![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Strategy is concerned with |
- Long term direction - Environment which the entity operates - The resources at it's disposal - Returns made to stakeholders |
|
|
Two different approaches to strategic planning |
- Rational Planning (traditional approach) - Emergent Approach |
|
|
Rational Planning description |
- Set goals first then design strategies to achieve them - Separate the planning and selection of strategies from the implementation |
|
|
Emergent approach |
- Develop and adapt strategies as circumstances change - Managers therefore have a significant degree of autonomy |
|
|
Benefits of the rational planning approach |
- Provides framework - Encourages long term planning - Goal congruence - Considers stakeholders - Optimises use of resources - Considers environment changes - Monitors progress |
|
|
Criticisms of Rational Planning approach |
- Does not guarantee success - Businesses need to be dynamic - Reduced initiative and innovation - Internal politics |
|
|
Criticisms of Rational Planning approach |
- Does not guarantee success - Businesses need to be dynamic - Reduced initiative and innovation - Internal politics |
|
|
Mission Statements |
- Purpose - Strategy - Policies - Values |
|
|
Mission Statements |
- Purpose - Strategy - Policies - Values |
|
|
Mission Statements |
- Purpose - Strategy - Policies - Values |
|
|
Mission statement Benefits |
-Helps instill core values in an organisation -Communicates nature of the organisation to stakeholders Can help with strategic planning as goals can be set against the basis of the statement |
|
|
Criticisms of mission statements |
- Just a PR exercise - Full of generalisations and meaningless terms - May be ignored by managers |
|
|
Criticisms of mission statements |
- Just a PR exercise - Full of generalisations and meaningless terms - May be ignored by managers |
|
|
Smart Goals |
Specific Measurable Achievable Relevant Time Bound |
|
|
Not for profit organisations |
- Primary objective is to maximise the benefit of the target stakeholder - Benefits may be intangible and difficult to measure - Multiple objectives -Diverse range of stakeholders |
|
|
Stakeholders |
Groups or persons with an interest in what the organisation does
Medelow's matrix
Level of interest
Low High Minimal Keep informed Power low effort
High Keep satisfied Key players Keep participated
|
|
|
Stakeholder conflicts |
Maximise shareholder wealth vs spending profits on CSR initiatives Spending on marketing vs spending the money directly Different directors who want to pursue different strategies |
|
|
PESTEL analysis |
Political factors Economic factors Social and demographic Technology factors Ecological/environmental factors Legal factors |
|
|
Porter's diamond |
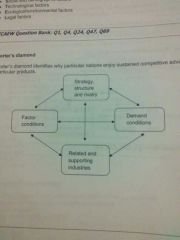
|
|
|
Porter's Five Forces |
- Threat of new entrants - Threat of substitute products - Power of suppliers - Power of customers - Competitive rivalry |
|
|
PFF Threat of new entrants |

|
|
|
PFF - Threats of substitute products |
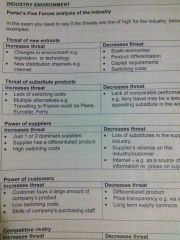
|
|
|
PFF - Power of suppliers |
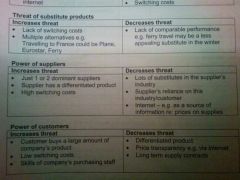
|
|
|
PFF - Competitive Rivalry |

|
|
|
PFF - Power of Customers |

|
|
|
Critical Success Factors |
Resources (9Ms) -Men - Money - Management -Make up - Machinery - Method - Markets - Materials - Management information
Competencies -Competitive architecture - Internal - employees - External - suppliers - Network - collaborating firms -Reputation - Innovative ability |
|
|
Critical Success Factors |
Resources (9Ms) -Men - Money - Management -Make up - Machinery - Method - Markets - Materials - Management information
Competencies -Competitive architecture - Internal - employees - External - suppliers - Network - collaborating firms -Reputation - Innovative ability |
|
|
Porter's value chain analysis |

|
|
|
Product life cycle |
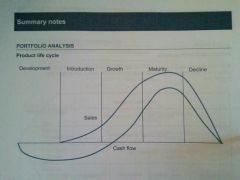
|
|
|
BCG Matric |

|
|
|
SWOT Analysis |
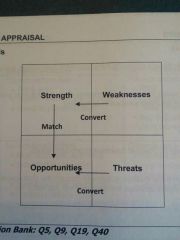
|
|
|
GAP Analysis |

|
|
|
Porter's Generic Strategies |
Overall cost leader - Economies of scale - Latest technology - Cheap labour/ relocate to cheaper countries to produce goods Differentiator - Brand image - Augmented features - Customer service levels Focus / Niche - focus on a specialist area of the market Must pick one |
|
|
Directions for growth |
Ansoff's Matrix Vertical integration Conglomerate diversification |
|
|
Ansoff's Matrix |
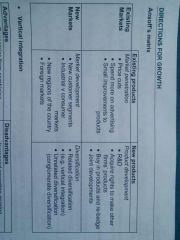
|
|
|
Vertical integration |
Advantages Economies from combining operations and avoiding the market Access to knowledge Reduce Five Forces Disadvantages Increased operating gearing Capital requirements Reduced flexibility Differing managerial requirements |
|
|
Conglomerate diversification |
Advantages Spread risk Can grow quickly Invest surplus cash Stretch the brand and reputation Disadvantages No synergies No additional benefit for shareholders Lack of common identity Fail on one business could threaten the rest |
|
|
Marketing Definition |
The management process that identifies, anticipates and supplies customer need efficiently and profitability |
|
|
Market research |
Desk Company records, industry journals, government statistics Field Questionnaires, observation, group interviews Test marketing, experimentation |
|
|
Market mix |
4 ps Product Brand, quality, USPs, Benefits to customer
Promotion Advertising, sales promotions, public relations, personal selling Place Direct - retail, mail order, internet sales, and personal selling Indirect - wholesaler, distributer, agent, franchisee Price Cost, competition, customers, corporate objectives |
|
|
Pricing strategies (5) |
Price discrimination Different prices for same product in different parts of the market Penetration Low short term Price skimming High price when first launched, then reduce Going rate For establishes market Cost + |
|
|
Types of organisations |

