver, reverse |
|
|
What plays a role in all 3 stages of lipoprotein metabolism?
Describe Stages 1, 2, and 3. |
Liver.
Chylomicrons collect the FFA and cholesterol esters that have been absorbed into the intestinal cells; LPL removed the FFA, and the remnants are recycled through the liver. Liver --> VLDL --<LPL>--> LDL --> LDL receptor on peripheral cells --> stored as TriG ABCA1 interacts w/HDL which gets the FAs onto it and goes back to the liver w/ receptor SRB-1 |
|
|
What stimulates/inhibits lipolysis by Hormone sensitive lipase (HSL)?
|
glucagon, corticosteroids, ACTH, catecholamines = stim
Insulin = Inhibit |
|
|
What are the two sources of LDL cholesterol? Which is the main one?
Do genetics play a major role in LDL lvls in plasma? What effects does a decrease in cellular cholesterol have on homeostasis in hepatic cells? (2) |
Major: endogenous synth in the liver; minor: diet
Yes. upregs HMG-CoA reductase upregs LDL receptor |
|
|
Each 1% increase in total cholesterol lvl is associated w/ a __% increase in CHD risk.
|
2%
|
|
|
We have never had an epidemic like this that we have been able to track so thoroughly and see. As I told you, this is conservative.
About 60 million adults, or __ percent of the adult population, are now obese, which represents a ____ of the rate since 1980. |
30, doubling.
|
|
|
Why do high lvls of LDL increase atherosclerosis? (3)
|
LDL becomes oxidized and this induces an inflammatory response in the vessel wall
Oxidized LDL is ingested by macrophages that form foam cells Death of foam cells create a lipid-rich core in complex atherosclerotic plaques |
|
|
Stable atherosclerotic plaque characteristics? Vunerable? Which clinical manifestations are they associated with?
|
thick fibrous cap with smaller lipid core --> stable angina
thin or digested fibrous cap = prone to eruption --> unstable angina & MI |
|
|
There are 5 drugs classes and one non-drug way to tx lipid dz. Name 'em.
True or False: Lowering LDL may slow progression, stabilize or reverse atherosclerosis Lowering LDL improves endothelial cell function and reduces inflammation in the vessel wall Lowering LDL reduces myocardial infarction and death |
Therapeutic lifestyle change (TLC)
Class 1: statins Class 2: bile acid-binding resins Class 3: cholesterol absorption inhibitor Class 4: niacin Class 5: fibric acid all are true. |
|

Fill it in, foo'.
|
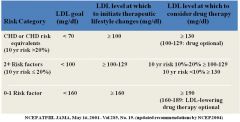
|
|
|
What are the features of the TLC diet?
How effective is diet therapy? |
Sat fat <7% of total calories
cholestrol <200mg/day increased viscous fiber and plant stanols/sterols weight management increased physical activity moderately... may only be effective in 5 to 10% of pts. |
|
|
All statins (class 1 drug therapy) target ______.
Do they have additional activities? Atorvastatin (Lipitor) and Simbastatin (Zocor) are newer drugs that are ____ effective than the older formulations like fluvastatin. Are statins effective at reducing risk of MI and death in pts with normal cholesterol lvls? Elevated cholesterol lvls? Known CAD? No CAD? |
HMG-CoA reductase
Yes, they do. more. All categories, yes. |
|
|
What does HMG-CoA reductase usually do? How do statins interfere?
What is their ultimate effect? do they also lower HDL and TriG? |
reduces Acetate --> cholesterol (in the liver)
- it is the rate limiting enzyme! They act as competitive inhibitors decrease LDL in blood by 20-55% by lowering cholesterol synth and increasing # of LDL receptors in the liver. Yes. |
|
|
What are some side effects of statins? Treatment?
Relative contraindications? Absolute contraindications? |
mild elevations in liver enzymes (transaminases)
- if they get to 3x normal, discontinue statins. Rhabdomyolysis presenting as muscle pain or weakness w/ elevated CPK lvls (2x upper limit of normal) - use co-enzyme Q10 concurrent use of certain drugs (cyclosporings, macrolide antibiotics, anti-fungals, cytoP-450 inhibitors) active or chronic liver dz |
|
|
What class of drugs are cholestyramine, colestipol, and colesevelam?
How do they work? |
Class 2: bile-acid binding resins.
b/ negatively charged bile acids in the intestine, preventing reabsorption... liver makes more by converting cholesterol --> cycle continues. also increase LDL receptors in liver which reduce LDL blood lvls. |
|
|
Bile Acid Binding resins:
- side effects? - relative contra? - absolute? |
constipation, bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea
may interfere w/ absorption of fat soluble Vits. may interfere w/ abs of meds such as digitalis, thiasizes, warafarin, aspirin TriG > 200 dysbetalipoproteinemia TriG > 400 |
|
|
Class 3: Cholesterol absorption inhibitors
- example - mechanism - upsides to the class? - response? - have they been shown to prevent HD or heart attacks? |
Ezetimibe (Zetia)
localizes on intestinal brush border; targets the nieman-pick C1-like protein that is critical for cholesterol absorption no effect on vitamin abs, long half life moderate response (15-20% LDL decrease w/ v.small HDL increase and TriG decrease) No, not as a single agent - remember, most cholesterol comes from liver synth. |
|
|
Class 4: Nicotinic acid (Niacin)
- what is is? - major effect? - mech? - effect? - side effects? - relative contra? - absolute contra? |
- water soluble B-vitamin
- most effective agent available for raising HDL - reduces VLDL generation and actv LPL; also b/ liver uptake of HDL molecules - 15-35% increase in HDL, moderate decreases in LDL and TriG - flushing, upper GI distress, peptic ulcers, nausea, indigestion, diarrhea, hepatoxicity, hyperglycemia, gout - diabetes, peptic ulcer - chronic liver dz, severe gout |
|
|
Difference b/t Niacin and Niaspan?
|
Niaspan is a programmed release formula with once a day bedtime dosing
- less flushing - better tolerance |
|
|
Gemfibriozil (Lopid)
- class? - primary purpose? - side effects? - absolute contraindications? |
- class 5: fibric acid derivitives
- most powerful serum TriG reducers - nausea and gallstones - severe renal dz, severe hepatic dz |
|
|
Fenofibrate (Tricor)
- class? - primary purpose? - only indicated for which pts? |
- Fibric acid derivitives
- most powerful at reducing serum TriGs - v.high TriG lvls at risk for pancreatitis |

