![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are three phases of Project Management?
|
Planning, Scheduling, Controlling
|
|
|
Explain Critical Path in Project Mgmt
|
The critical path is the steps needed that cannot be shortened. IE: A-B-E-J-K all must be completed in order. Most complex item, such as motor may be critical path
|
|
|
Activity on Node AON
|
A network in which the activities are represented by nodes. This is the model illustrated in the book.
|
|
|
CPM
|
Critical path method. A deterministic network technique that is similar to PERT but allows for project crashing. The series of activities that have zero slack. It is the longest time path through the network. ** Times are known with certainty- no estimating!
|
|
|
PERT
|
Program Evaluation and Review Technique. A network technique that allows three time estimates for each activity in a project. (helps to estimate)
|
|
|
Dummy Destination
|
If transporation supply / demand tables are unbalanced, we add a dummy column or row to balance. For example, if we have too many desks, we add a destination column that requires the overage. (it never ships)
|
|
|
First step in Schedule Development
|
1. Define Activities
|
|
|
Second Step in Schedule Development
|
2. Sequence Activities A ... B ... C... D
|
|
|
Third step in Schedule Development
|
3. Estimate Activity Times. How long to make a handle? How long to sand the wood? How long to wood the sand?
|
|
|
Fourth step in Schedule Development
|
4. Construct schedule.
|
|
|
For assignment problems, what do the columns represent?
|
The tasks.
|
|
|
FOr assignments, what do the rows represent?
|
The ROWS are the BROS / Machinos!
|
|
|
Media Selection
|
Maximize audience exposure within limited conditions. (We wanna be on the radio)
|
|
|
Marketing Research
|
How valuble is it? If the state of nature is favorable market, worth it?
|
|
|
Production Mix
|
What to produce? We consider time, funds needed, return on investment, etc.
|
|
|
Assignment Programming (key ideas)
|
1 worker to each 1 job. Need equal rows/cols- "dummy row/col".
|
|
|
Portfolio Selection Model
|
Goal: Maximize revenue, within constraints of financial accounts.
|
|
|
All LP Models have 4 common properties
|
1.All seek to maximize or minimize some qty (the objective function) 2. All have restrictions or constraints 3. Must have alternate options to choose 4. Objective / Constraints must be represented as inequalities ><=.
|
|
|
Feasible solution vs Optimal Solution
|
Feasible will work. Optimal is best
|
|
|
Alternate Optimal Solution
|
situation in which more than one optimal solution is possible. It arises when the slope of the objective function is the same as the slope of a constraint.
|
|
|
Corner Point
|
A point that lies on one of the corners of the feasible region. This means that it falls at the intersection of two constraint lines.
|
|
|
Corner Point Method
|
The method of finding the optimal solution to an LP problem by testing the profit or cost level at each corner point of the feasible region. The theory of LP states that the optimal solution must lie at one of the corner points.
|
|
|
define Dual Price
|
The dual price for a constraint is the improvement in the objective function (goal) value that results from a one-unit increase in the right-hand side of the constraint. How much profit do we get when we add one more hour?
|
|
|
Feasible Region
|
The area satisfying all of the problem’s resource restrictions; that is, the region where all constraints overlap. All possible solutions to the problem lie in the feasible region.
|
|
|
Isocost Line
|
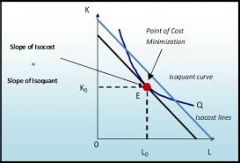
A straight line representing all combinations of X1 and X2 for a particular cost level.
|
|
|
Economic simulations
|
, often called econometric models, are used by governments, bankers, and large organizations to predict inflation rates, domestic and foreign money supplies, and unemployment levels
|
|
|
corporate operating system
|
model sales, production levels, marketing policies, investments, union contracts, utility rates, financing, and other factors
|
|
|
Systems Simulation
|
models the dynamics of a large system (more complex than the Monte Carlo methods we have studied)
|
|
|
Operational Gaming
|
where there are 2 or more competing players (such as military games or business games)
|
|
|
Project Budgeting - Key factors
|
-Divide task cost by the weeks it takes. IE: $30K task A is $10K per week. Task A first week: $10K. Task B first week: $12K. Total first week: $22K.
|
|
|
Northwest Corner Rule
|
1. Exhaust the supply (factory capacity) of each row before moving down to the next row
2. Exhaust the demand (warehouse) requirements of each column before moving to the right to the next column Check that all supply and demand requirements are met. |
|
|
Flow Chart symbols: Oval, Diamond, Rectangle
|
Oval: Start or End.
Diamond: Decision Rectangle: Action |
|
|
Linear Programming
|
A mathematical technique used to help management decide how to make the most effective use of an organization’s resources.
|
|
|
Mathmatical Programming
|
The general category of mathematical modeling and solution techniques used to allocate resources while optimizing a measurable goal. LP is one type of programming model.
|
|
|
Nonnegativity Constraints
|
Each X1, X2, etc. has to be greater than 0. Boss assigns work- everyone has to punch some hours.
|
|
|
Objective Function
|
The goal, mathematically stated as our intent to maximize or minimize sometin'.
|
|
|
Redundancy
|
The presence of one or more constraints that do not affect the feasible solution region. A redundant constraint is one that doesn't affect us.
|
|
|
Sensitivity Analysis
|
The study of how sensitive an optimal solution is to model assumptions and to data changes. It is often referred to as postoptimality analysis.
|