|
|
|
Pros and cons of decentralisation |
Pros Senior management free to concentrate on strategy Better local decisions due to local expertise Better motivation Quicker responses / flexibility Training / career path Cons Loss of control Dysfunctional decisions as lack of goal congruence Poor decisions made by inexperienced managers Training costs Duplication Extra costs |
|
|
Transfer pricing |
Why - help assess the performance of the divisions - help build in the cost of manufacturing into the final sales price of the product Methods Full costs Variable costs Opportunity costs Negotiation 2 part Dual pricing Issues May lead to goal congruence In questions consider whether a good price or not |
|
|
Corporate Governance |
Good corporate governance is achieved by lining up the interests of directors and stakeholders UK CG code best practice examples Chairman different to Chief Executive Balance made between executive and independent NEDs Audit committee to be made of NEDs Director's renumeration to he overseen by renumeration committee Sound risk management and accountability Fostering relationships with stakeholders / shareholders |
|
|
Risk management definition |
The process of identifying and assessing the risks and then developing, implementing and monitoring of a strategy to be able to respond to those risks |
|
|
Risk management process |
1. Identify strategic objectives
2. Consider risk appetite Reactor, defender, analyser, prospector 3. Risk identification PESTEL, Five forces 4. Perform risk analysis Likelihood, impact 5. Risk evaluation and response Transfer, Accept, Reduce, Avoid 6. Risk monitoring and reporting Turnbull guidance, risk registers 7. Review process and feedback |
|
|
Organic growth vs acquisition |
Advantage of acquisitions - quicker - get round barriers to entry - one less competitor - Synergies Disadvantages - Entry costs may be too high -clash of cultures - Easier to control growth if organic - Reputation of target company |
|
|
Synergies in acquisition |
Marketing and sales - Common sales team Operating - Economies of scale, rationalism, use of same distribution channels Financial synergies - sale of surplus assets, spread of risk so cheaper capital cost Management synergies - transfer and funny learning, increased opportunities |
|
|
Joint development strategies 4 |
Joint venture - contractual, two different companies, set up new company Strategic alliance - loose agreement to share knowledge and business opportunities Licensing - the right to exploit an invention/resource in return for the profit Franchising - right to exploit a business brand in return for a capital amount + share of profits |
|
|
Key issues 🔑 for joint development |
- sharing out risks and returns -splitting of capital and operating costs -Possible conflicts over operating decisions -Small firms may not have critical mass to go it alone - Level of support -Danger of other party gaining information that could be used against them |
|
|
Strategy Evaluation and performance measurement |
Suitability Does it give the firm good fit with environment Do new products fit with existing ones Feasibility Is the time scale achievable Do we have the right resources Performance evaluation Balanced score card for the long term
|
|
|
Balanced Score Card - financial and none financial |
Customers What do the value Internal What CSFs come from internal processes Innovation Learning ability Financial Value for shareholders |
|
|
Benchmarking |
Internal Competitive Activity Generic |
|
|
Business plan pro-forma |
Cover sheet Contents Introduction and terms of reference Executive summary The market The product/service The management team Business operations Financial projections
|
|
|
Roles of Human Resources l |
Recruitment Training Appraisals Rewards |
|
|
R&D (two functions) |
Product research also process research |
|
|
4 Vs of operations |
Volume Variety Variation in demand Visibility |
|
|
Capacity planning |
Made to stock (maintain) Made to order) just in time Manipulate demand (advertising, change price) |
|
|
Procurement mix |
Quantity Quality Price Delivery |
|
|
Supply chain management |
Responsiveness Reliability Relationships |
|
|
Lewis's forcefield |
Cultural Barriers Structural inertia Group inertia - team norms. May make some roles redundant Power structures redistribution of power chain may cause threats Personal barriers Habit, security, pay, fear of the unknown Psychological contract people are currently happy with their effort : reward ratio. Will be difficult to change this. |
|
|
Managing change |
Iceberg - unfreeze, move refreeze |
|
|
Appropriate management styles for change |
Education and communication Participation Intervention |
|
|
Mintzberg |
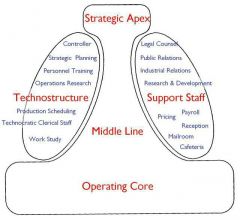
|
|
|
Handy Shamrock |
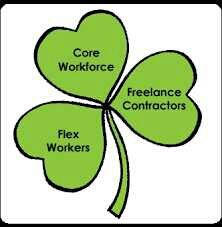
|
|
|
Advantage of outsourcing |
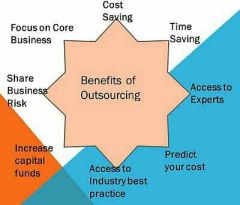
|
|
|
Outsourcing disadvantages |

|

