![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
QUALITY CONTROL |
A process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintain/improved and manufacturing errors are reduced/eliminated. - training - creating standards for quality - testing |
|
|
QUALITY ASSURANCE |
A component of quality management - focused on providing confidence that quailty standards will be met. |
|
|
TQM |
Total Quality Management (philosophy) Total quality in everything the business does. - fishbone analysis - quality circles - quality assurance - suggestion boxes - department meetings - appraisal - training |
|
|
CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT |
Kaizen (philosophy) Continuous improvement - always somewhere quality can be improved. Japanese term 'change for the better'. Used to make work enviroment more efficient/effective (team atmosphere). - improve procedures - motivation - less tiring work - safer work |
|
|
QUALITY CIRCLES |
Management technique - small groups of workers that meet regularly - discuss ways to improve production. |
|
|
SIGNIFICANCE OF QUALITY |
Most important to firms operation. Do it righ first time - no cost - it can cost to correct an error.
Important because: - satisfy customers (stop using alternatives) - gain loyalty (long-term revenue and profitability) - technology (favourable opinions to uphold repuation - help compete) |
|
|
QUALITY |
Fitness for purpose. |
|
|
INNOVATION |
A new method, idea, product, etc. |
|
|
INNOVATION'S ROLE IN BUSINESS SUCCESS |
Buisnesses need more than good products to survive - innovative processes/management.
To drive down costs/improve productivity. |
|
|
TYPES OF INNOVATION |
Incremental and Radical Innovation |
|
|
INCREMENTAL INNOVATION |
Making improvements gto exsisting processes, products or services.
e.g. Automation in work force, improve web accessability - reducing need for stores. |
|
|
RADICAL INNOVATION |
Creating new processes, products or services in respones to market need/opportunity. Using technology to solve issue/breakthrough innovations. |
|
|
CHANGE MANAGEMENT |
The management of change and development within a business. Thoughtful planning and sensitive implementation - consoltaion with people involved. Forcing change = problems. |
|
|
LEADERSHIP IN CHANGE MANAGEMENT |
LESS AUTOCRATIC - MORE DEMOCRATIC
Collaboration with workers to voice their opinions on the method in managing the change. |
|
|
IF A BUSINESS USES CHANGE MANAGEMENT THE MUST... |
Careful decisions to maintain sustainability and have a good public face - media. |
|
|
INVESTMENT APPRAISAL |
An evaluation of the attractiveness of an investment, using methods such as average/accounting rate of return, internal rate of return, net present value, or payback period. |
|
|
PAYBACK PERIOD |
The length of time it takes for an investment to cover the intitial outlay cost in profit. Simple method - used by smaller businesses, and used by larger businesses as a screening to narrow choices. |
|
|
PAYBACK PERIOD FORMULA |
Initial investment / return per year = payback period 500k / 150k = 3.3 years |
|
|
AVERAGE/ACCOUNTING RATE OF RETURN |
The amount of profit that a business can expect based on the investment made. Evaluate profitability of a investment project. |
|
|
AVERAGE/ACCOUNTING RATE OF RETURN FORMULA |
Average profit / average money invested x 100 = percentage (rate of return on investment) |
|
|
NET PRESENT VALUE |
A calculation that compares the amount invested today to the present value of the future cash receipts from the investment. |
|
|
EXAMPLE OF NET PRESENT VALUE |
For example, an investment of $1,000 today at 10 percent will yield $1,100 at the end of the year; therefore, the present value of $1,100 at the desired rate of return (10 percent) is $1,000. The amount of investment ($1,000 in this example) is deducted from this figure to arrive at net present value which here is zero ($1,000-$1,000). A zero net present value means the project repays original investment plus the required rate of return. A positive net present value means a better return, and a negative net present value means a worse return, than the return from zero net present value. |
|
|
