![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
discrete data definition
|
values are whole numbers (integers);
usually counted, not measured Examples: # of complaints per day, # of TVs in a household, # of rings before the phone is answered |
|
|
continuous data definition
|
can potentially take on any value, depending only on the ability to measure accurately;
often measured, fractional values are possible; examples: thickness of an item, time required to complete a task, temperature of a solution, height, in inches |
|
|
discrete probability distribution graph
|
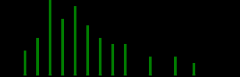
|
|
|
continuous probability distribution graph
|
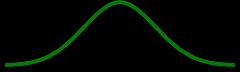
|
|
|
discrete random variables definition
|
have outcomes that typically take on whole numbers as a result of conducting an experiment;
finite number of values |
|
|
continuous random variables definition
|
have outcomes that take on any numerical value as a result of conducting an experiment;
infinite number of outcomes; examples: length of time a customer waits in a checkout line weight of a tractor-trailor at a weight station |
|
|
a discrete probability distribution is...
|
a listing of all the possible outcomes of an experiment for a discrete random variable;
along with the relative frequency of each outcome |
|
|
A discrete probability distribution meets the following conditions:
|
1. each outcome in the distribution needs to be mutually exclusive with other outcomes in the distribution
2. the probability of each outcome, P(x), must be between 0 and 1 3. the sum of the probabilities for all the outcomes int he distribution must be 1 |
|
|
The mean, μ, of a discrete probability distribution...
|
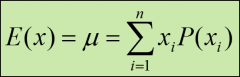
is the weighted average of the outcomes of the random variables that comprise it;
Also known as the espected value, E(x) μ = The mean of the discrete probability distribution xi = The value of the random variable for the ith outcome P(xi) = The probability that the ith outcome will occur n = The number of outcomes in the distribution |
|
|
Variance of a discrete probability distribution...
|
is a measure of the spread of the individual values around the mean of a data set;
|
|
|
formula for the variance of a discrete probability distribution
|
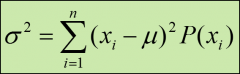
σ^2 = The variance of the discrete probability distribution
xi = The value of the random variable for the ith outcome μ = The mean of the discrete probability distribution P(xi) = The probability that the ith outcome will occur n = The number of outcomes in the distribution |
|
|
expected monetary value (EMV) definition
|

the mean of a discrete probability distribution when the discrete random variable is expressed in terms of dollars;
the EMV represents a long-term average, as if outcomes from the distribution occurred many times |
|
|
characteristics of binomial distributions
|
1. experiment consists of a fixed # of trials, denoted by n
2. each trial has only 2 possible outcomes, a success or failure 3. the probability of a success p and the probability of a failure q are constant throughout the experiment 4. each trial is independent of the other trials in the experiment |
|
|
examples of binomial distributions
|
a survey response to a question is yes or no;
an electronic component is either defective or acceptable; new job applicants either accept an offer or reject it |
|
|
Binomial distributions formula
|
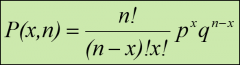
P(x,n) = The probability of observing x successes in n trials
n = Number of trials x = Number of successes p = Probability of a success q = Probability of a failure |
|
|
formula for calculating the mean of a binomial distribution
|
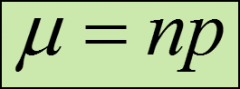
μ = The mean of the binomial distribution
σ = The standard deviation of the binomial distribution n = The number of trials p = The probability of a success q = The probability of a failure |
|
|
formula for calculating the standard deviation of a binomial distribution
|
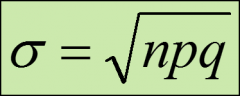
μ = The mean of the binomial distribution
σ = The standard deviation of the binomial distribution n = The number of trials p = The probability of a success q = The probability of a failure |
|
|
Poisson distribution...
|
is useful for calculating the probability that a certain number of events will occur over a specific interval of time or space;
examples: # of customers per hour, # of flaws per meter of cloth, # of accidents per month |
|
|
Characteristics of a poisson process
|
1. experiment consists of counting the number (x) of occurrences of an event over a period of time, area, distance, or other type of measurement
2. the mean (λ) has to be the same for each equal interval of measurement 3. the # of occurrences during one interval has to be independent of the number of occurrences in any other interval 4. the intervals defined in the poisson process cannot overlap |
|
|
formula for the Poisson probability distribution
|
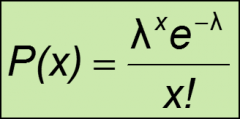
x = The number of occurrences of interest over the interval
λ = The mean number of occurrences over the interval e = 2.71828 P(x) = The probability of exactly x occurrences over the interval |
|
|
formula for the variance of a Poisson distribution
|
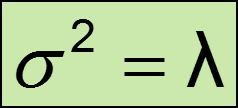
the variance of the distribution is the same as the mean
|
|
|
what is a common use of the Poisson distribution?
|
to determine the probability of customer arrivals
|
|
|
Binomial probabilities can be calculated using the Poisson distribution when the following conditions are present:
|
when the # of trials, n, is greater than or equal to 20
AND when the probability of a success, p, is less than or equal to 0.05 |
|
|
formula for using the poisson equation to calculate binomial probabilities
|
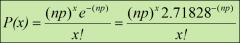
|

