![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Element
|
The entry on which data are collected.
|
|
|
Define Population
|
The collection of all the elements of interest.
|
|
|
Define Sample
|
A subset of the population.
|
|
|
What is the "sampled population?"
|
The population from which the sample is drawn.
i.e. all registered voters in Texas |
|
|
What is a sample frame?
|
A list of the elements that the sample will be selected from.
i.e. a list of all registered voters in Texas. |
|
|
Define Parameters
|
Numerical characteristics of a population.
i.e. population mean annual salary, population standard deviation of annual salary, etc. |
|
|
Define Simple Random Sample
(Finite Population) |
A simple random sample of size n from a finite population of size N is a sample selected such that each possible sample of size n has the same probability of being selected.
|
|
|
Give an example of constructing a frame
|
Assigning each element on a list of 2500 a number of 1 to 2500
|
|
|
Define Sampling Without Replacement
|
Once an element has been included in the sample, it is removed from the population and cannot be selected a second time.
|
|
|
Define Sampling With Replacement
|
Once an element has been included in the sample, it is returned to the population. A previously selected element can be selected again and therefore may appear in the sample more than once.
|
|
|
Define Sample Statistic
|

|
|
|
Define Point Estimator
|
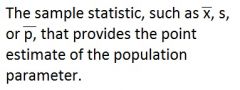
|
|
|
Define Point Estimate
|
The value of a point estimator used in a particular instance as an estimate of a population parameter.
|
|
|
Define Target Population
|
The population for which statistical inference such as point estimates are made. It is important for the target population to correspond as closely as possible to the sampled population.
|
|
|
Define Sampling Distribution
|
A probability distribution consisting of all possible values of a sample statistic.
|
|
|
Define Unbiased
|
A property of a point estimator that is present when the expected value of the point estimator is equal to the population parameter it estimates.
|
|
|
Define Standard Error
|
The standard deviation of a point estimator.
|
|
|
Define Relative Efficiency
|
Given two unbiased point estimators of the same population parameter, the point estimator with the samller standard error is more efficient.
|
|
|
Define Consistency
|
A property of a point estimator that is present whenever larger sample sizes tend to proved point estimates closer to the population parameter.
|
|
|
Define Stratified Random Sampling
|
A probability sampling method in which the population is first divided into strata and a simple random sample is then taken from each stratum.
|
|
|
Define Cluster Sampling
|
A probability sampling method in which the population is first divided into clusters and then a simple random sample of the clusters is taken.
|
|
|
Define Systematic Sampling
|
A probability sampling method in which we randomly select on of the first k elements and then select every kth element thereafter.
|
|
|
Define Convenience Sampling
|
A nonprobability method of sampling whereby elements are selected for the sample on the basis of convencience.
|
|
|
Define Judgment Sampling
|
A nonprobability method of sampling whereby elements are selected for the sample based on the judgement of the person doing the study.
|
|
|
What is the finite population correction factor?
|

|
|
|
Define The Central Limit Theorem
|

|
|

|
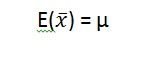
|
|

|
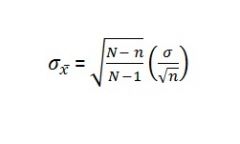
|
|

|
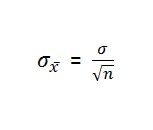
|
|

|
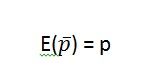
|
|

|
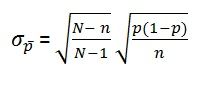
|
|

|
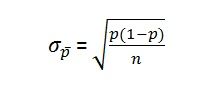
|
|
|
What is the formula to determine the numbers of different simple random samples of size n that can be selected from a finite population of size N?
|
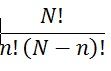
|
|
|
Define a Random Sample for an Infinite Population
|
A random sample of size n from an infinite population is a sample selected such that the following conditions are satisfied:
1) Each element selected comes from the same population 2) Each element is selected independently |
|
|
Compare population parameter and point estimator
|
Population parameter is the actual value (if a census was taken) but a point estimator is the value created from the sample.
|
|
|
When a population is finite, what percentage of a population can the sample be in order to use the standard deviation formula for an infinite population?
|
5% or less
|
|
|
What are the three properties of good point estimators?
|
Unbiased, efficiency, and consistency
|