BUSINESS LOCATION ANALYSIS |
- check demographics (traffic, demographic, lifestyle, competitive, foot traffic data) - 'perfect' customer - access to customers/suppliers - close proximity to competition - benefit from money spent e.g. marketing - transport - resources - clustering (increase productivity) |
|
|
MISSION STATEMENT |
A formal summary of the aims and values of a business. |
|
|
CORPORATE OBJECTIVES |
A well defined goal set by a company the often affects internal decisions. |
|
|
S.M.A.R.T. GOALS |
Goals characterised by - Specific, Measurable, Achieveable, Realistic, Time-Bound aspects. |
|
|
MARKETING AUDIT |
A strategic tool used to review the effectiveness of a marketing program. |
|
|
BOSTON MATRIX |
A measurement of how successful a company's products are compared to competitors' products, calculated by looking at each product's share of sales in its particular market and that market's rate of growth. |
|
|
BOSTON MATRIX DIAGRAM |
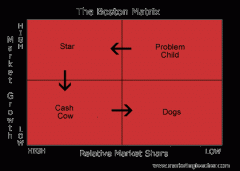
|
|
|
MARKET RESEARCH |
The action or activity of gathering information about consumers need and preferences. |
|
|
MARKET RESEARCH INCLUDES: |
- market size - market share - target market - market segments |
|
|
MARKET ANALYSIS/ STRATEGIES: |
- porters five forces - SWOT analysis - marketing mix - ANSOFF matrix |
|
|
PORTERS FIVE FORCES |
Analyzes 5 competitive forces that shape every industry. Shows strengths and weaknesses, competition, possible new entrants, power to suppliers/customers and threat substitutes. |
|
|
SWOT ANALYSIS |
Identify internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. |
|
|
ANSOFF MATRIX |
Named after Igor Ansoff - marketing tool.
Links marketing strategy with its strategic direction and present four growth strategies.
Market Penetration, Market Development, Product Development and Diversification. |
|
|
MARKET PENETRATION |
By pushing exsisting products in their current market segments. |
|
|
MARKET DEVELOPMENT |
By developing new markets for existing products. |
|
|
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT |
By developing new products for the existing markets. |
|
|
DIVERSIFICATION |
By developing new products for new markets. |
|
|
SALES FORECASTING |
A projection of what sales revenue will be for a specific period in the future. |
|
|
MARKETING BUDGETS |
A projection of costs required to promote a business' products/services.
e.g. advertising, web development, public relations, staff. |
|
|
CONTINGENCY PLANNING |
A plan devised for an outcome other than in the expected plan. It is often used for risk management. |
|
|
ETHNOBOTANY |
The scientific study of the relationships that exist between people and plants. |
|
|
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS |
Legally recongized exclusive rights to creations of the mind.
e.g. copyright, trademarks, patents, trade secrets etc. |
|
|
TRADE AGREEMENT |
An international agreement on conditions of trade in goods and service OR an agreement resulting from collective bargaining. |
|
|
PUTAKE |
Reason For Being - - not just profit - collectivley owned resources - whakapapa based groupings (hapu & iwi) - multiple bottom line - cultural expression - self sustaining
|
|
|
TURANGA |
The positioning of the business (anchor) -
- collectively owned assets - trading decisions different to tradition business models due to collective assets.
|
|
|
TIKANGA |
Values, rules, priorities and ways of doing business - - not just about profit - measure against mulitple bottom line
Values: - Kotahitanga = maori unity, sense of belonging - Whanaungatanga = ethic of belonging - Wairuatanga = spirituality - Manaakitanga = hospitality, generousity, care & giving |
|
|
KAITIAKITANGA |
Guardianship (natural resources e.g. land, people) - sustainability, enviromental protection - Kaitaki = guardians responsible for protecting resources for future generations (not short-term/individual profit) |
|
|
RANGITIRATANGA |
Leadership, authority, guardianship - the exercise of leadership (utilisation current & future) - strategic development, relationship development, problem solving, conflict resolution, risk analysis.
Is about: - mana - respect - empowerment |

