![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Production methods: Job |
ONE AT A TIME Pros: bespoke. To your measurements Very motivated workers & simple product organisation. Cons: Skilled labour and craftsmen is expensive Wide range of tools may be required Long lead time between start and finish High selling costs |
Wedding dress *dances like Taeyang* |
|
|
Method of production: Batch |
MORE THAN ONE AT A TIME Goods can be switched over to make something different on the same production line. Pros: Production can be changed according to demand. Standard production, less labour Employers specialise to become good at their job Lower skilled workers, lower wages paid. Cons: Small batches have higher average units costs (EOS) Workers become less motivated with repetitive work Idle time between batches need to be managed. |
Cakes, pottery, furniture. |
|
|
Production methods: Flow/continuous. |
FLOW IN A CONTINUOUS PROCESS WITH MACHINARY. Requires semi skilled workers and produces alot.
Pros: Average cost per units are lower due to large quantities. Automaised and computerised production= best quality and designs. Stocks and materials can be held & ordered JIT basis.
Cons: high set up costs Low motivation of staff, repetitive tasks. Break down & lost production may be costly |
|
|
|
Production method: Cell |
GROUPS OF WORKERS WITH DIFFERENT SKILLS. Pros: minimal handling of product reduces costs. Motivating for workers to see completed product. Lead times reduced Less time moving place to place. Cons: May be tension in or between cells if work gets competitive. Huge investment in machinary for each cell |
|
|
|
Productivity |
How efficient a firm is. The amount a worker makes hence LABOUR. Measurements will be different depending on industry. Measurements may be hard to QUANTIFY on larger products. |
|
|
|
Ways to improve productivity |
JIT (just in time) TQM (total quality management) Cell production: reconstruction of manufacturing layout Imployee motivation: financial |
|
|
|
FORMULAS |
LABOUR PRODUCTIVITY = output (time period) ÷ No. Of employees (per time period) ×100 CAPITAL PRODUCTIVITY = Output ÷ capital employed (cost of machinary) ×100 |
|
|
|
Factors influencing productivity |
Quality of inputs (materials) Labour shift organisation of workers ( optimum amount of employees) Investment in new technology. |
|
|
|
Link between productivity and competitiveness |
More produced= more competitive the prices (economy efficient) Business will enjoy EOS Mote efficient business (EOS) |
|
|
|
Efficiency |
Production at minimum average costs. EOS goes down as output increases. DIS Av cosgs go up as output increases |
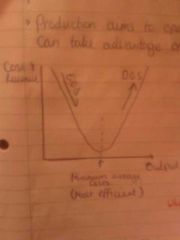
|
|
|
Efficiency formula |
Av cost = total cost ÷ output Where Totsl cost = fixed cost + variable cost |
|
|
|
Productivity and efficiency |
Firms have higher output per employee are more efficient Can lead to COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE and prices are LOWER THAN COMP. Can become MARKET LEADER ( low prices/ high prices compared to production costs) QUALITY MAY SUFFER AS A RESULTS OF TRYING TO PRODUCE ITEMS TOO RAPID |
|
|
|
Intensives |
Labour intensive = a lot of workers working intensely. (Sweatshops) Capital intensive = has more machinary than people. |
Apple, cars |

