![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fungi:
Eukaryotic cells Cell wall contains chitin and ______ |
glucan
|
|
|
Fungi:
Cell membrane contains _______ instead of cholesterol as in mammals |
ergosterol
|
|
|
Endemic dimorphic fungi in US
(3) |
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Coccidioides immitis Histoplasma capsulatum |
|
|
Opportunistic fungi (4)
|
Candida sp
Aspergillus sp Mucor sp. Pneumoncystis jiroveci |
|
|
Dimorphic
Exist in 2 morphologically different forms: 1)? multicellular, thread-like hyphae found in environment (free-living phase) 2)? single cell form found in tissues (parasitic phase) |
1)Molds-
2)Yeasts- |
|
|
Histoplasma
Blastomyces Paracoccidioides Coccidioides Penicillium |
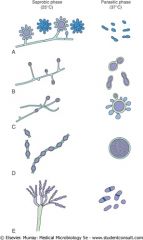
Mold and yeast forms:
A, B, C, D, E? |
|
|
What Fungus?
Soil organism Growth in soil enhanced by bird or bat guano (poop) Specific types of environments Caves Chicken coops Old buildings |
Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
|
Histoplasma capsulatum Endemic in parts of the central and eastern United States along _____________ river valleys.
|
Ohio and Mississippi
Microfoci in Central and South America, Africa, India, and Southeast Asia. |
|
|
Histoplasma capsulatum:
Microconidia are inhaled Transform into ______ |
yeasts
|
|
|
Histoplasma capsulatum:
Phagocytosed by macrophages but are not killed Killing of intracellular yeast depends on Th1 cell activation of ________ through release of g-IFN By this time, organisms have spread widely in lung |
macrophages
|
|
|
Histoplasma capsulatum:
_________ form around infected macrophages Later they calcify (can see this on CXR) Organisms remain viable in granulomas for years Can be reactivated if person becomes immune suppressed |
Granulomas
|
|
|
Histoplama:
_____% of population living in endemic areas are skin-test positive. |
80
|
|
|
miliary
|
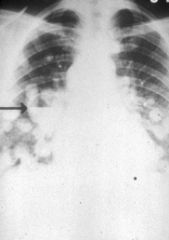
Chest radiograph showing
__________ densities in both lung fields plus thin-walled cavity with fluid level. Histoplasmosis. |
|
|
Diagnosis of histo
|
Culture of sputum or lung tissue
Histologic examination of biopsied lung tissue shows yeast within macrophages |
|
|
Treatment of histo
|
Severe infections- amphotericin B
Mild to moderate infections- itraconazole |
|
|
What fungus?
Soil organism Found in decaying leaf litter Found in southern and mid-western US Infection follows inhalation of conidia |
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Blastomycosis |
|
|
Organism can enter blood and go to skin to form lesions
Blastomycosis |

?
|
|
|
Diagnosis of Blastomycosis
|
Histopathology
See budding yeast cells Serology |
|
|
Treatment of Blastomycosis
|
AmphoB or an azole for more mild disease
|
|
|
What fungus?
Found in lower Sonoran life zone is semi arid regions of southwest US Probably associated with burrows of desert animals Grows rapidly following rain; drought and windy conditions spread organism large distances |
Coccidioides immitis
Coccidioidomycosis |
|
|
The ecological niche of C. immitis is the Sonoran desert, which includes the deserts of the _________ and northern Mexico (figure 18). It is also found in small foci in Central and South America.
|
Southwest (California, Arizona, New Mexico and Texas)
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of Coccidioidomycosis:
Inhalation of arthroconidia directly into ______ |
alveoli
|
|
|
arthroconidio
|
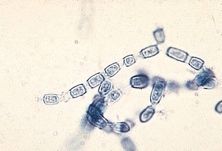
what part of Coccidioidomycosis?
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of Coccidioidomycosis:
arthroconidia transform into a spherule containing _______ |
endospores
|
|
|
spherule containing endospores.
