![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What treatment can prevent episode of hepatic encephalopathy?
|
Rifaximin. A minimally absorbed antitiotic<br />
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/short/362/12/1071
|
|
|
What are the common primary sources of brain metastasis?
|
Lung cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, colorectal cancer<br />
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/362/12/1119
|
|
|
What is the typically site of brain metastasis?
|
Grey-white junction<br />A result of hemotogenous spread. Regions of the brain receiving a greater blood supply are more susceptible to developing metastases
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/362/12/1119
|
|
|
What is the preferred diagnostic test for brain tumor?
|
MRI<br />
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/362/12/1119
|
|
|
Who is good candidate of stereotactic radiosurgery?
|
Patients who have one to four brain metastases, no larger than 4 cm in diameter, from metastatic cancer. <br />
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/362/12/1119
|
|
|
Who is good candidate for surgical resection of brain metastasis?
|
Patients with larger lesions (&gt;3.5 cm in diameter), no known primary diagnosis, symptomatic mass effect, or clinically significant edema<br />
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/362/12/1119
|
|
|
What treatment is used to minimize the rish of stereostatic radiosurgery complication?
|
iv. dexamethasone before treatment<br />
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/362/12/1119
|
|
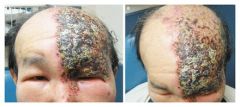
What is the diagnosis?<br /><img src="95ec7dd84688846dbe795396668fe68a.jpg" />
|
Herpes Zoster + bacterial superinfection<br />
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/362/12/1128
|
|
|
What is the DDx list for neurologic dysfunction disseminated in both space and time, with intervening remissions, and syns and symptoms spread to diverse regions of the brain and spinal cord?
|
Multiple slecrosis, Infectious disease (Lyme, syphilis, AIDS), Rheumatologic disease (SLE, Sjogren syndrome), Genetic disease (MELAS), Cocaine abuse, CNS vasculitis, lymphoma<br />
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/362/12/1129
|
|
|
What is the clinical symptoms and signs of hyperprolactinemia in women?
|
Oligoamenorrhea, infertility, and galactorrhea<br />
|
|
|
|
How to restore fertility function in patient with prolactinoma?
|
Give GnRH<br />Prolactinoma will affect normal GnRH secretion.
|
|
|
|
What bone complication is amenorrheic women with prolactinoma at risk of?
|
Bone fracture due to estrogen deficiency<br />
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical symptoms and signs of men with prolactinoma?
|
Hypogonadism, decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, infertility, gynecomastia, and, in rare instances, galactorrhea<br />
|
|
|
|
Pearls: women usually present with microadenomas, while men present with macroadenomas, often with headache, visual symptoms, or both, in addition to hypogonadism
|
<br />
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of secondary hyperprolactinemia?
|
Women in childbearing age. Renal or hepatic failure (because of reduced prolactin clearance), primary hypothyroidism (TRH pituitary effect), or neurogenic stimulation (nipple stimulation), Medicaltion (e.g.:dopamine antagonist), Pituitary stalk infiltrative disease<br />
|
|
|
|
When will prolactin level return to normal in childbearing women?
|
Prolactin levels normalize within approximately 6 months after delivery in nursing mothers and within weeks in non-nursing mothers<br />
|
|
|
|
What medication can cause hyperprolactinemia?
|
Antidepressants and antipsychotic agents (risperidone, in particular), dopaminergic blockers (e.g., metoclopramide), some antihypertensive agents, opiates, and H2-receptor blockers<br />
|
|
|
|
Pearls: Elevations in prolactin levels that result from stalk compression rarely exceed 150 µg per liter, but the use of antipsychotic agents or metoclopramide can increase prolactin levels to more than 200 µg per liter. Clinical manifestations of drug-induced hyperprolactinemia are similar to those of prolactinomas, except for tumor mass effects
|
<br />
|
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic procedure for hyperprolactinemia?
|
<span style="color:#000000;">Rechecking</span> an elevated prolactin level for confirmation, pregnancy test, levels of thyrotropin and free T4, and renal and hepatic function.<br />After those, MRI with contrast<br />
|
|
|
|
What addtional test should be done in amenorrheic women?
|
Pituitary function (LH/FSH), bone density<br />
|
|
|
|
What is the indication for treatment of prolactinoma?
|
Macroadenoma (>10mm), enlarging microadenoma, infertility, bothersome galactorrhea, gynecomastia, testosterone deficiency, oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, ance and hirsutism <br />
|
|
|
|
What is the primary treatment for microadenoma?
|
Dopamine agonist (bromocriptine and cabergoline)<br />
|
|
|
|
When is gonadal-steroid hormone replacement therapy indicated in prolactinoma patient?
|
When patient with low gonadal-steroid hormone level<br />
|
|
|
|
What is the primary treatment for macroadenoma?
|
Dopamine antagonist. Goal is to shrink or stabilized the tumor, prevent neurologic complications. <br />As long as the tumor is stable and hormone deficiency is replaced, hyperprolactinemia is not harmful.
|
|
|
|
When is surgery indicated in macroadenoma?
|
Poor response to medication or presence of contraindication, clinically significant visual-field compromise and MRI shows continued chiasmal compression, CSF leak during administration of dopamine agonist. <br />
|
|
|
|
What is the common side effect of dopamine agonist?
|
Gastrointestinal symptoms and orthostatic hypotension are common<br />
|
|
|
|
How long should prolactinoma been treated?
|
Discontinuation of dopamine agonist therapy can be attempted in selected patients who have had normal prolactin levels for at least 2 years and minimal residual tumor volume<br />
|
|

