![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Four parts of a computer system? |
Hardware, software, data and user. |
|
|
|
RAM (Hardware) |
Random Access Memory. RAM is volatile, it holds data when the power is on. When turned off, all of the data is lost. Smallest unit is a byte which holds one character (one letter, number, etc.) RAM is the memory that the CPU goes to get what is needed. |
|
|
|
CPU (Hardware) |
Central Processing Unit. Manages all devices and performs processing of data. Procedure to transform raw data into useful information. Divided between processor and memory. |
|
|
|
Memory (Hardware) |
Consists of chips attached to the mother board. Holds the data, programs instructions and any documents the user wants to retain. |
|
|
|
Input Devices (Hardware) |
Accepts data and information from the user or from another computer system. Ex: keyboard, mouse, user. |
|
|
|
Output devices (Hardware) |
Return processed data back to the user or to another computer system. Ex: printer, monitor, speakers. |
|
|
|
Communication devices (Hardware) |
Perform both input and output, allowing computers to share information. Ex: modems, network interface cards. |
Can make the words "in" and "out" from the first word |
|
|
Storage Devices (Hardware) |
Holds the data not currently being used by the CPU. Ex: hard drive disk, optical disk drive. |
|
|
|
What is software? |
Software is electronic instructions that tell the computer what to do. |
|
|
|
System Software |
Exists primarily for the computer itself to help the computer perform specific functions. |
Functions |
|
|
Application Software |
Tells the computer how to accomplish tasks the user requires such as creating a document or editing an image. Ex: Word |
|
|
|
Storage devices |
RAM, hard drive, motherboard |
|
|
|
Operating software (OS) |
All computer need an OS. It tells the computer how to interact with the user and its own devices. Ex: Windows, Mac, UNIX |
|
|
|
Cyberbullying |
Bullying someone through social media or an online platform. |
|
|
|
Cyber Luring |
When someone communicates with another person and makes them meet up in real life. The person gains the trust of the individual and asks them to meet where they will most likely commit a crime. |
|
|
|
ISP |
Internet Service Provider. Organization that provides services for accessing, using or participating on the internet. Ex: Rogers, Bell. |
|
|
|
Peripherals |
Not a part of an actual computer but intended to work with one. Basically computer add-on's. Ex: printer, monitor, speakers, mouse. |
|
|
|
Recommendations for setting up computers in a business |
Networked computers- share programs, information, resources, peripherals. Saves money, can connect to computers in other locations. Local Area Network- working in the same building. Star Topology- all computers and peripherals are connected to one main server/HUB so if one crashes, no others are affected. Licensing Agreement- be able to share software. |
|
|
|
LAN |
Local Area Network. Groups of computers that are connected in a network that are in the same building. Ex: the Lab or school |
|
|
|
WAN |
Wide Area Network. Group of computers connected in networks that are located in a variety of locations in a large area. Ex: all of the KPRDSB schools. |
|
|
|
Bus Topology |
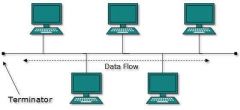
All computers and peripherals are attached to one main cable. One broken network can bring down part or the entire network. |
|
|
|
Star Topology |
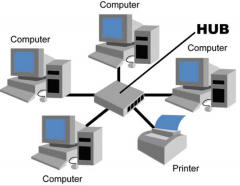
All computers and peripherals are connected to one switch or HUB at the center of the networks. One broken connection doesn't affect anything else. |
|
|
|
Modems |
A device or program that allows a computer to transmit data over. Ex: telephone, cable wires. |
|
|
|
Online Safety/Privacy |
-No personal information -Use privacy settings -Turn off GPS -Only interact with people you know Common sense. Use it. |
|
|
|
Netiquette "do's" |
-Use proper spelling and grammar -Be respectful -Use proper salutations/closings -Acknowledge and return messages properly |
|
|
|
Netiquette "don'ts" |
-Forward junk mail -Text inappropriate pictures -Use sarcasm -Use punctuation excessively -Use your real name |
|
|
|
Elements of Design (Microsoft Office) |
Bold, italic, underline, strike through, outline, shadow, reflection, glow, font, colour |
|
|
|
Function of Word |
Create documents |
|
|
|
Function of PowerPoint |
Create presentations |
|
|
|
Function of Excel |
Create spreadsheets for business and marketing |
|
|
|
Function of Publisher |
Make visual presentation like a poster or brochure. |
|
|
|
What are transitions? |
Effects that manipulate how a slide looks while it's changing. |
|
|
|
What are animations? |
Effects that manipulate how a picture comes in, appears, looks. |
|
|
|
Excel Functions |
Mathematical equations Minimum, maximum, sum, average
=SUM(A1:A5) |
|
|
|
What is ergonomics? |
The study of how the physical health of workers is affected by their workplace. |
|
|
|
What health issues can arise from poor workplace setup? |
Musculoskeletal injuries. Things such as Carpel Tunnel Syndrome in which the wrist is unable to move properly. Often caused by long hours of typing or the chair is not adjusted to the persons height. |
|
|
|
Proper chair setup |
-4 to 5 legs -37.5 to 52.5 cm from the floor -Firm seat back |
|
|
|
Proper desk setup |
-Enough space to avoid leg injuries -Smooth, round edges -Medium-light coloured surfaces -Dull finish to reduce glare |
|
|
|
Proper keyboard setup |
-Elbows height -Arms at 90 degrees -Fingers on home row |
|
|
|
Proper monitor setup |
-Flat -Top of screen at eye level -Distance of 45 to 60 cm -Cleaned of dust |
|
|
|
What are ethics? |
-What is considered to be right or wrong -Each person's ethics are different -"Legal" and "ethical" are two different ideas |
|
|
|
What is an ethical dilemma? |
When you have to make a decision regarding what actions to take in a situation. Sometimes doing the right thing means there is a negative consequence for you. |
|
|
|
What is phishing? |
When someone attempts to get your personal information. Usually businesses offering free things that require personal information to receive it. |
|
|
|
Ethical issues with technology |
-Pirating or illegally copying and distributing media -Identity theft, phishing, privacy issues -Hacking and viruses -Cyberstalking and online harassment -Spyware and cookies -E-commerce and misleading advertisement-shills |
|
|
|
Ethic of Justice |
-Follows the rules and laws -No exceptions -Believe in fairness and equality -Can be cold, inflexible and uncaring |
|
|
|
Ethic of Care |
-Considering the bigger picture -Bends the rules -Cares about feelings -Responsibility to reduce harm and suffering for others -Reliance on gut instincts |
|
|
|
Code of Ethic |
-Written documents explaining how the the business and its employees will behave. -Most big businesses have a code of ethics. |
|
|
|
What is hardware? |
Hardware is the physical components of the computer system. Ex: monitor, motherboard, printer |
|
|
|
What is data? |
Data is raw unprocessed information that you key or scan into the computer. Ex: numbers. letters, symbols |
|
|
|
What are users? |
Users are the people who operate the computer. Ex: you, me |
|