Endospores can be released and travel through the body leading to extrapulmonary disease |
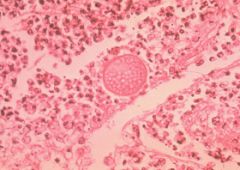
Describe this Coccidioidomycosis picture
|
|
|
Coccidioidomycosis
AKA ____ fever |
Valley
|
|
|
Diagnosis of Coccidioidomycosis
|
Culture of fluid from any involved site
Will grow on many media in few days Serology- see notes page Histopathology See spherules |
|
|
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis
|
Long term treatment required with Ampho B for severe disease or an azole for mild to moderate disease
|
|
|
Candida _______ is responsible for most infections
|
albicans
|
|
|
Causes of Candida infection in certain situations
|
T cell immune suppression
Antibiotic therapy Insertion of catheter Neutropenia |
|
|
Disease associations of infection with Candida
|
Thrush
Vaginal yeast infections Esophagitis Candidemia Pneumonia Hepatospenic candidiasis |
|
|
Diagnosis of Candida infection
|
Culture of blood or biopsied lung tissue
Blood agar or Sabouraud’s agar |
|
|
Most common species causing human disease: Aspergillus ______ and A. _______
|
A. fumigatus, A. flavus
|
|
|
Pts At risk for aspergillus: - neutropenic, transplant patients, patients on long term ________
|
corticosteroids
|
|
|
Most common manifestation of Aspergillus
|
sinusitis, pneumonia
|
|
|
Histopathology of Aspergillus infection-
|
see acutely branching septate hyphae; may see fruiting bodies in lung
|
|
|
Agar for diagnosis of aspergillus
|
Sabouraud’s agar
|
|
|
Treatment of Candida and Aspergillus
|
Increase neutrophil count with rG-CSF if patient is neutropenic
Anti-fungals: Amphotericin B, voriconazole, caspofungin |
|
|
What fungus?
Once thought to be a protozoan, now classified as fungus May be part of normal flora May be acquired by inhalation of air-borne cysts Most individuals acquire the organism by 3 yrs of age |
Pneumocystis jiroveci
|
|
|
Pts at risk for Pneumocystis jiroveci
|
HIV infected with CD4 cell counts <200/cmm
Occasionally seen in other severely immune suppressed patients |
|
|
Pathogenesis of P. jiroveci:
Replicates in the ______ layer above the alveolar epithelium |
surfactant
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of P. jiroveci:
Replicates in the surfactant layer above the alveolar epithelium Forms trophozoites and _____ |
cysts
|
|
|
Diagnosis:
Pneumocystis jiroveci |
Microscopic examination of BAL fluid stained with Giemsa, toluidine blue, methenamine silver
See thin walled trophozoites and thick walled cysts containing 4-8 nuclei |
|
|
Treatment and prevention
Pneumocystis jiroveci |
TMP/SMX
|
|
|
A 25-year-old man was admitted to a Colorado hospital with a 12-day history of fever, weight loss, fatigue, arthralgias, and productive cough. He had been treated by a private physician with two antibiotics during the preceding 8 days. On hospital admission, a computed tomography (CT) scan demonstrated bilateral pulmonary diffuse nodular opacities. A subsequent open lung biopsy revealed small budding yeasts. After 10 days of culture, Blastomyces dermatitidis was identified and confirmed by DNA probe (GenProbe, San Diego, California *), both at the local hospital laboratory and at CDC. The patient was treated with intravenous (IV) ___________ for 10 days, followed by a prescribed 6-month course of oral ________.
|
amphotericin B
itraconazole |
|
|
One week later, a 35-year-old man sought care for a 15-day history of fever, fatigue, shortness of breath, arthralgias, skin lesions (punctate lesions on arms and trunk and lesions resembling erythema nodosum on legs), cough, chest pain, and weight loss. His symptoms did not improve after 9 days of treatment with two antibiotics, and he was admitted to the same hospital as patient 1. A CT scan revealed diffuse, bilateral pulmonary nodules. The consulting physician for this patient also had seen patient 1; on the basis of work history and clinical course of the disease, the consultant suspected a fungal pneumonia. Specimens obtained by transbronchial biopsy/lavage were negative for fungal elements by microscopic examination and culture. Open lung biopsy specimens revealed small budding yeasts morphologically indistinguishable from those found in patient 1. Biopsy specimens grew B. dermatitidis after 21 days of culture. The patient received IV __________ for 14 days, and at discharge, a 6-month prescribed course of oral __________.
|
amphotericin B
itraconazole |
|
|
On March 30, 2001, CDC was notified by Pennsylvania Department of Health (PDH) of an acute respiratory febrile illness in 44 students from two colleges who traveled to Acapulco, Mexico, for spring break vacation during March 3--18. Within 7--14 days of their return from Acapulco, 21 students presented to health-care providers with illness characterized by fever, chills, dry cough, chest pain, and headache. Two students were hospitalized. On the basis of clinical symptoms and chest radiographs that revealed bilateral, nodular patchy infiltrates, acute pulmonary ____________ was the suspected illness.
|
histoplasmosis
|
|
|
The number of cases of Coccidioidomycosis in Arizona has increased in recent years
1995 reported as 14/100,000 (2X more than in previous yrs Most of new cases were in elderly patients who developed more serious disease Why? |
More elderly moving to AZ from areas where this fungus is not endemic
|

