![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Herzberg’sMotivation-Hygiene Theory
|
Some factorseliminate job Dissatisfaction (Hygiene factors) and other factors increase jobSatisfaction (Motivators )
Motivators = job satisfaction, promotional opportunities, personal growth, recognition, responsibility. Hygiene = job dissatisfaction, quality ofsupervision, pay, policies, working conditions, job security |
|
|
Extrinsic Motivation |
motivation tobehavior is to earn award or avoid punishment, other rewards like pay andbonus.
|
|
|
Intrinsic Motivation |
psychological rewardsfor work; choice, progress, meaningfulness, competence
|
|
|
McClellands 3 Needs
|
Need for Achievement = Personal achievement rather than for rewards,desire to do something better than it has been before.
Need for Power = Desire for impact/influential, enjoysbeing in charge. Need for Affiliation = Desire to be liked and accepted, friendship.Prefer cooperative situations rather than competitive ones. |
|
|
Drive Model |
Autonomy – The desire to direct our own livesMastery – The urge to get better and better at somethingthat matters
Purpose – The yearning to do what we do in the service ofsomething larger than ourselves |
|
|
Expectation Theory |
Motivational strength is determined by probabilities of an outcome and the attractiveness of that outcome to theindividual.
|
|
|
Reinforcement Theory |
Behavior is a function of its consequences.Positive reinforcement strengthens behavior, negative reinforcement alsostrengthens behavior, punishment weakens behavior.
|
|
|
Job Characteristics |
five “core” job characteristics (i.e. skillvariety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback) that affectfive work-related outcomes (i.e. motivation, satisfaction, performance, andabsenteeism and turnover) through three psychological states (i.e. experiencedmeaningfulness, experienced responsibility, and knowledge of results).
|
|
|
Job Characteristics (picture) |
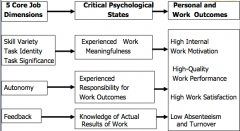
|
|
|
Love of it =? |
the whole video wasabout people who loved their jobs. With the right mindset you can love any job
|
|
|
Utilizing Groups Advantages and Disadvantages |
Advantages: Greater pool of knowledge, Different perspectives, generate more alternatives, acceptance of decision.
Disadvantages: Time consuming, ambiguousresponsibility (who takes responsibility of the outcome?), goal displacement, pressures to conform(groupthink). |
|
|
Group Decision example |
A decision that affects the group, changing the health insurance for employees. Like we saw in thevideo in class, the employees took changes like that better even though it tookmoney out of their pay.
|
|
|
Individual Decision example |
Decision that had little affect on the group, time constraint. Buying supplies |
|
|
Decision Making Styles Matrix |
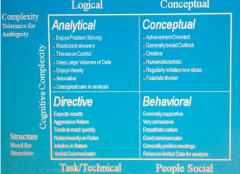
|
|
|
Bias and traps |
Pitfalls that distort our ability to develop solutionsand ideas.
For example:Selective perceptionbias = Seeing what a person expects to see Confirmation bias = Whenpeople seek information to support their point of view and discount informationthat does not Escalation ofcommitment = Getting locked into a bad decision to continue a course of actionto avoid quitting, admitting error, avoid embarrassment, etc. |
|
|
Sources of Power |
Legitimate power:formal or official authority
Coercive power:administration of negative actions Reward power: controlover desired resources Expert power: powerof knowledge Referent power:strength of relationships with followers. Charisma. |
|
|
Empowerment |
grantingemployees more active and responsible role, strengthening their sense ofeffectiveness and sharing power, responsibility to managetheir own work as much as possible.
Goal is to facilitateemployees in the decision making process |
|
|
Empowerment Pros & Cons |
PROS: get to manage own work, improvesquality, increases productivity, saves money, etc.
CONS:not all staff want to be empowered,requires more managerial effort, constant change – keeps things unsettled, riskthat empowerment efforts may fail, etc. |
|
|
Leaders are |
persons who are able to influence others and whoposses “managerial” authority. (soul) – visionary, passionate.
Coping with change, developing influential relationships with others
|
|
|
Managers are |
about coping with complexity, (mind) – rational,consulting
|
|
|
Traits of an effective follower |
Manage themselveswell; think for themselves, work independently without supervision.
Committed to a purposeoutside themselves: a cause, a product, work team, organization, an ideaetc. Build competence andfocus their efforts for maximum impact; master skills and hold higher work standards than required. Courageous,honest, and credible. hold high ethical standards, own up to their mistakes. |
|
|
How to become a good follower |
Learn about your boss(their environment, what they expect)
Listen (what and howboss says) Read (memos, etc) Ask (how othersexperienced your boss) |
|
|
Trait approach to understanding leadership |
List of common traits that are exhibited byleaders.
Kouzes & Posner’sfive traits: Honest, competent,forward-looking, inspiring, intelligent |
|
|
Trait approach, disadvantages and advantages |
Disadvantages:not all people who exhibit these traits are leaders.Its also difficult to determine what exact set of traits make the mosteffective leader.
Advantages: a benchmark for identifyingsuitable leaders. It can help a leader’s strength and weaknesses. |
|
|
Behavioral approach to leadership |
Identifybehaviors that differentiate effective leaders from ineffective leaders.
Michigan = employee and production orientated. (concerned with these) Ohio state = leader initiating structure and consideration of others Managerial grid = concern for people vs production. |
|
|
Contingency approach to leadership
|
choosewhat leadership style to utilize depending on what is effective with his team.(what style is more effective in a certain situation)
|
|
|
Path Goal Theory |
How a leader makes desirable rewards in the workspace,increases motivation and support by clarifying paths, or behaviors that willhelp them achieve their goals.
Ex: make sure my employees know they are supported byconsidering their welfare and creating a cohesive work environment, give them opportunities for growth and recognize their hardwork. |
|
|
Video Leadership Challenge, 5 practices |
Model theyway = set an example and set achievable goals.
Inspiring a sharedvision = creating a vision gets employees excited for the future. Challenge aprocess = take risksand experiment with different ideas. Enablingothers to act = collaborative efforts from others who are not otherwise involved.(trust and sense of power). Encourage the heart = recognize employees/ morale and motivation. |
|
|
4 Major laws pertaining to HR |
Equalemployment opportunity: prohibits discrimination.
Compensationand benefits: lawsthat provide for min. Wages, medicalleave, unemployment and workers compensation Laborrelations: employees may establish labor unions and requires organizationsto bargain with legally formed unions, also limits union power Health andsafety: safe working conditions, etc. |
|
|
Example of business goals drives HR goals |
Hiring. If a business’ goal is to hire motivatedindividuals with a certain skill set, HR’s goal will be to create a hiringprocess that will help them hire the best individuals for the job.
|

