![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
fractional saturation of mgb equation?
|
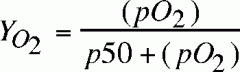
|
|
|
Helix of the histidine that ligates heme( the 5th coordination site)?
residue # in mgb, b-chain, a-chain? |
Helix F8
mgb = residue 93 hgb b-chain = residue 92 hgb a-chain = 87 |
|
|
6th coordination site in the deoxy state? helix and residue numbers?
|
helix E7
mgb = residue 64 hgb b-chain = residue 63 hgb a-chain = residue 58 |
|
|
fractional saturation of HGB
|
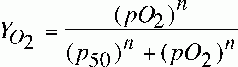
|
|
|
Hill equation of HGB
|
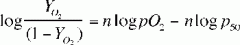
|
|
|
The _____ subunits of hgb may or may not be identical while the ____ subunits are identical
|
alpha = maybe identical
beta = identical |
|
|
What residue facilitates the rotation of the alpha/beta dimer when o2 binds?
|
His F8
|
|
|
Deoxy/T-state stabalizing interactions?
|
-C-terminius of Beta HIS lies on top of helix C in alpha and interacts with Asp 94 of the same β2 by charge-charge interaction and with Lys 40 of the α1 through charge-charge interactions
-N-terminal (NH3 grp) residue of α1 interacts with the guanidinium group of carboxyl terminal residue (Arg) of α2 via charge-charge + Cl- -guanidinium group of the C- terminal residue Arg141 of the α1 interacts with Asp126 of α2 -Tyr 140 of α1 hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl group of Val 93 in the same subunit. Similarly, Tyr145 in the β subunit forms a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of Val98. |
|
|
Bohr effect in terms of specific residue
|
excess protons protonate C terminus B2 146 His and stabalize the deoxy/T state
|
|
|
where does carbamation happen? effect?
|
carbamation happens N-terminus and stabalizes the salt bridge formation between alpha and beta chains
|
|
|
what residue is replaced by ser in fetal gamma subunit? effect?
|
his 143 is replaced by ser in fetal gamma subunit = positive charge replaced by negative = repels BPG = fHgb has less affinity for BPG = fHgb has higher O2 affinity
|
|
|
amino acid residues involved in binding 2,3BPG are
|
Lys82, His143, His2, and the N-terminal amino group of the β- chains?
|
|
|
How many residues in alpha chain of HGB?
How many residues in beta chain of HGB? |
alpha = 141
beta = 146 |
|
|
the plane of ______ and ______ is rotated to avoid collision with the heme
|
valFG5 and leuFG3
|
|
|
relative rotation of alpha-beta units in hgb?
|
15degrees
|
|
|
His F8 function in hgb?
|
proximal his that binds Fe(II)
|
|
|
His E7 function in hgb?
|
Distal histidine, protects the heme and forces O2 to bind at an angle
|
|
|
Phe CD1 function in hgb?
|
Heme contact
|
|
|
Leu F4 function in hgb?
|
Heme contact
|
|
|
Gly B6 function in hgb?
|
Allows approach of B and E helices
|
|
|
Pro C2 function in hgb?
|
Terminates the helix
|
|
|
Tyr HC2 function in hgb?
|
hydrogen bond between H and F helices
|
|
|
On assuming the R state the iron moves down ____ angstroms into the same plane as the porphyrin.
|
0.6A
|
|
|
_______________ interacts with Asp of the same β2 by charge-charge interaction and with Lys 40 R-group of the α1 through charge-charge interactions.
|
C-terminus of β2 (His146) interacts with Asp of the same β2 by charge-charge interaction and with Lys 40 R-group of the α1 through charge-charge interactions.
|
|
|
C-terminus of β2 (His146) interacts with _____ of the same β2 by charge-charge interaction and with_______ of the α1 through charge-charge interactions.
|
C-terminus of β2 (His146) interacts with Asp of the same β2 by charge-charge interaction and with Lys 40 R-group of the α1 through charge-charge interactions.
|
|
|
In deoxy Hb, the _____________________________ interacts with the carboxyl terminal residue Arg guanidinium group of α2, via charge-charge interactions. This involves a ____________.
|
In deoxy Hb, the amino group of the Val N-terminal residue of α1 interacts with the carboxyl terminal residue Arg guanidinium group of α2, via charge-charge interactions. This involves a chloride bridge.
|
|
|
In deoxy Hb, the amino group of the Val N-terminal residue of α1 interacts with the ___________________, via charge-charge interactions. This involves a chloride bridge.
|
In deoxy Hb, the amino group of the Val N-terminal residue of α1 interacts with the carboxyl terminal residue Arg guanidinium group of α2, via charge-charge interactions. This involves a chloride bridge.
|
|
|
In deoxy Hb, the ___________________________ of the α1 interacts with Asp126 of α2 and is similar in a2a1.
|
In deoxy Hb, the guanidinium group of the C- terminal residue Arg141 of the α1 interacts with Asp126 of α2 and is similar in a2a1.
|
|
|
In deoxy Hb, the guanidinium group of the C- terminal residue Arg141 of the α1 interacts with ____________________________
|
In deoxy Hb, the guanidinium group of the C- terminal residue Arg141 of the α1 interacts with Asp126 of α2 and is similar in a2a1.
|
|
|
In deoxy Hb, _________ hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl group of Val 93 in the same subunit. Similarly, _____________ subunit forms a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of Val98.
|
In deoxy Hb, Tyr 140 of α1 hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl group of Val 93 in the same subunit. Similarly, Tyr145 in the β subunit forms a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of Val98.
|
|
|
In deoxy Hb, Tyr 140 of α1 hydrogen bonds to the ____________ in the same subunit. Similarly, Tyr145 in the β subunit forms a hydrogen bond with _______________________
|
In deoxy Hb, Tyr 140 of α1 hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl group of Val 93 in the same subunit. Similarly, Tyr145 in the β subunit forms a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of Val98.
|
|
|
In deoxy Hb, Tyr 140 of α1 hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl group of Val 93 in the ___________. Similarly, Tyr145 in the β subunit forms a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of Val98.
|
In deoxy Hb, Tyr 140 of α1 hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl group of Val 93 in the same subunit. Similarly, Tyr145 in the β subunit forms a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of Val98.
|

